Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX



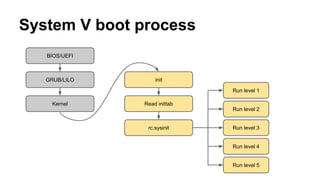
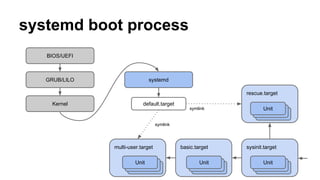


Systemd is an init system that replaces traditional init daemons. It allows for parallel startup of services through dependency-based activation of units which encapsulate system objects like services, devices, and mounts. Systemd also provides on-demand activation of services through sockets, buses, devices, and file paths. It aims to be backwards compatible with System V while offering improvements like parallel startup and centralized logging.





