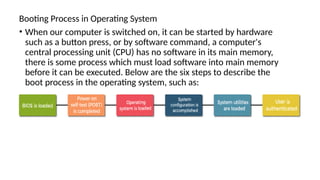
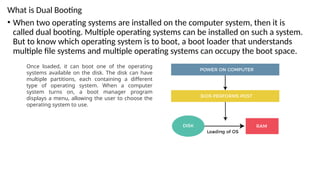
The document explains the booting process of a computer, detailing how the operating system is loaded into memory when the CPU is powered on. It describes two types of booting: cold booting, initiating a complete system startup, and warm booting, which restarts the computer while it's still on. Additionally, it outlines the steps involved in the boot process, including BIOS checks, the search for the master boot record, and the loading of key system files.