Embed presentation
Download to read offline



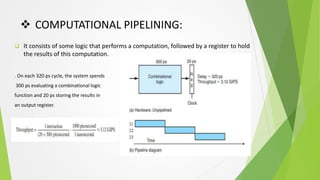
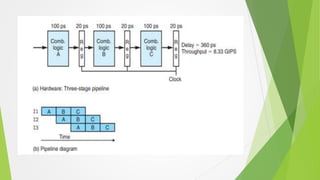

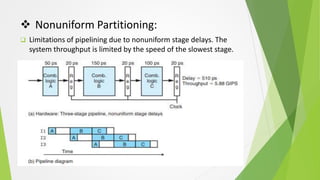


Pipelining is a technique that overlaps the execution of multiple instructions. The pipeline is divided into stages connected in a pipe-like structure. Instructions enter one end and exit the other. Common stages include fetch, decode, and execute. Pipelining increases overall instruction throughput. Pipelining consists of combinational logic that performs a computation followed by a register to store results. The clock signal controls the movement of instructions between stages on each cycle. Nonuniform stage delays can limit system throughput by the speed of the slowest stage.








