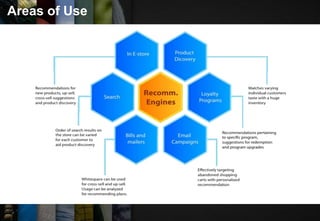
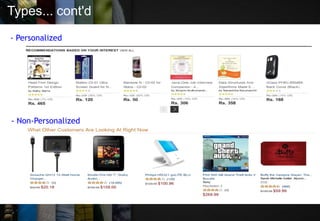
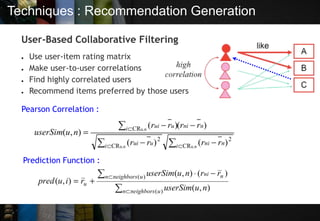
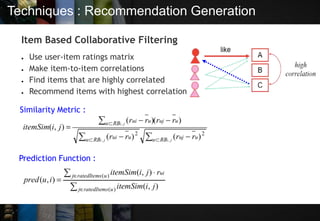
The document discusses recommendation systems, which are information filtering techniques that help users find relevant information amidst the vast amount of data available. It outlines the types of recommendation systems—personalized and non-personalized—and various methods such as collaborative filtering and content-based techniques, highlighting their advantages and limitations. Case studies of Amazon and YouTube illustrate how these systems can be effectively implemented to enhance user experience.