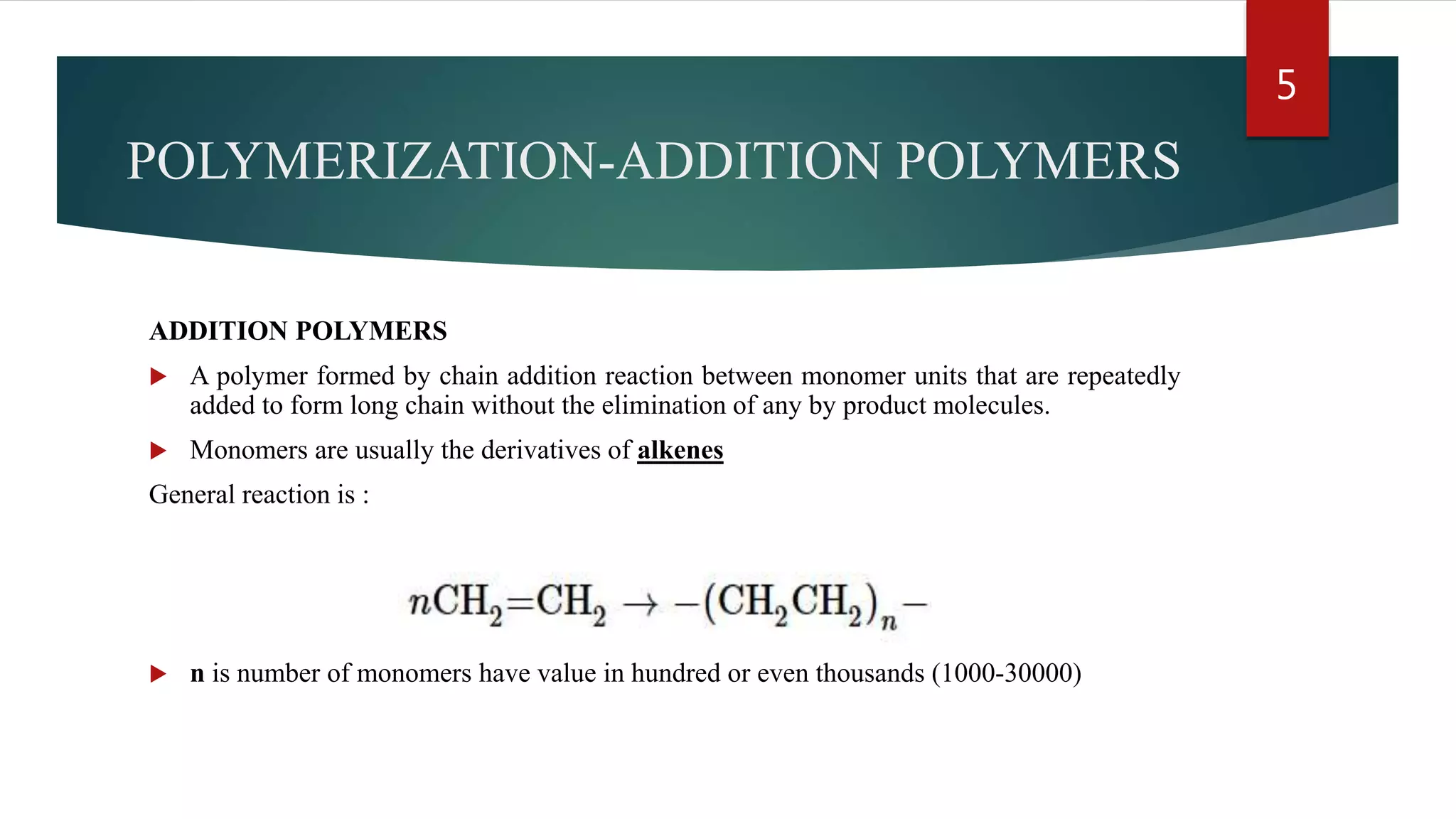
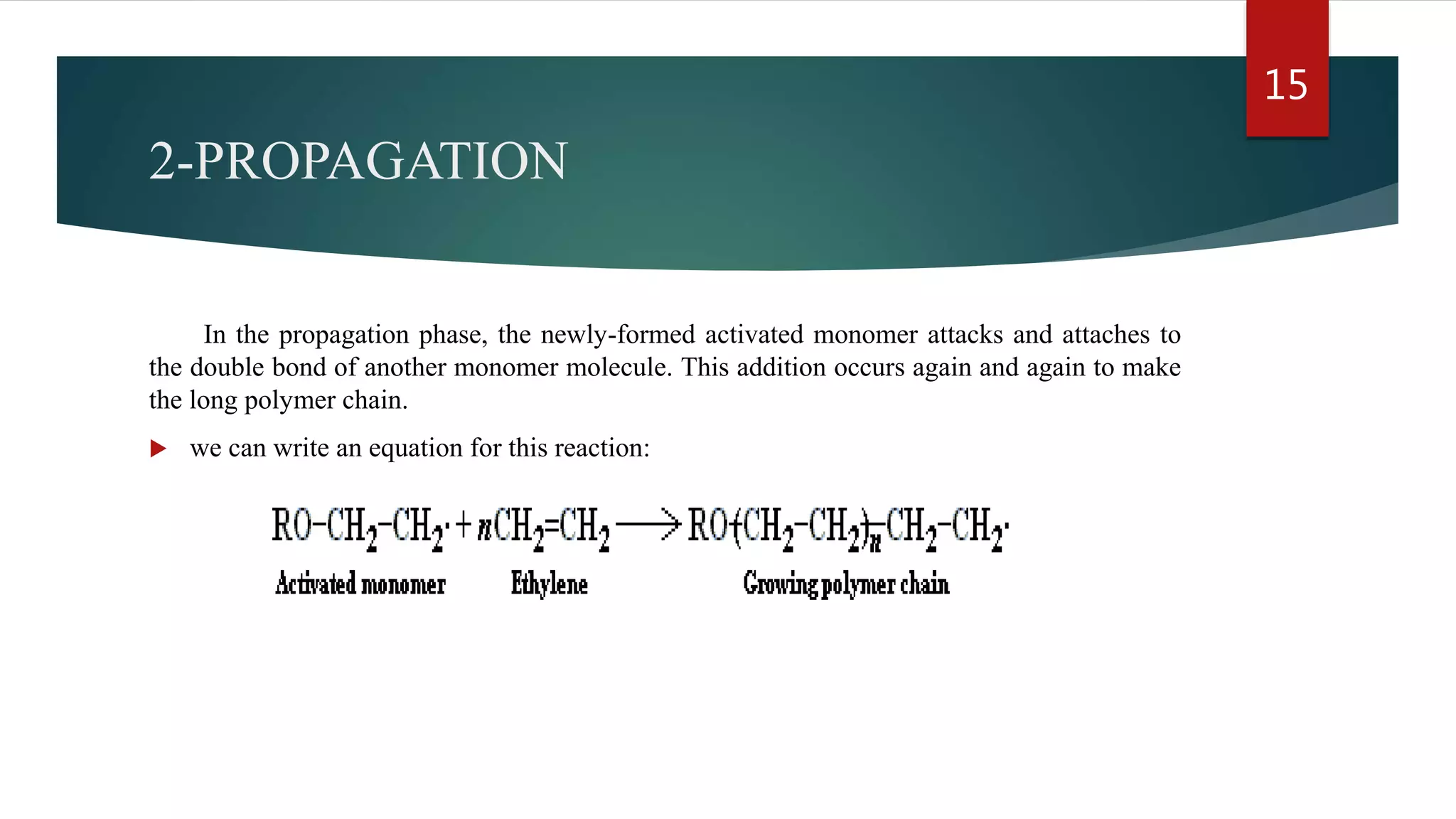
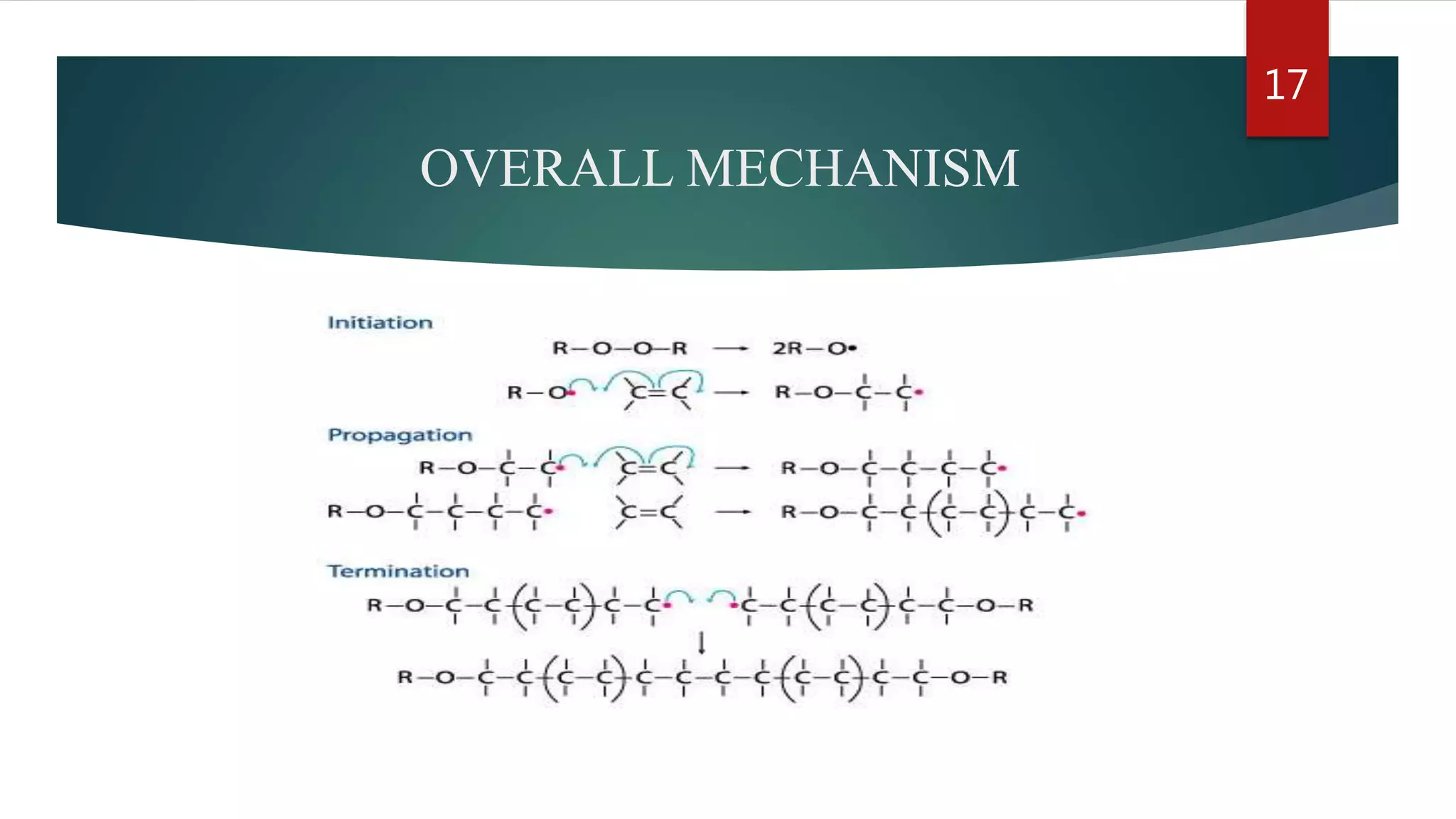
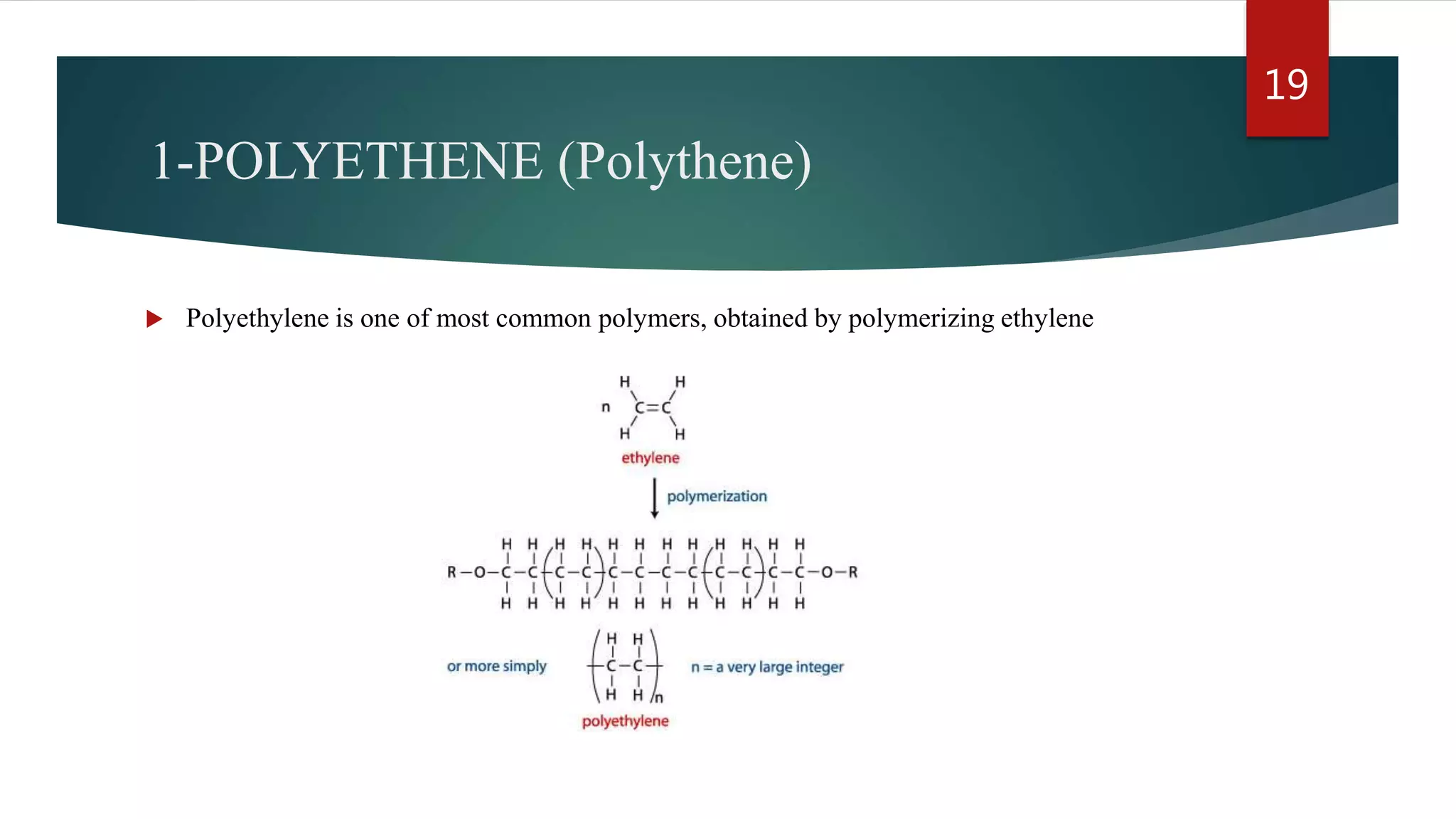
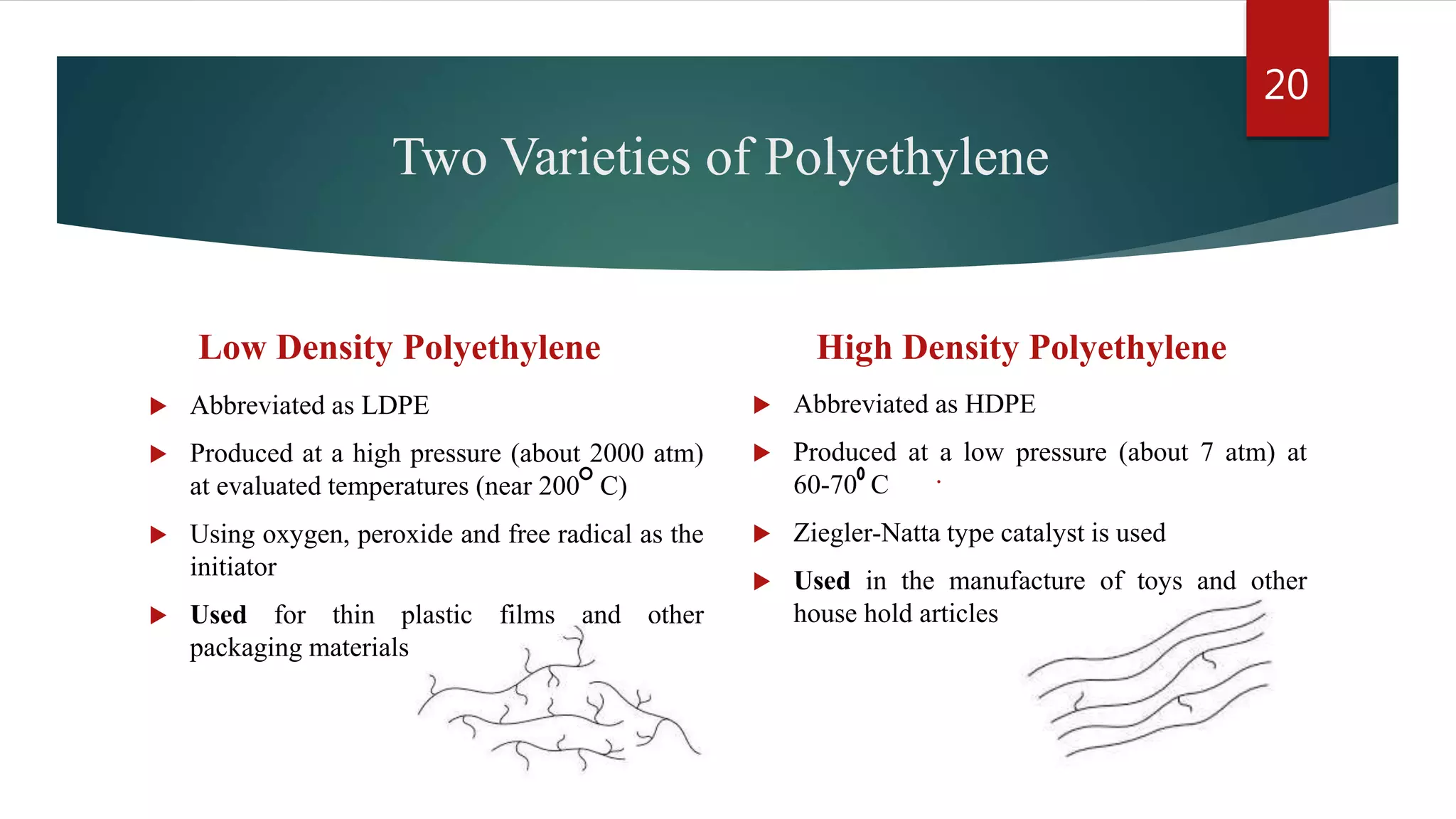
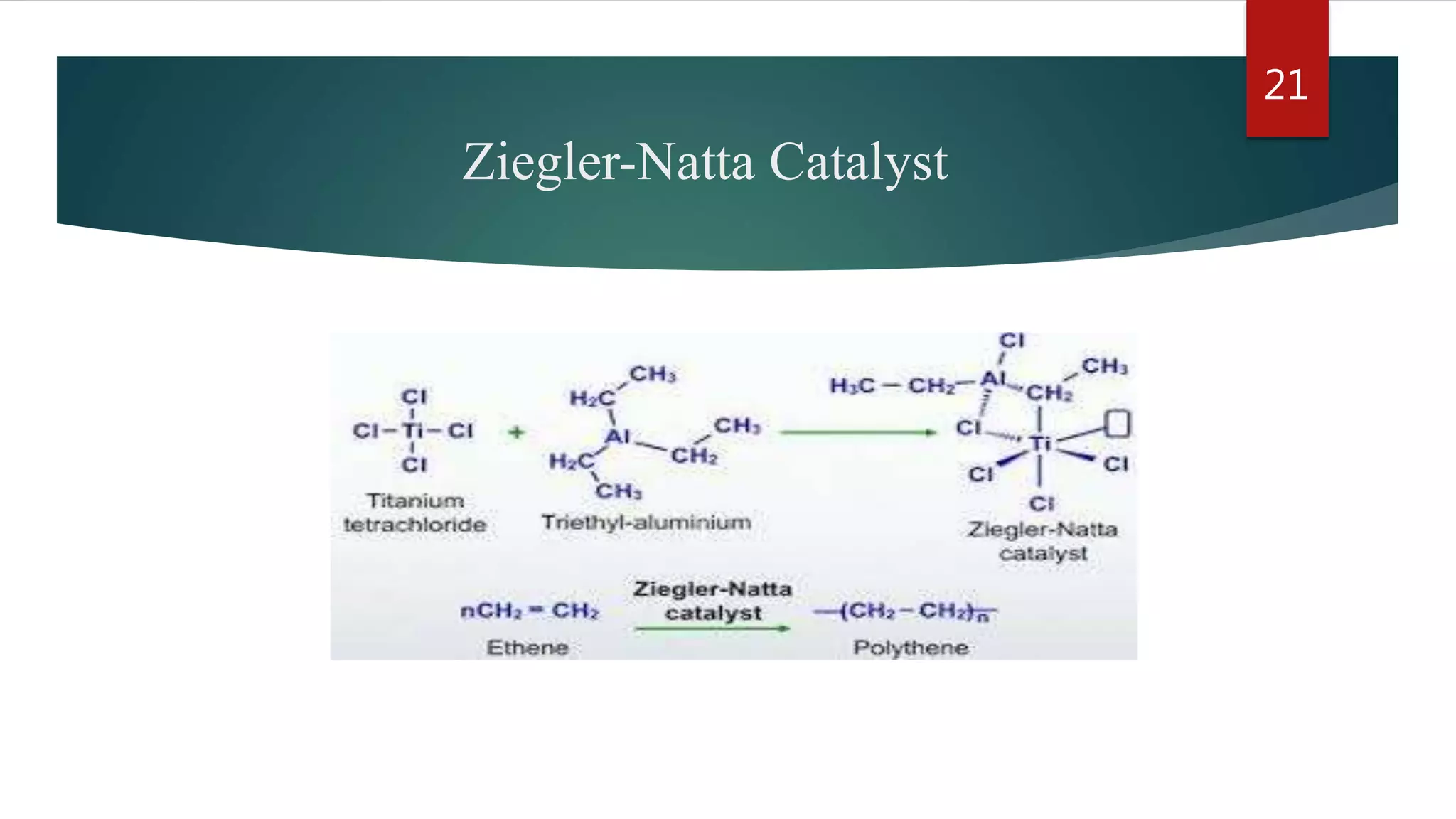
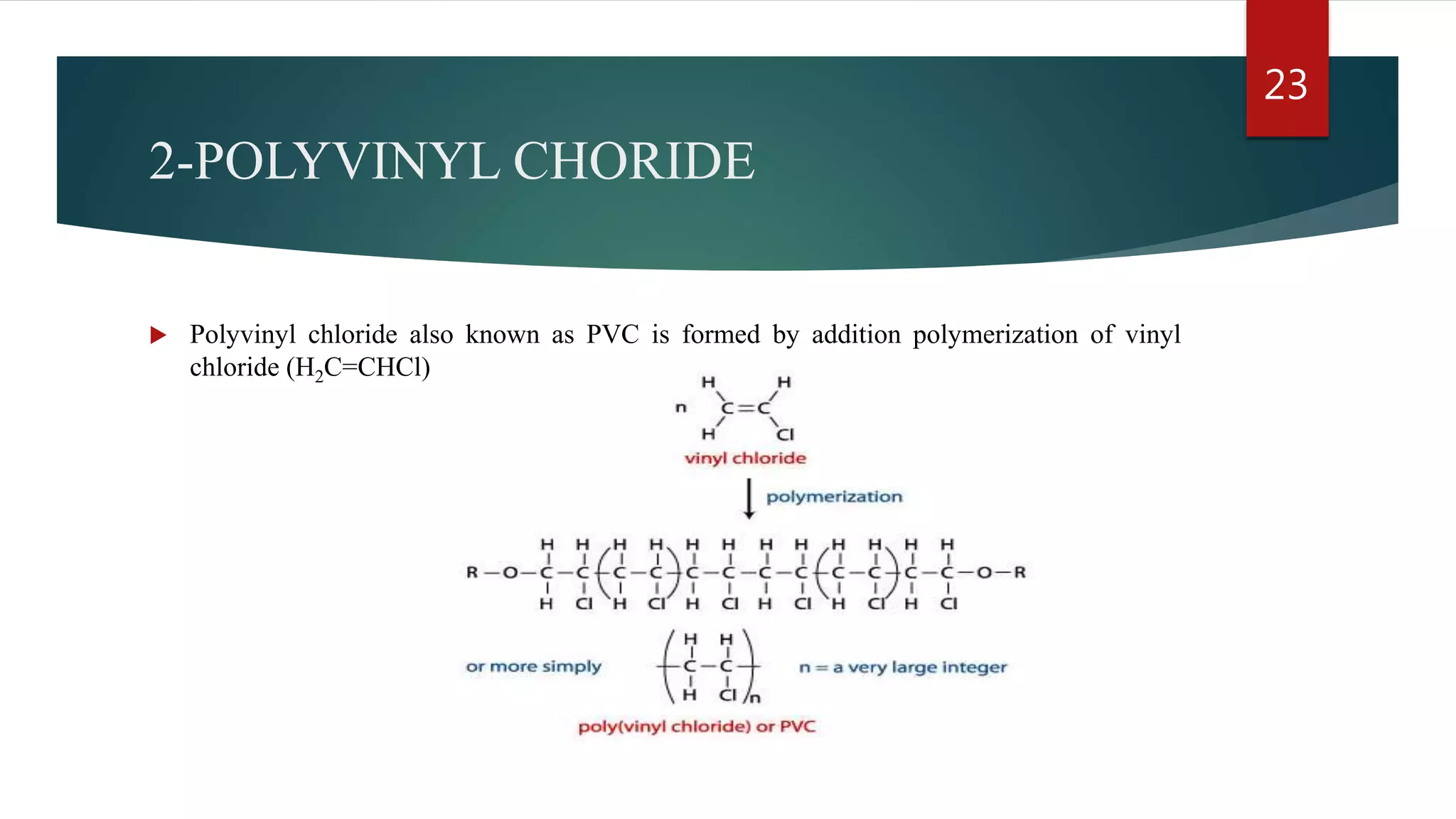
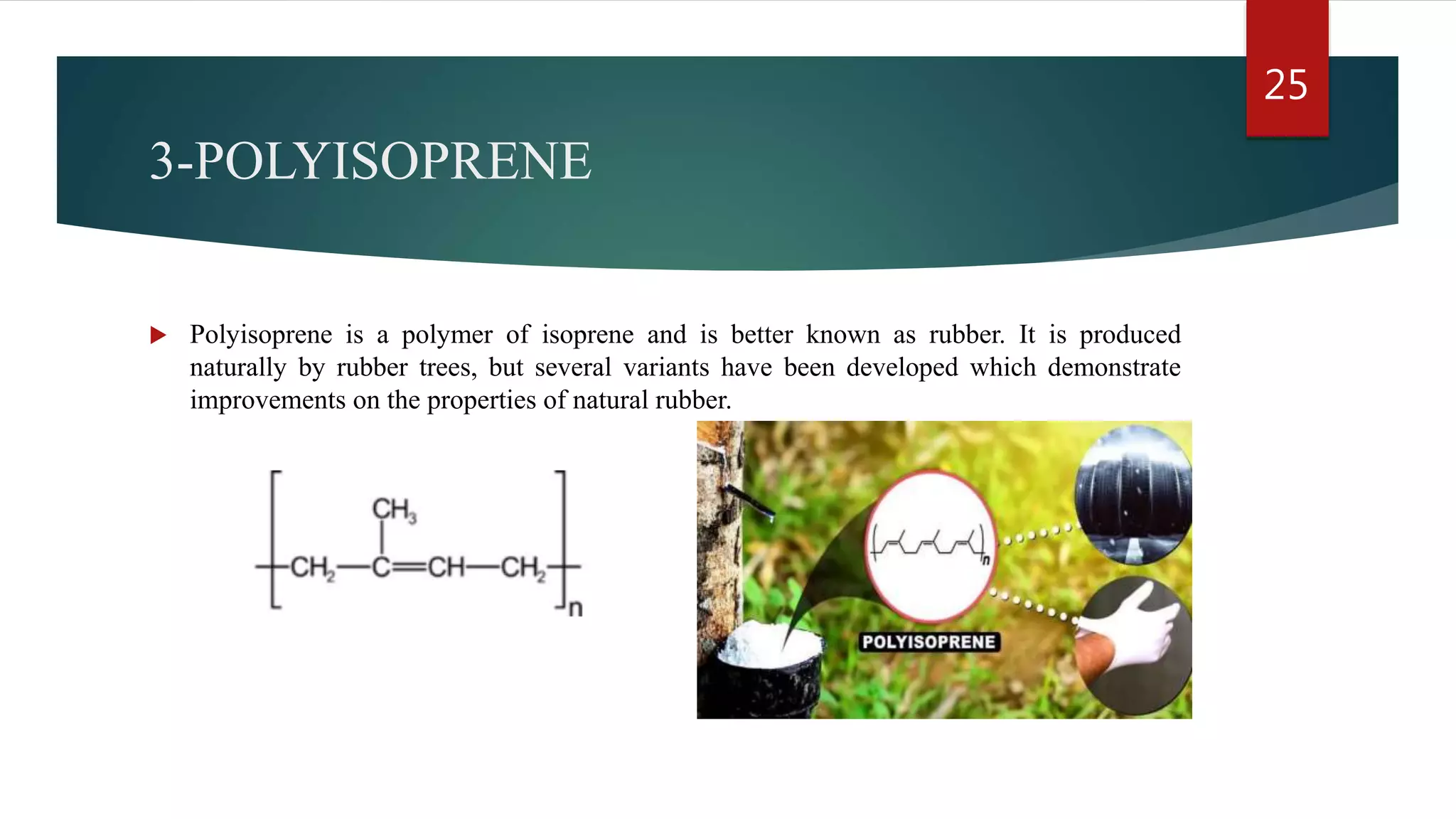
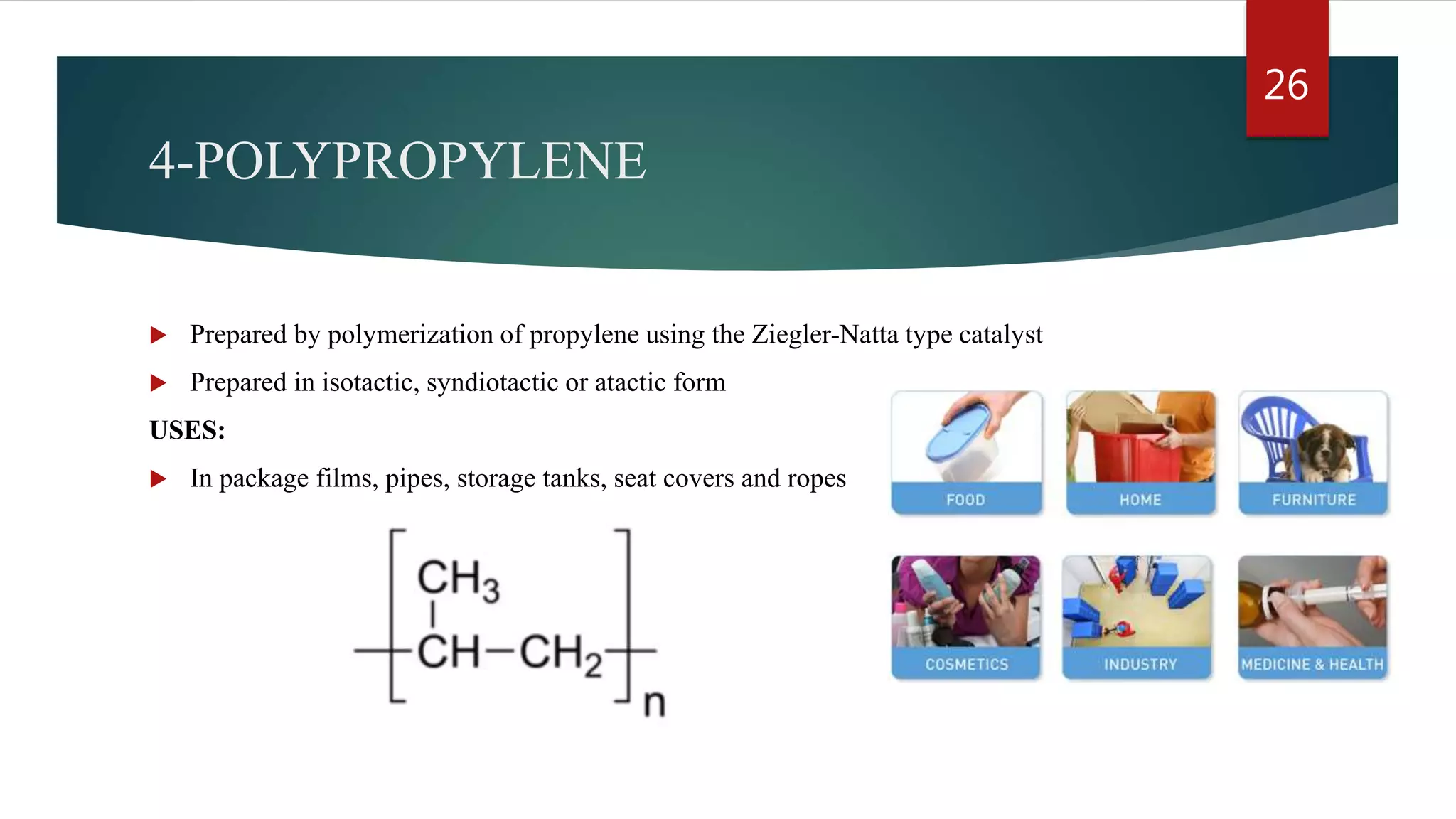
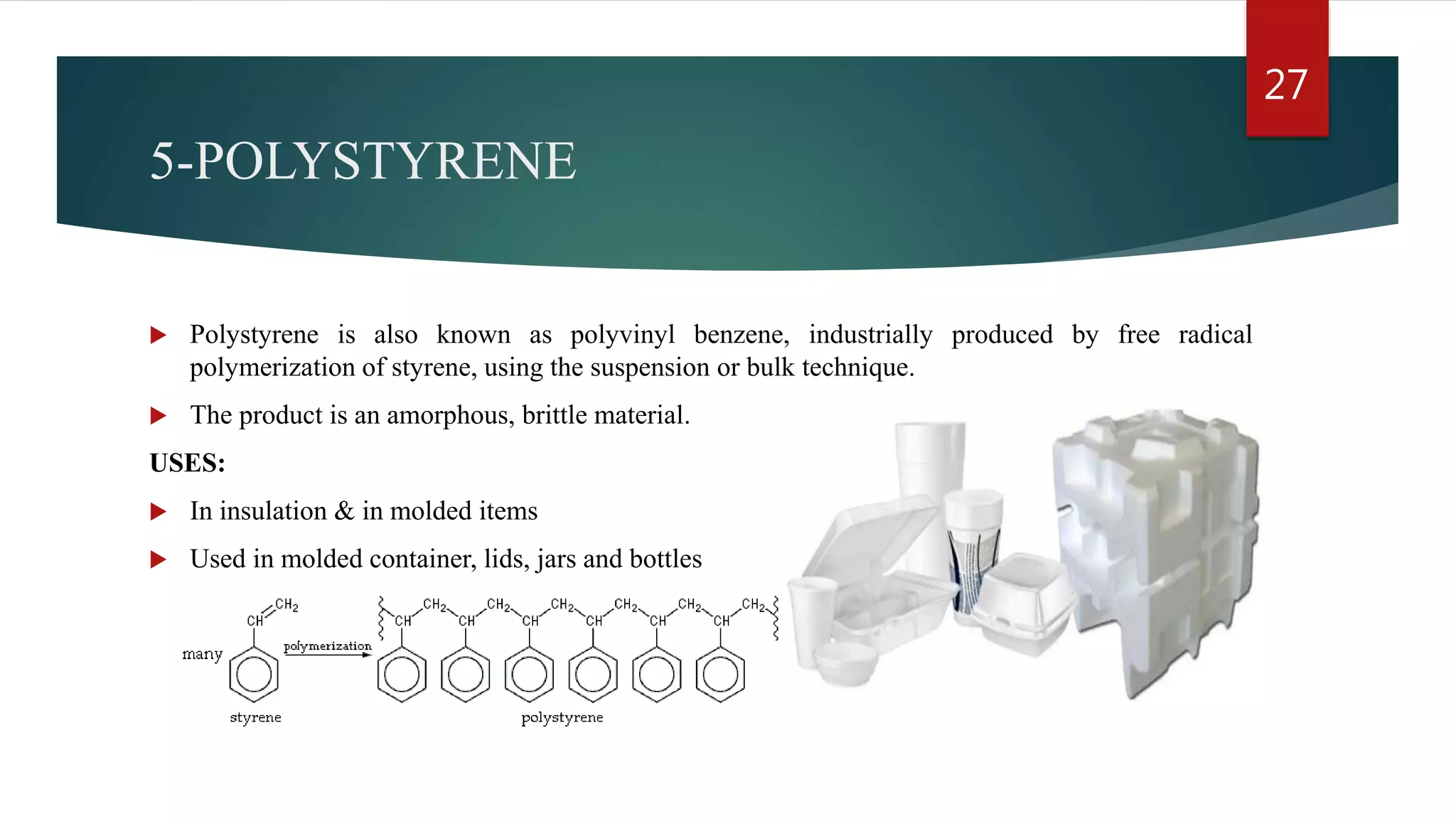
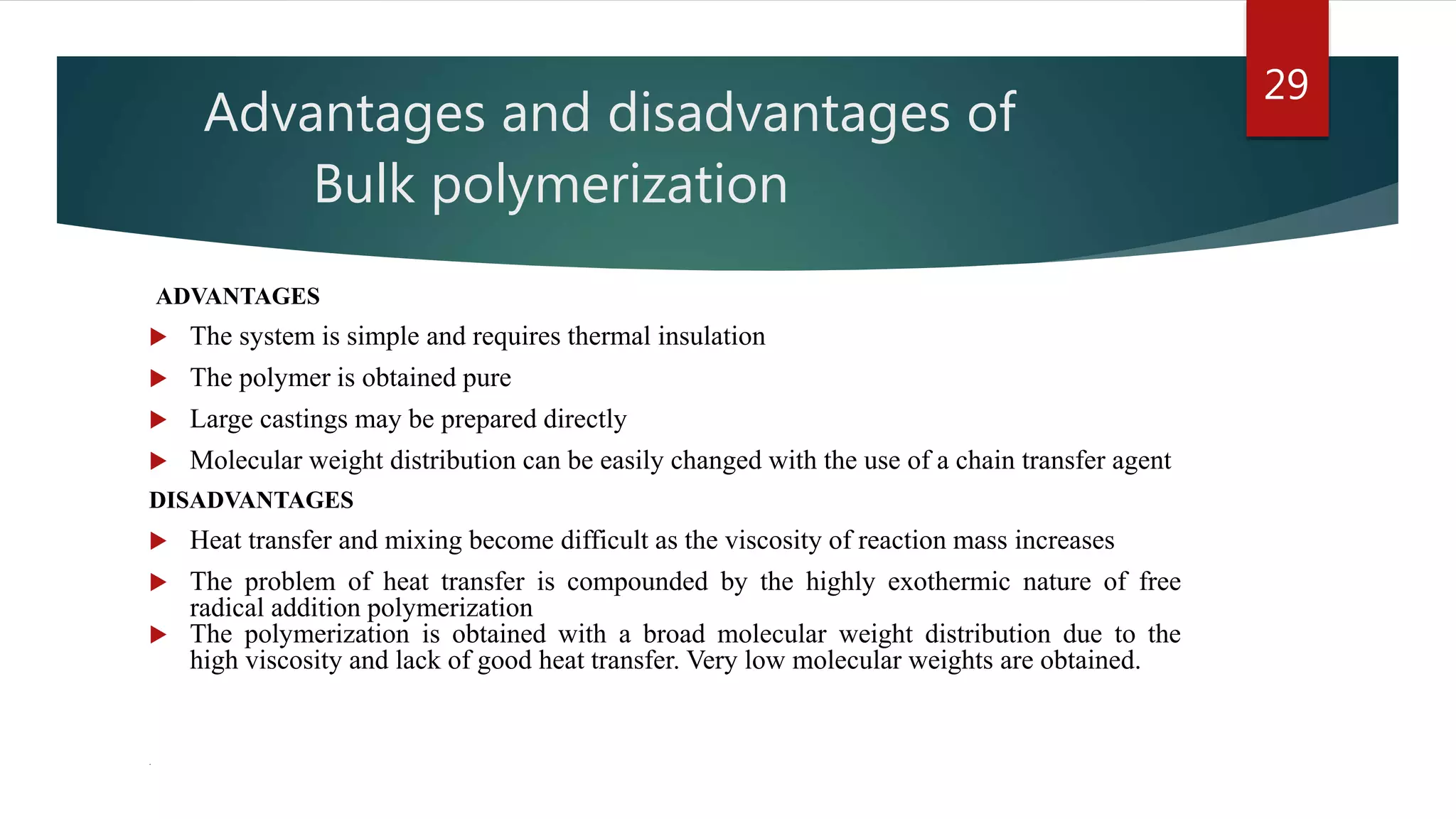
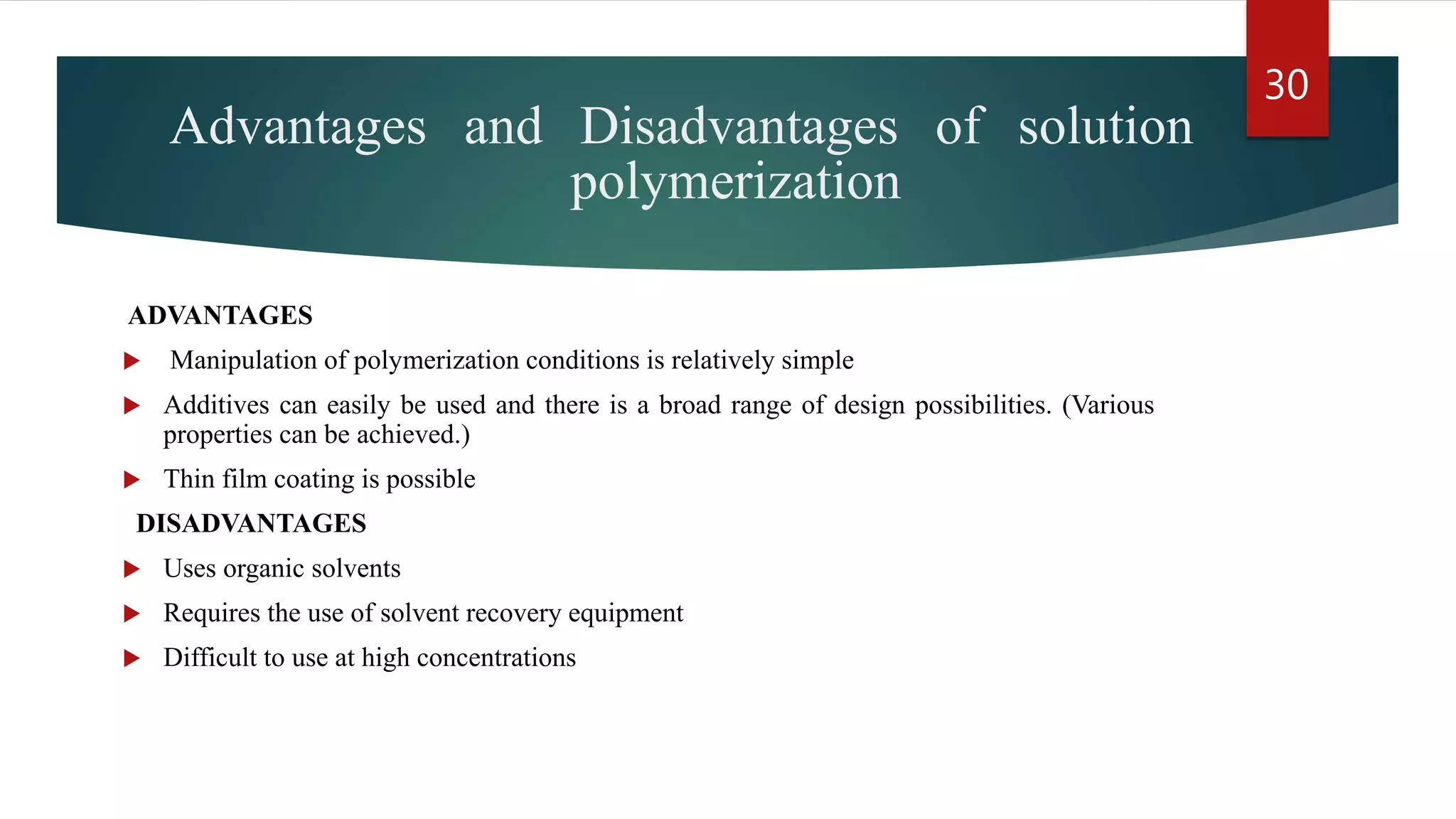
Addition polymerization involves monomers joining together through a chain reaction without producing any byproducts. Common addition polymers include polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, polyisoprene, polypropylene, and polystyrene. Addition polymerization can occur through bulk or solution polymerization. Bulk polymerization uses only the monomers while solution polymerization uses a solvent. Both methods have advantages like control over molecular weight but also disadvantages like poor heat transfer during bulk polymerization.