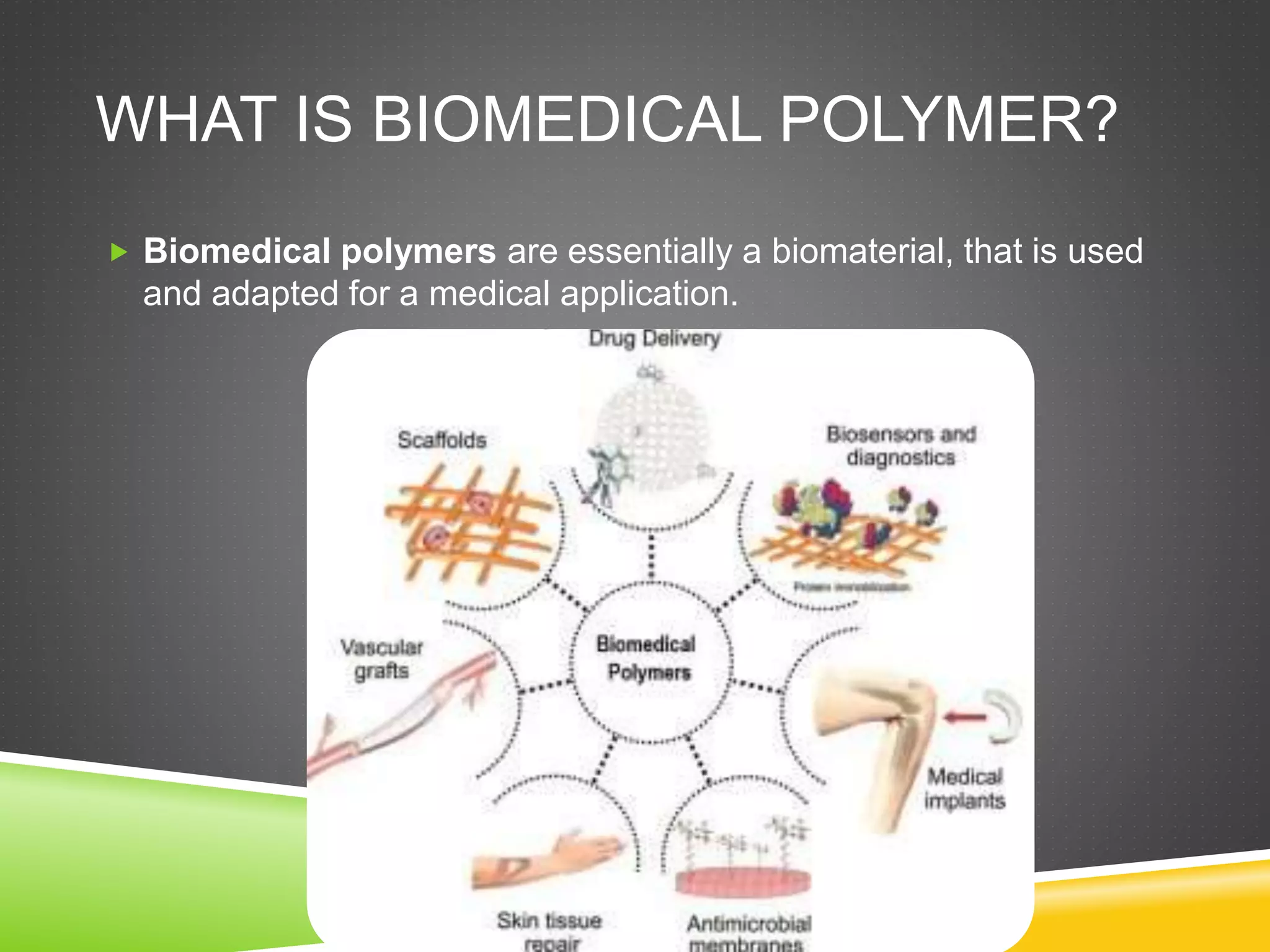
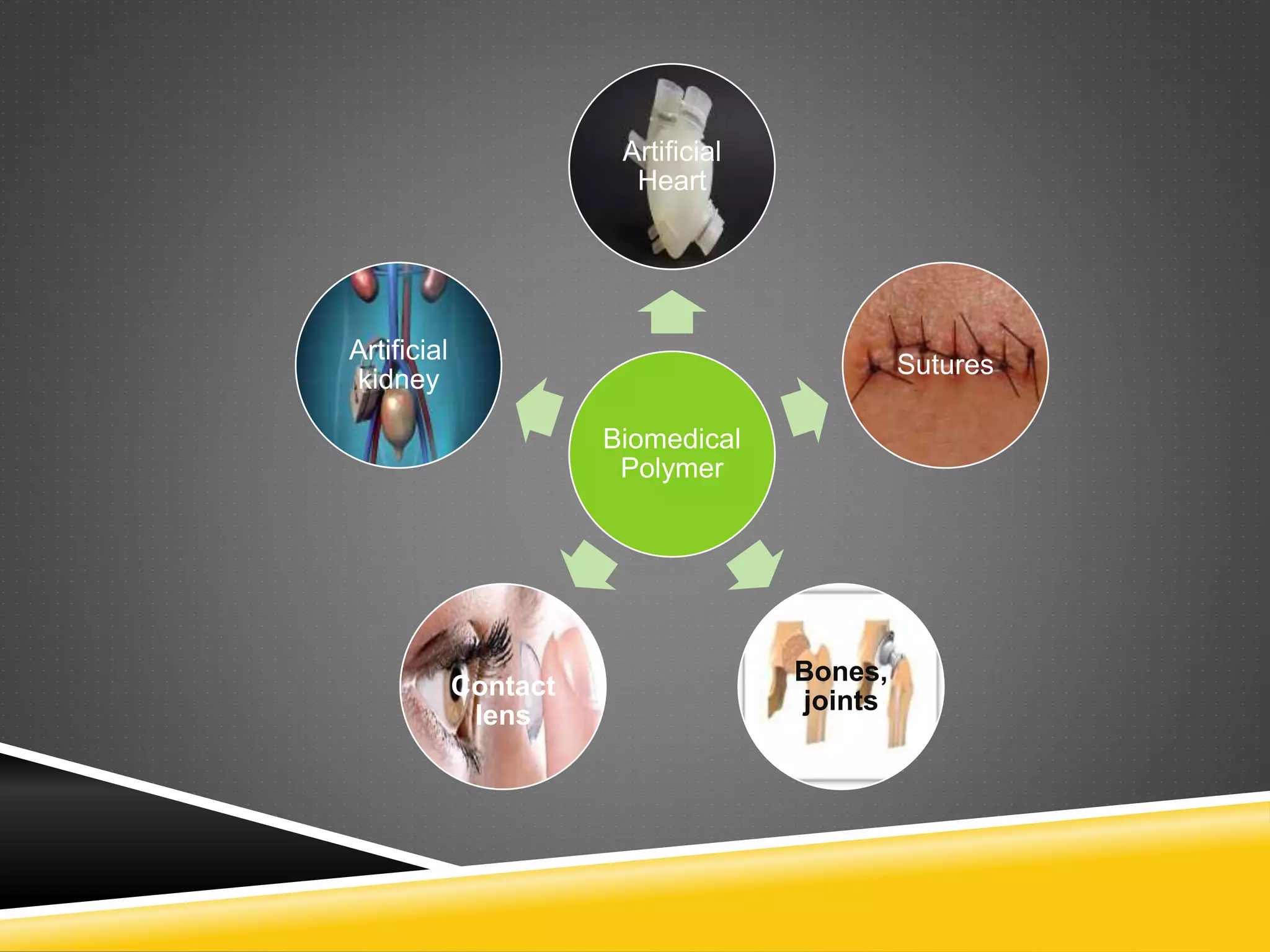
Biomedical polymers are materials adapted for medical applications, characterized by properties such as flexibility, biocompatibility, and resistance to biochemical attacks. They are classified into natural and synthetic polymers, with natural examples including collagen and alginate, while synthetic examples feature polytetrafluoroethylene and poly(caprolactone). Applications range from tissue engineering and drug delivery to cardiovascular devices and artificial organs.