Embed presentation
Downloaded 35 times




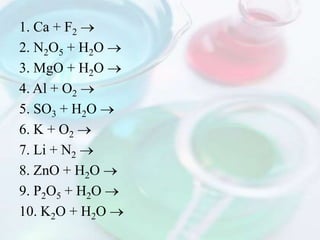



This document discusses different types of chemical reactions including synthesis, decomposition, single-replacement, double-replacement, combustion, and neutralization reactions. Synthesis reactions involve two or more reactants combining to form a single new product. Decomposition reactions involve a single reactant breaking down into simpler products. The document provides examples of common synthesis and decomposition reactions.







