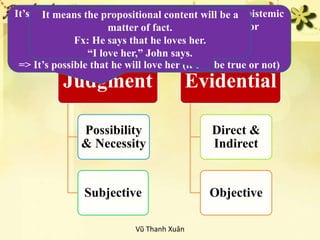
Modality refers to the speaker's attitude or opinion regarding the factual status of a proposition. There are two main types of modality: epistemic and deontic. Epistemic modality concerns beliefs, knowledge and truth, expressing levels of certainty. Deontic modality involves necessity or obligation and is concerned with actions. Mood is a syntactic concept referring to sentence structure, while modality is semantic and provides information about the speaker's perspective. Modality can be expressed through modal verbs, adverbs, adjectives and other means.