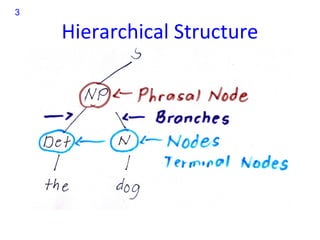
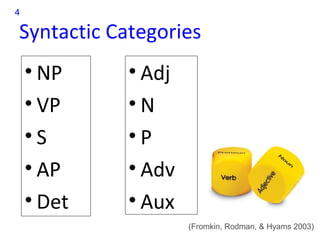
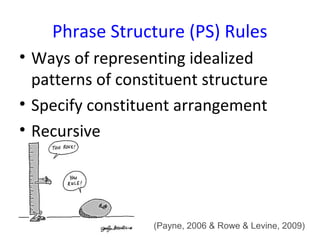
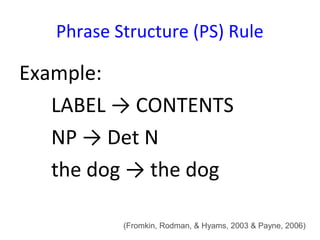
Transformational-generative grammar is a theory that represents a native speaker's innate knowledge of language. It includes an ideal mental representation of a language and rules for generating grammatical sentences. The theory proposes that speakers have unconscious knowledge of phonological, syntactic, and semantic rules and can use these rules to produce and understand an infinite number of sentences. Transformational rules allow speakers to derive new structures from underlying structures.








![2
Constituency
1. [Good girls] and boys
2. Good [girls and boys]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transformationalgenerativegrammar-130411032322-phpapp01/85/Transformational-generative-grammar-10-320.jpg)