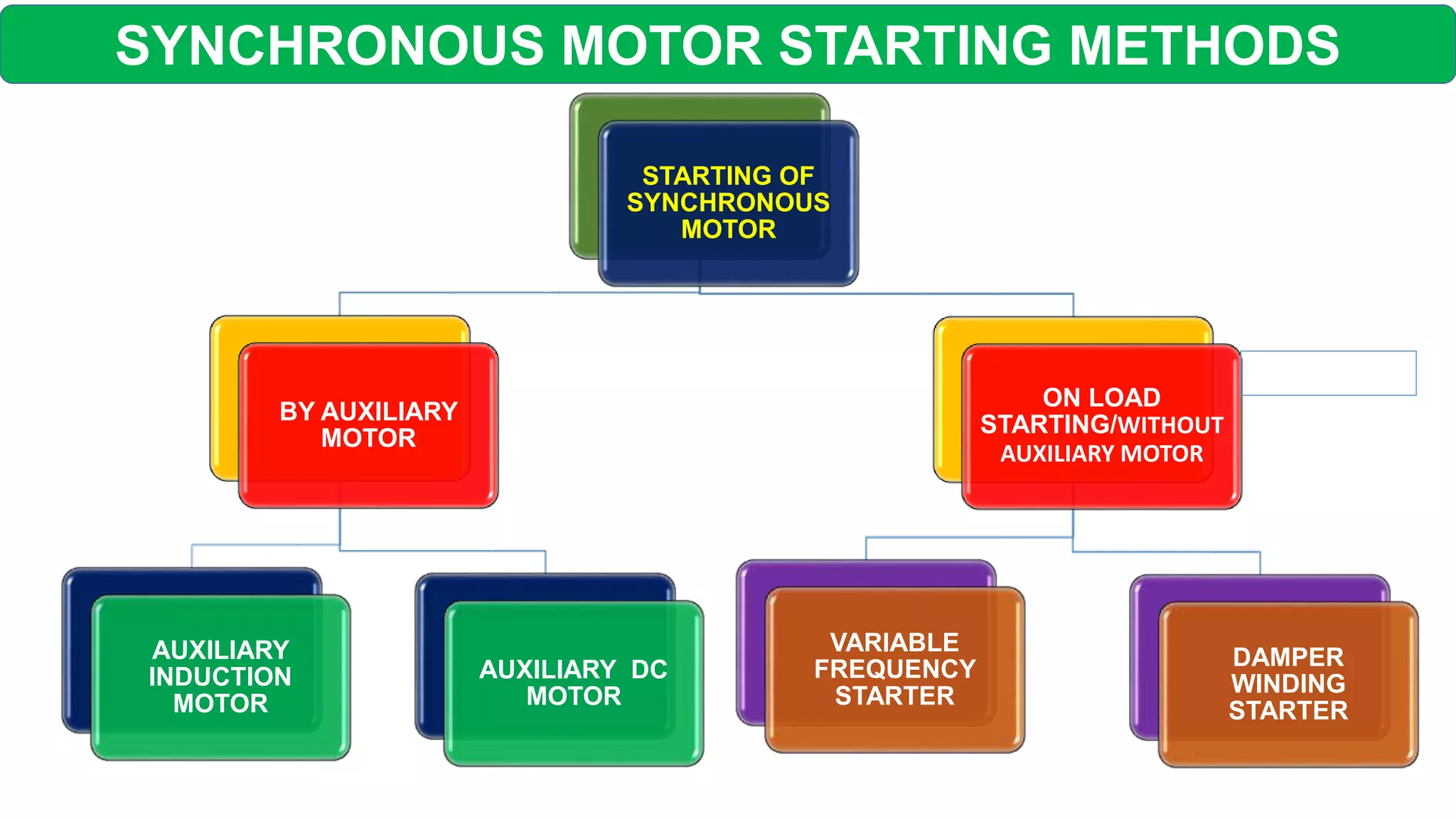
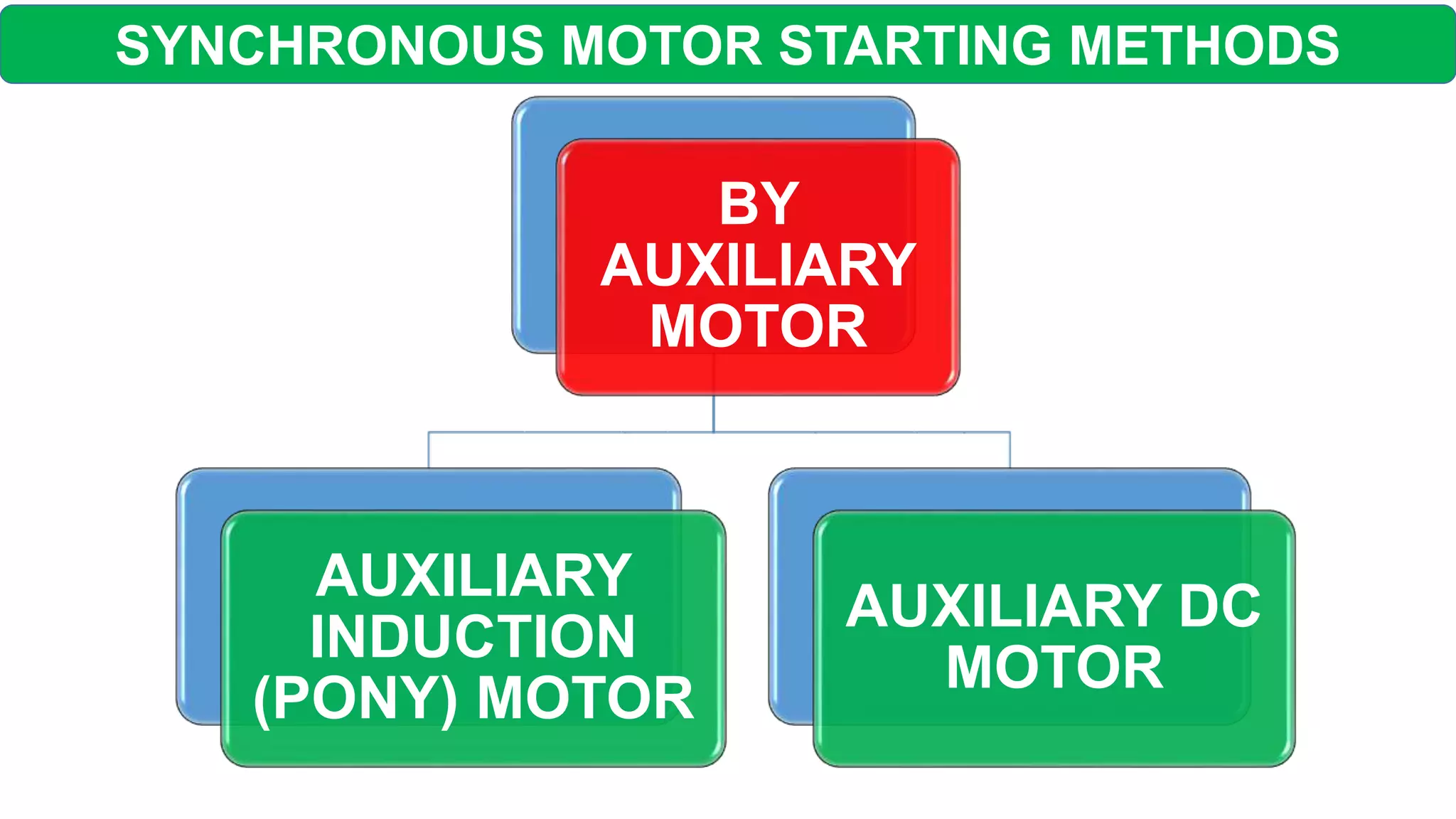
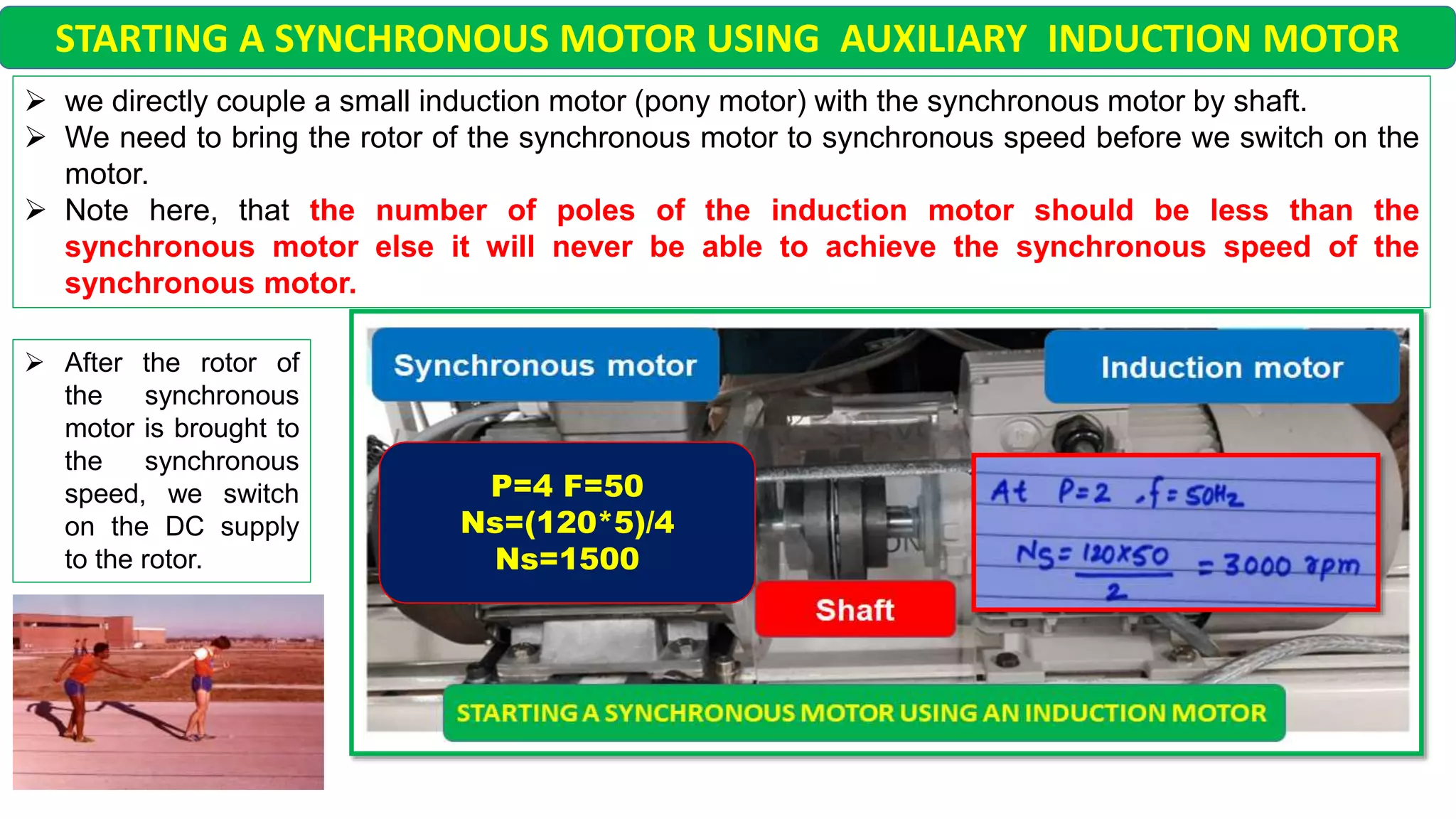
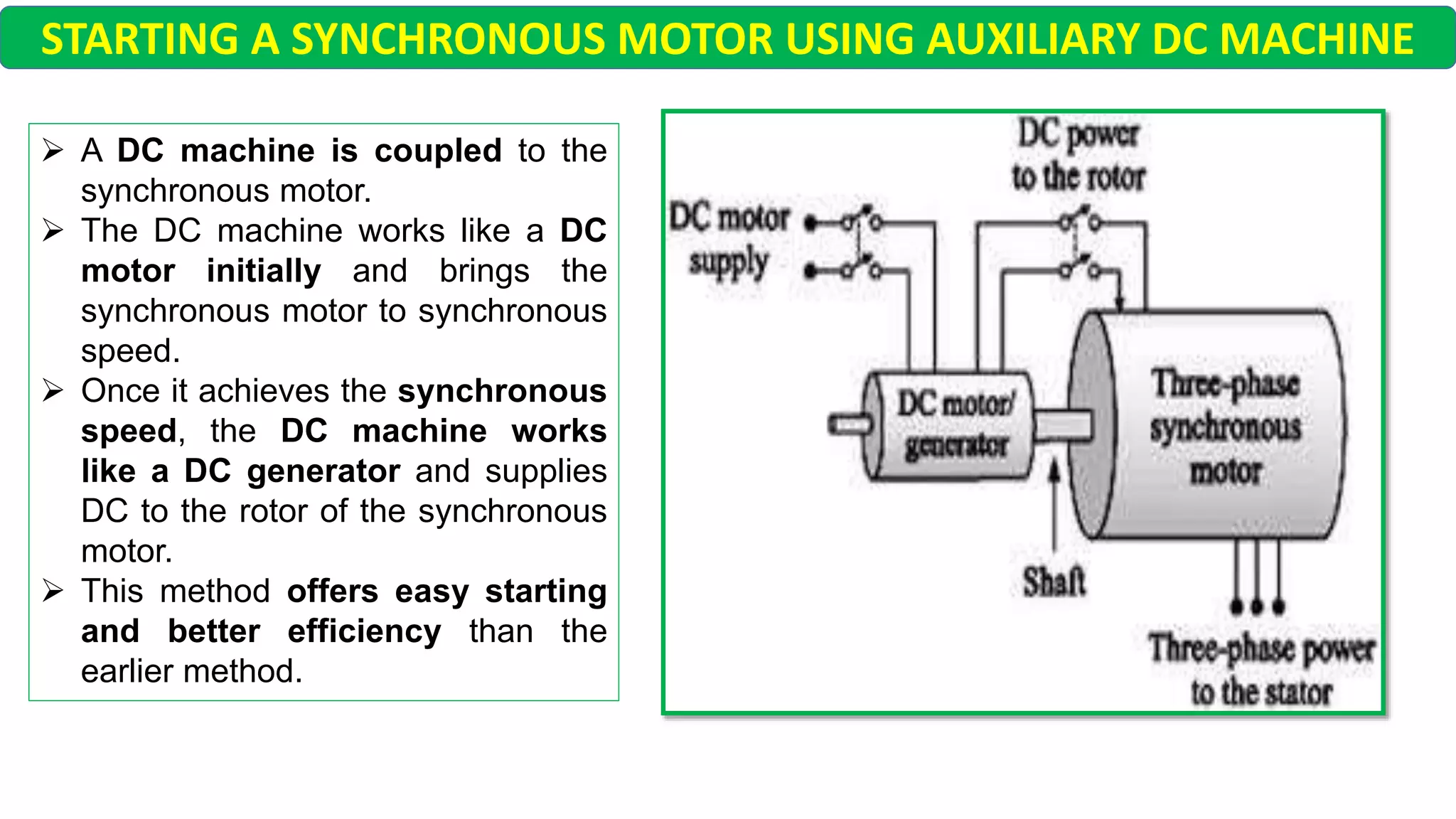
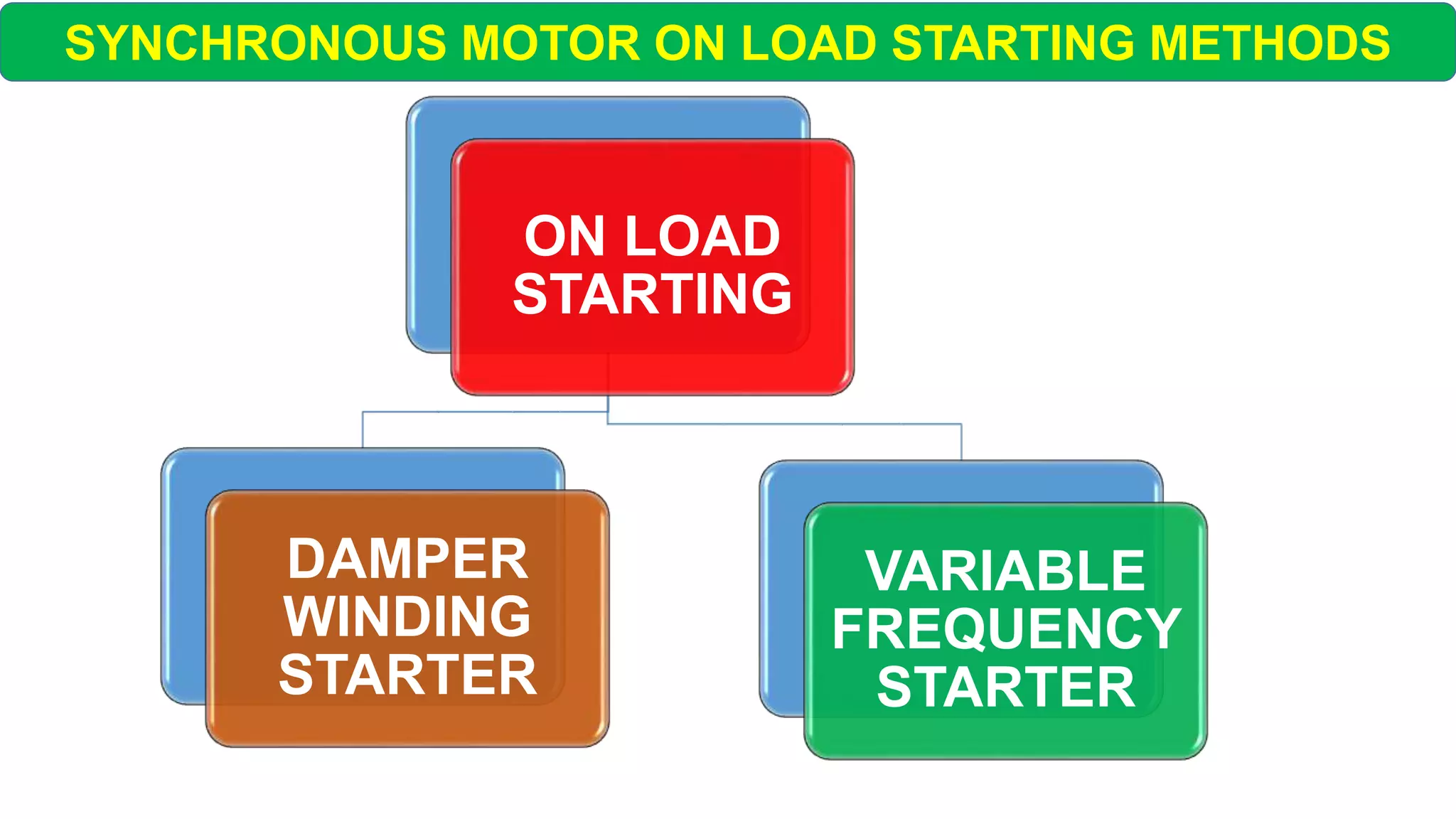
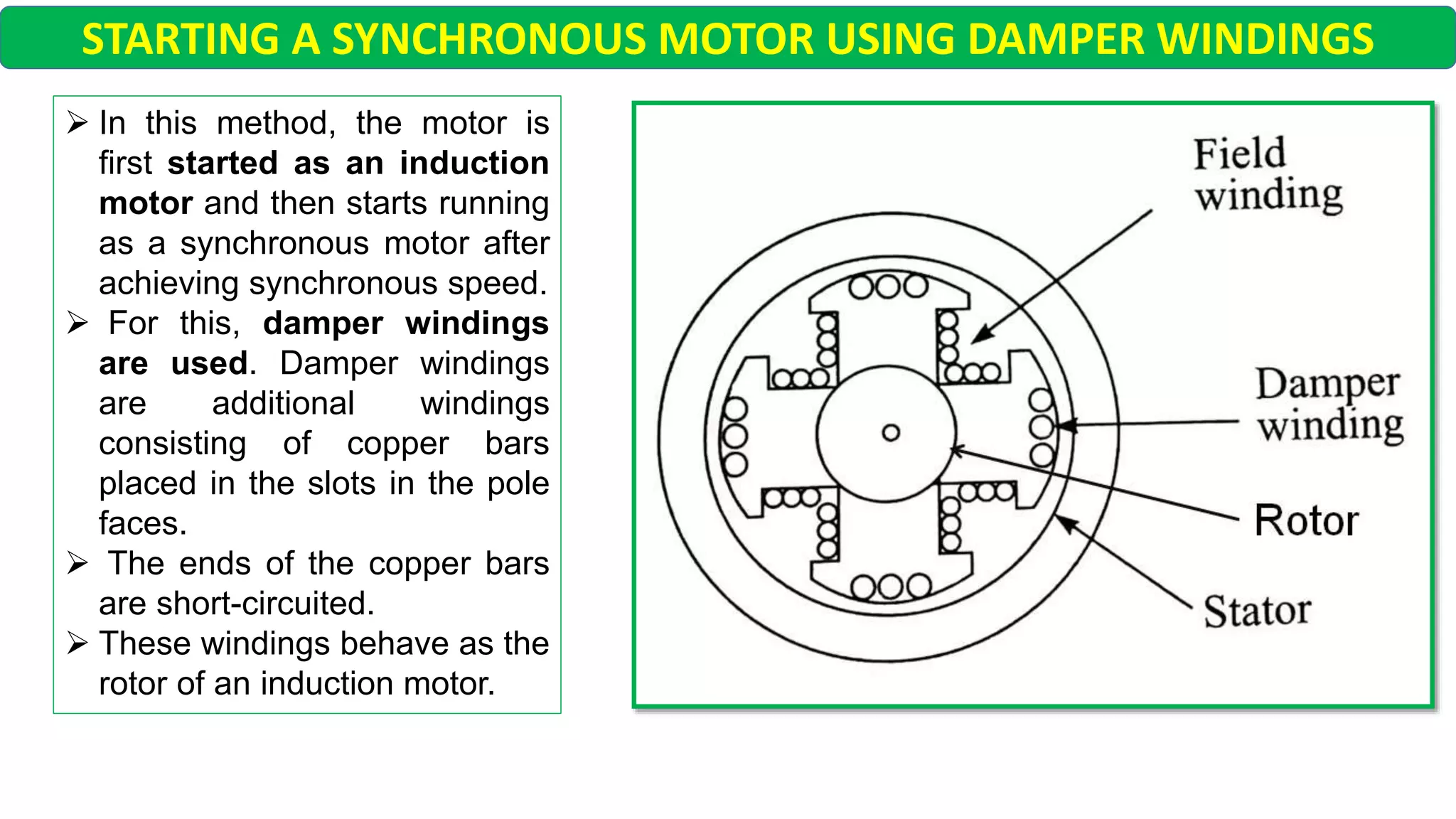
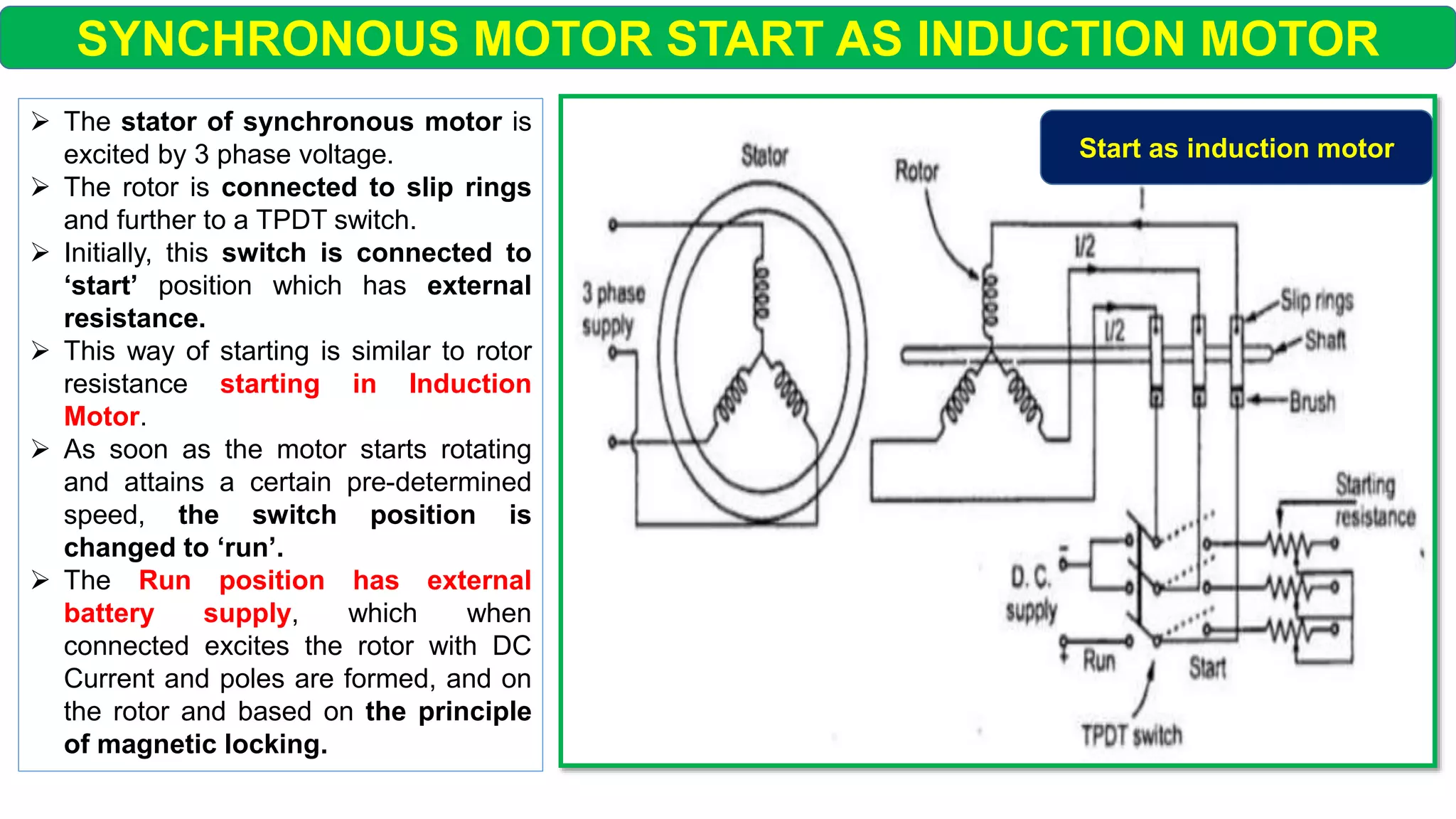
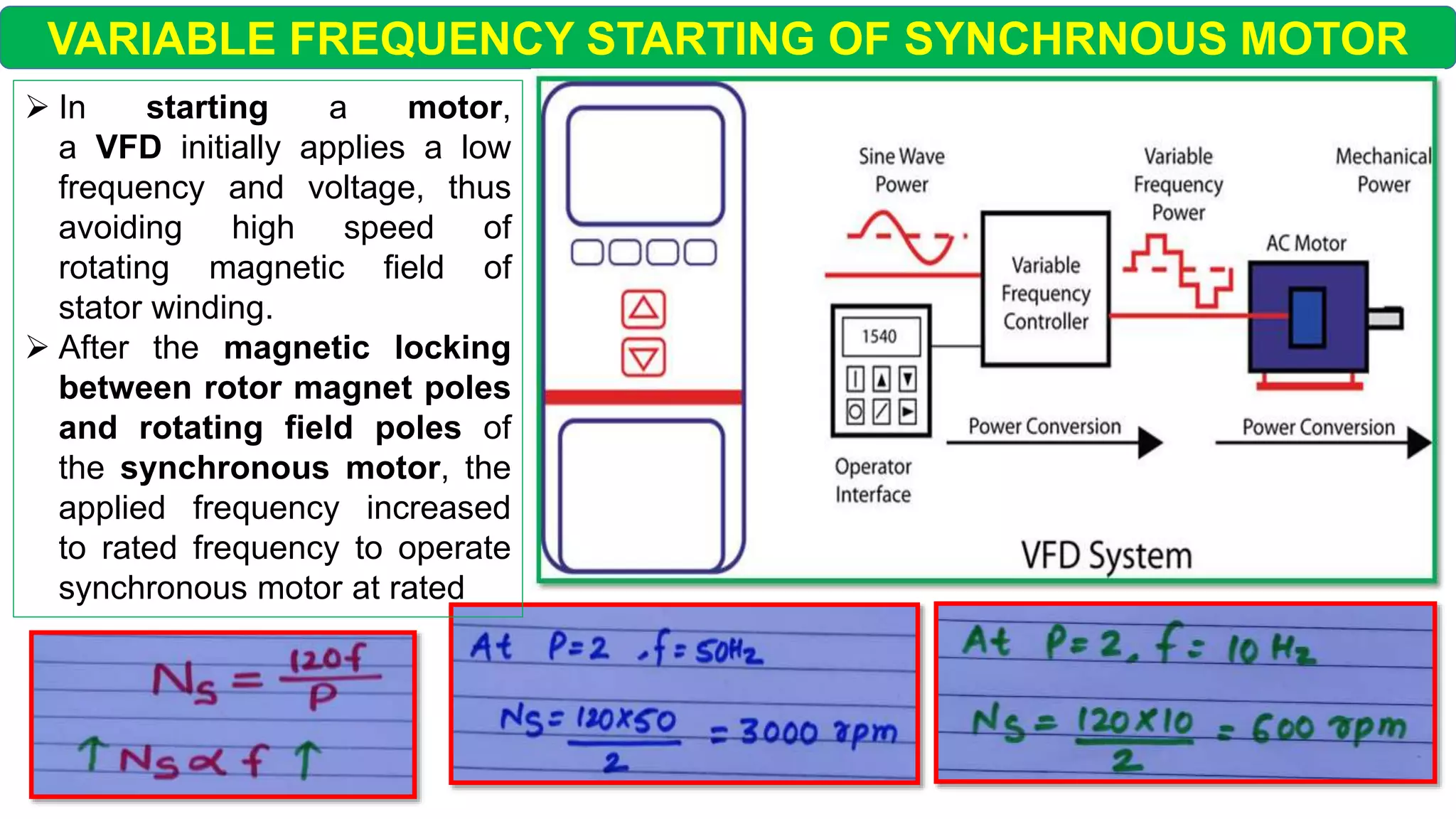
This document discusses different starting methods for synchronous motors. It describes using an auxiliary induction motor or DC motor to bring the synchronous motor rotor up to synchronous speed before excitation. It also covers on-load starting methods like using damper windings to start the motor as an induction motor initially or using a variable frequency drive to gradually increase frequency and avoid high starting torque.