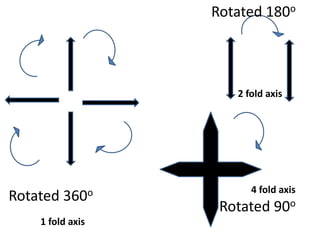
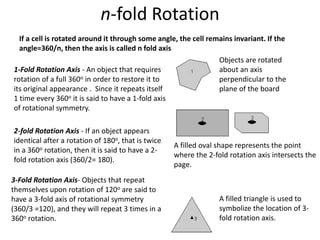
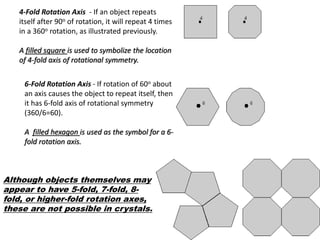
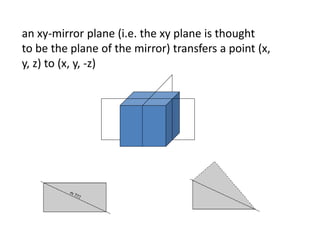
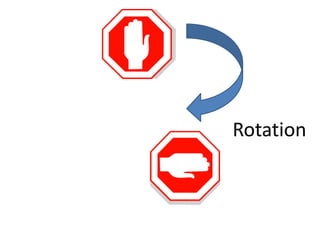
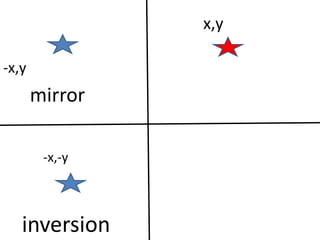
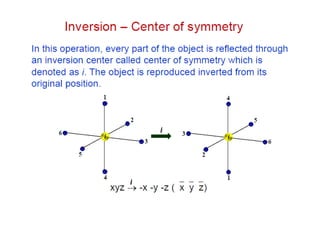
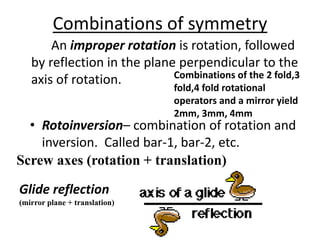
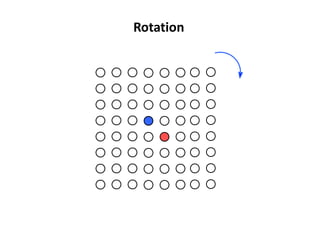
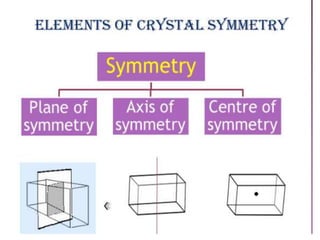
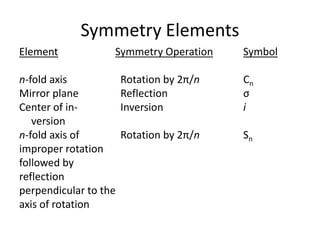
The document discusses various types of symmetry in objects, including rotational symmetry with examples of 1-fold, 2-fold, 3-fold, 4-fold, and 6-fold axes, as well as mirror symmetry and improper rotations. It explains the mathematical principles behind these symmetries and the significance of symmetry elements and operations. Additionally, it notes that higher-fold rotation axes (5-fold, 7-fold, etc.) are not possible in crystals.