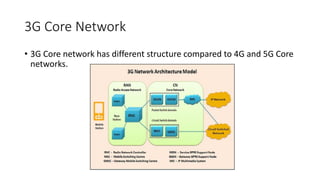
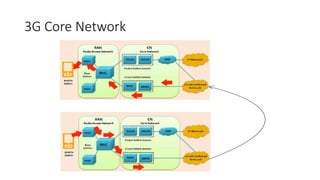
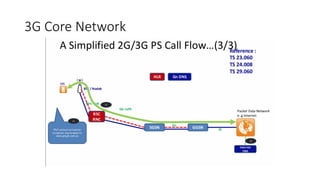
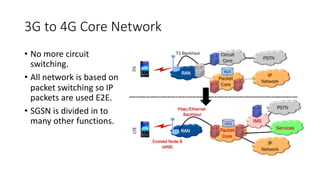
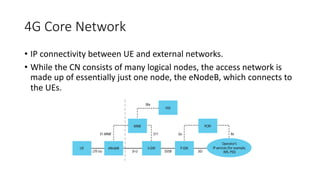
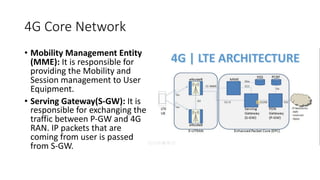
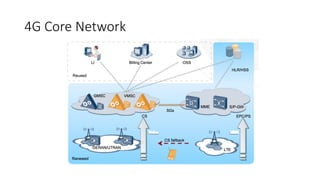
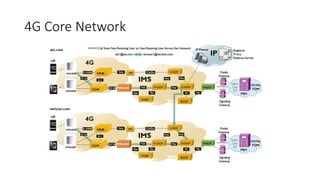
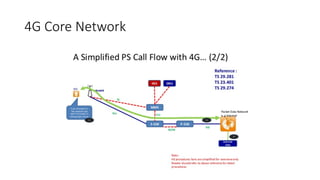
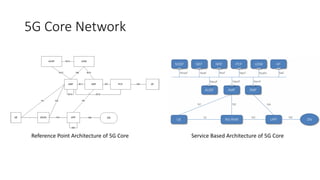
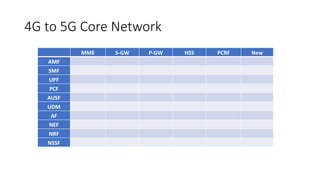
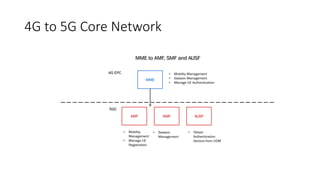
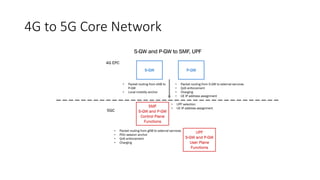
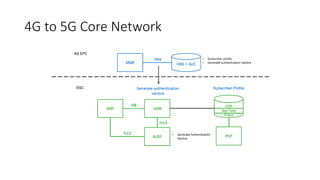
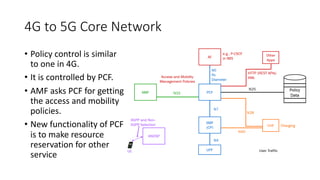
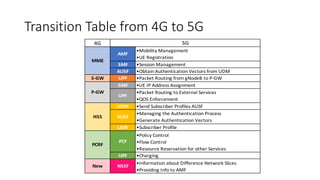
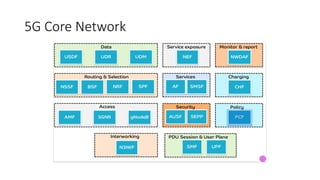
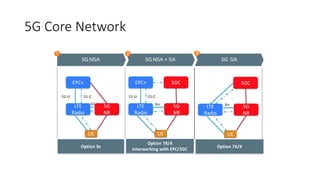
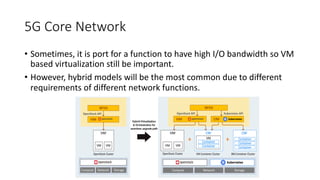
The document outlines the evolution of the core network from 3G to 5G, highlighting structural changes and technological advancements. It details the transition from circuit switching in 3G to packet switching in 4G and 5G, with increased functional specialization and the introduction of microservices in 5G architecture. The conclusion emphasizes the necessity for a flexible, scalable, and upgradable cloud-native 5G core, marking a significant shift in mobile network infrastructure.