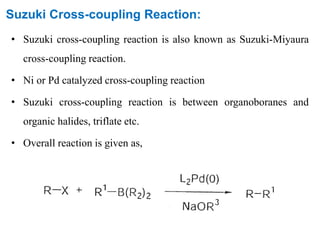
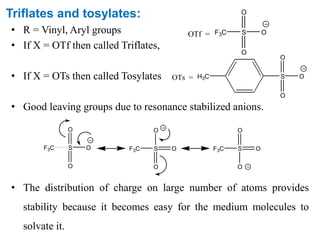
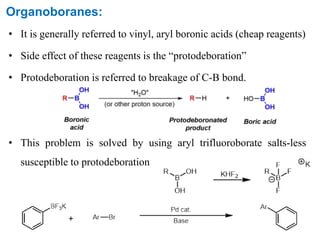
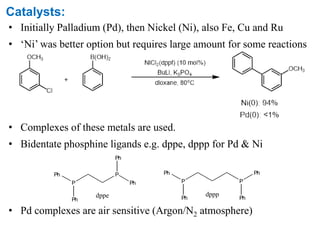
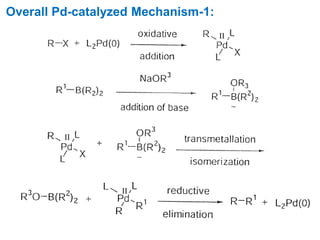
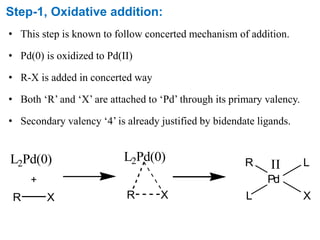
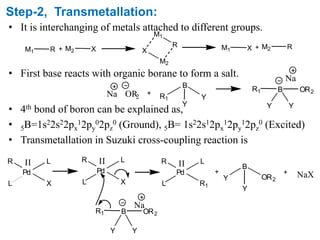
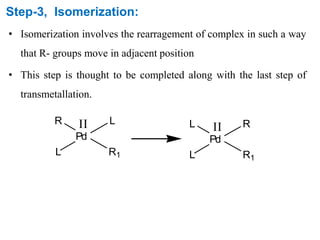
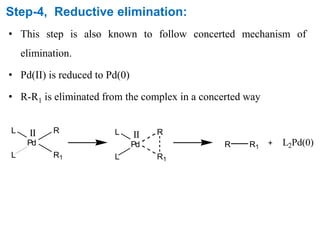
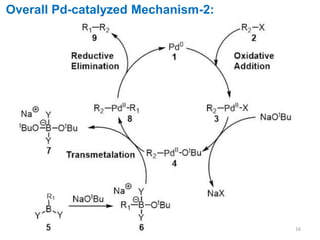
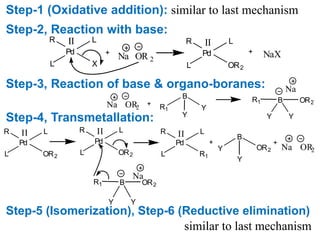
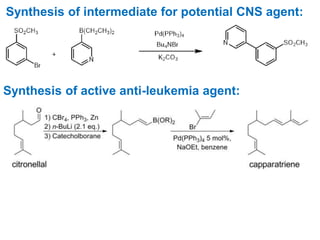
The Suzuki cross-coupling reaction involves the coupling of organoboranes and organic halides or triflates catalyzed by nickel or palladium. The reaction proceeds via an oxidative addition, transmetallation, isomerization, and reductive elimination mechanism. It has advantages over similar cross-coupling reactions as it uses cheaper and less toxic boronic acid reagents and produces easily removable inorganic byproducts. The reaction finds applications in synthesizing intermediates for potential CNS agents and active anti-leukemia agents.