Embed presentation
Download to read offline







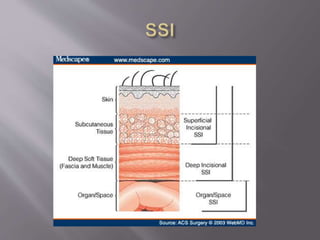




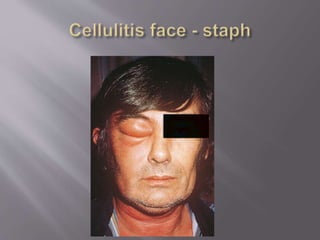



This document summarizes the history and key aspects of infectious diseases. It discusses early concepts from ancient Egyptians and Greeks, major advances in the 19th century including identifying specific bacteria and germs by Koch and Pasteur, the importance of hand washing by Semmelweis, and the discovery of penicillin by Alexander Fleming in 1928. It then outlines Koch's postulates for identifying causative agents of disease and lists risk factors for infection like malnutrition, metabolic diseases, and immunosuppression. The document also describes local and systemic presentations of infection, sources as primary or hospital-acquired, and specific infections like gas gangrene, tetanus, and necrotizing fasciitis. Prevention strategies mentioned include antibiotic pro















