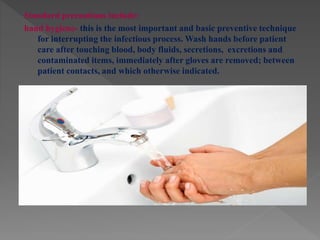
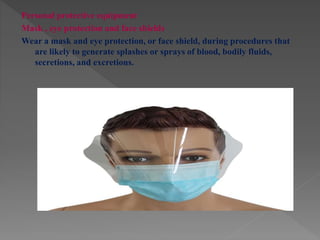
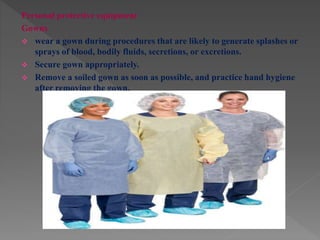
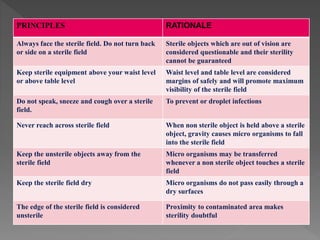
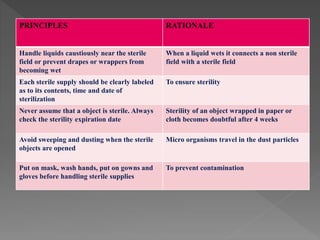
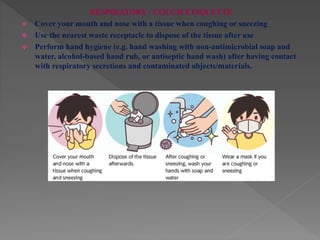
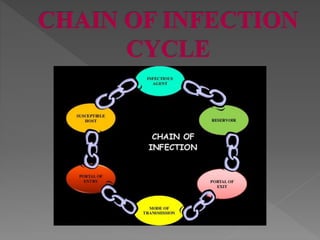
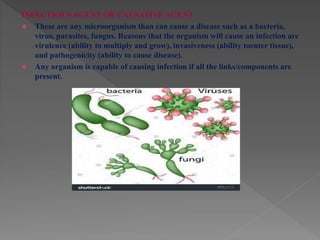
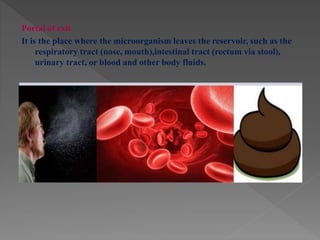
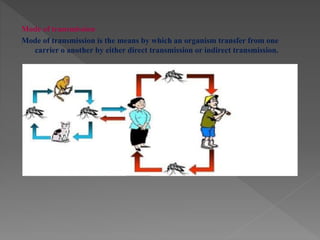
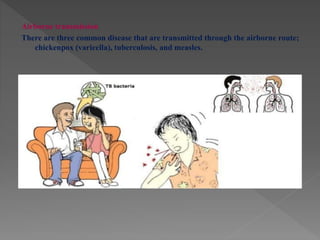
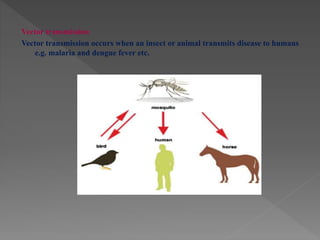
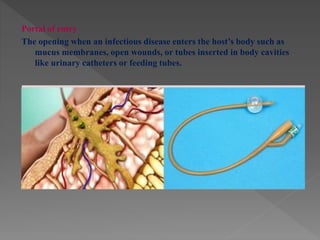
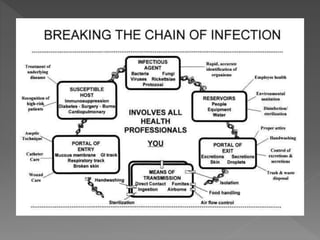
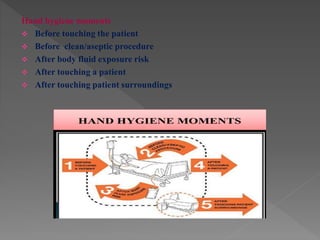
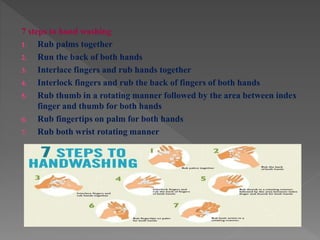
Standard precautions are a set of infection control practices used to reduce transmission of microorganisms in healthcare settings. They include proper hand hygiene, use of personal protective equipment like masks, gloves, and gowns, and cleaning and disinfection of rooms and equipment. Standard precautions protect both healthcare workers and patients and are the basic level of precautions used with all patients. They also include contact, droplet, and airborne precautions which have additional requirements for isolating patients with certain infectious diseases.