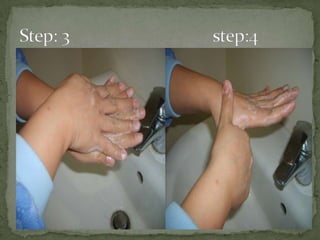
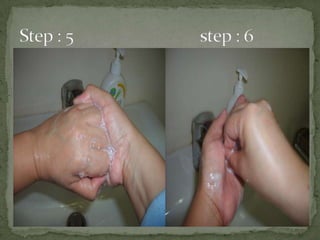
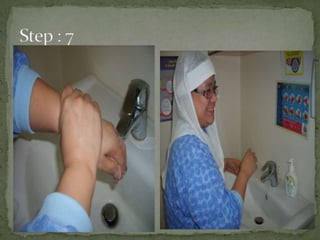
The document discusses handwashing and hygiene practices in a hospital setting. It defines different types of handwashing including medical, surgical, and hand hygiene. It explains that transient flora on hands can transmit diseases while resident flora is generally harmless. Regular handwashing with soap and water or alcohol-based rubs removes transient bacteria and prevents transmission of infections.