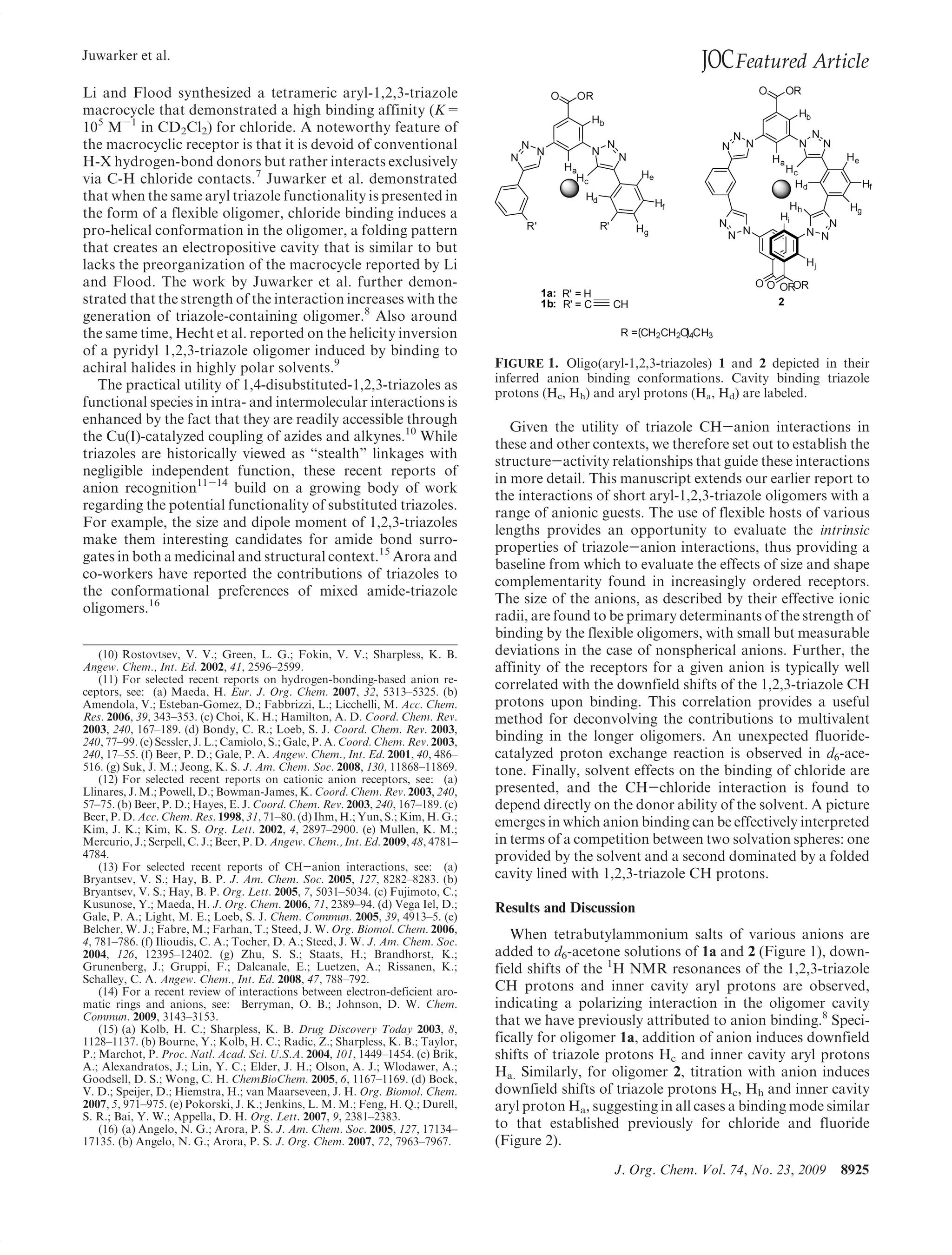
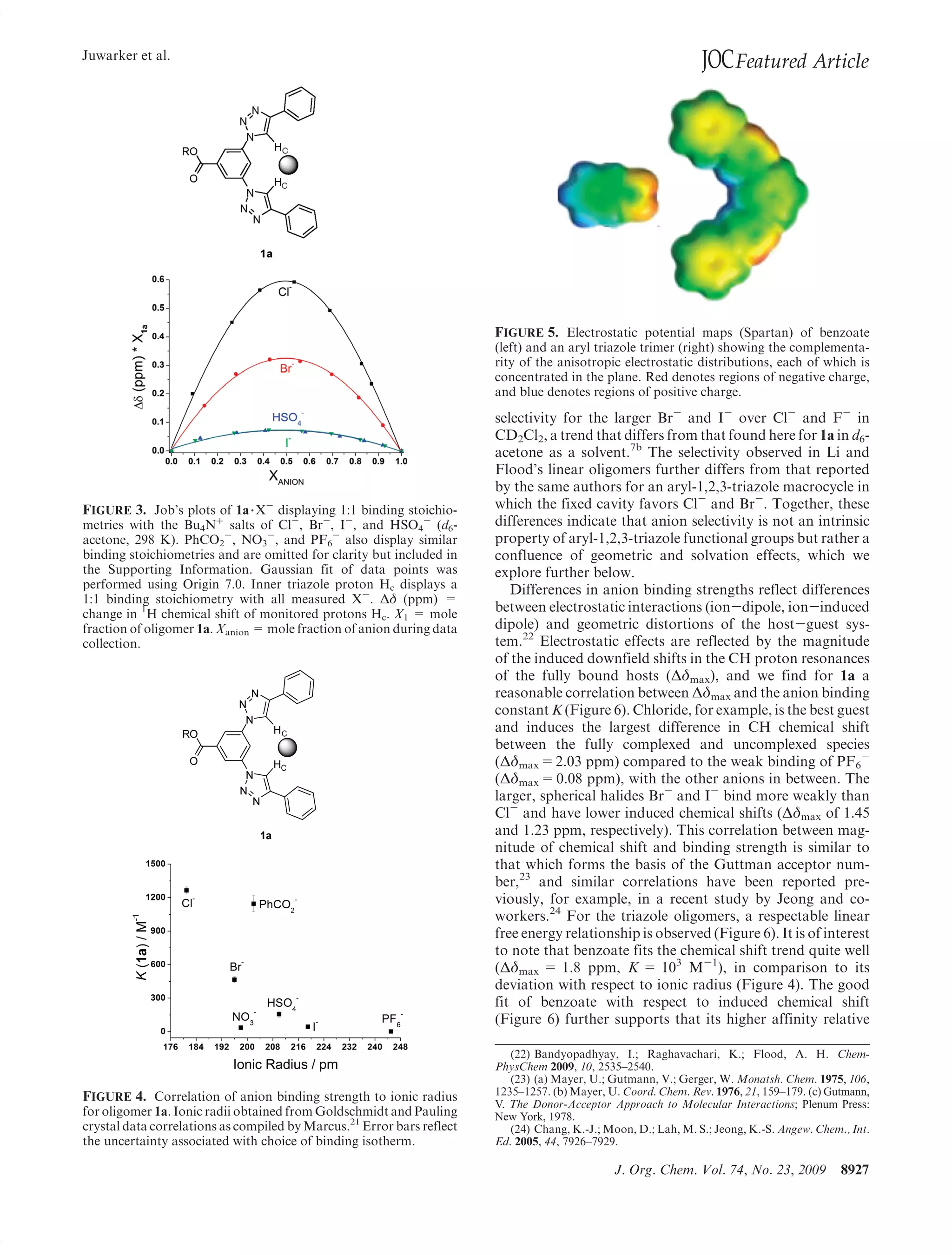
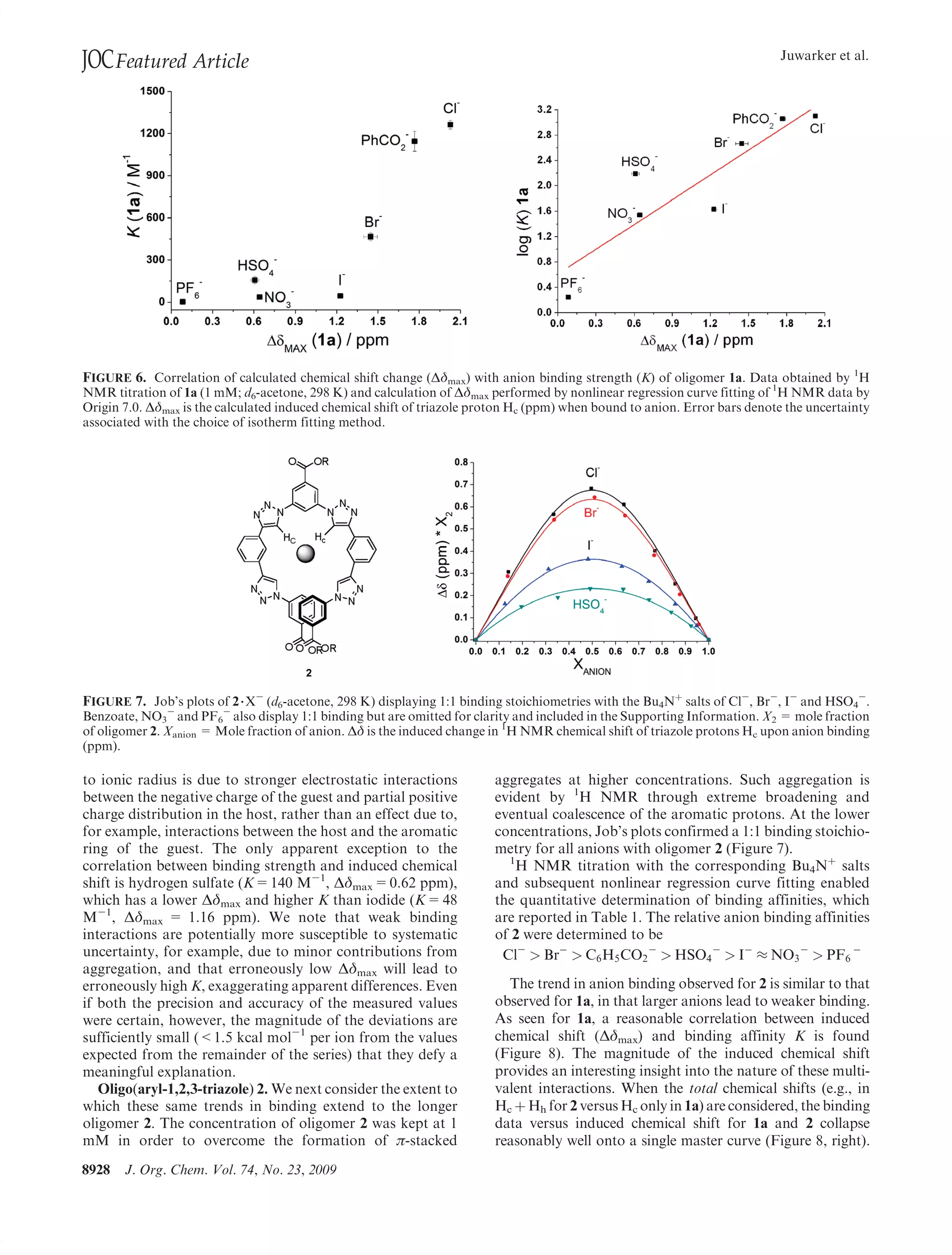
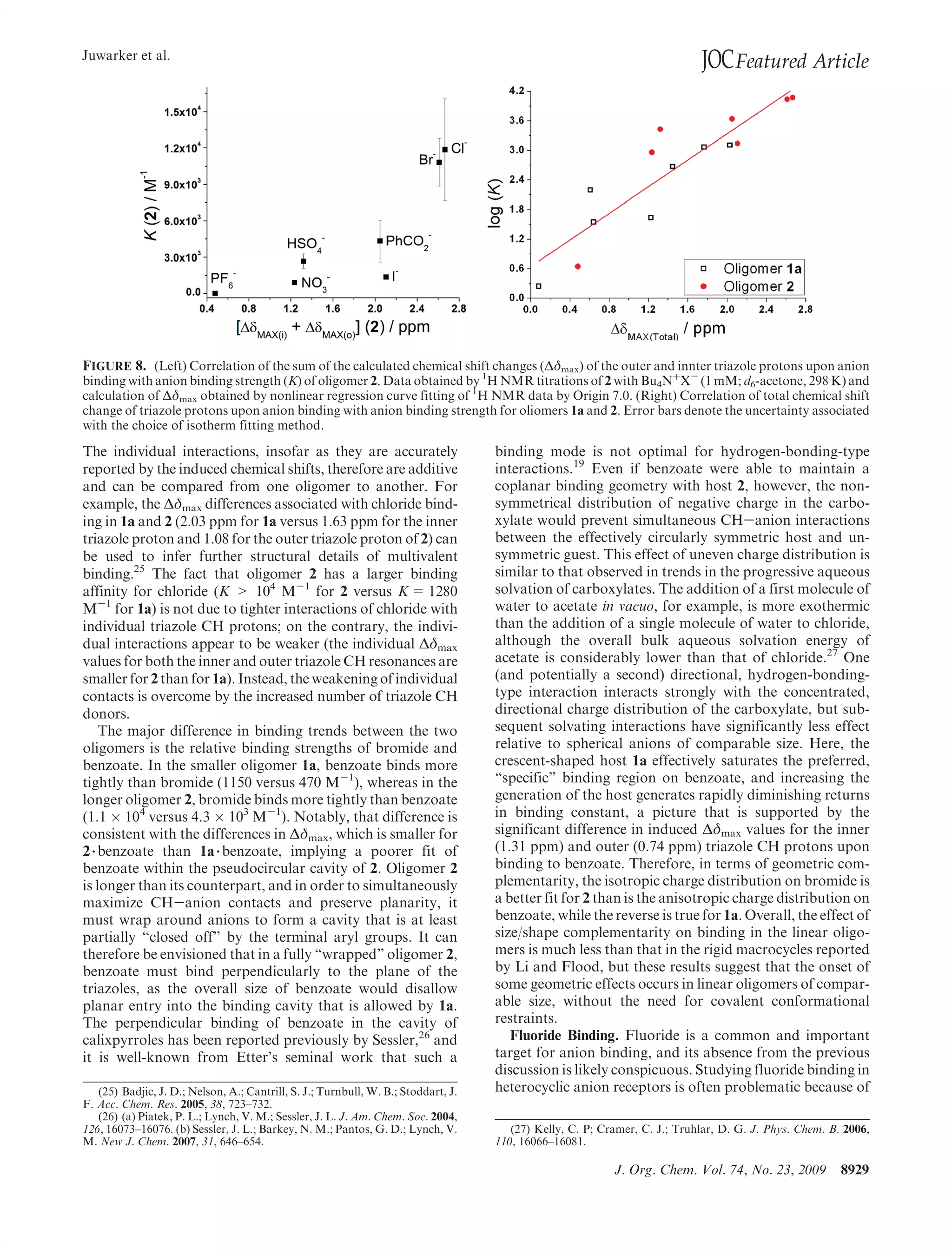
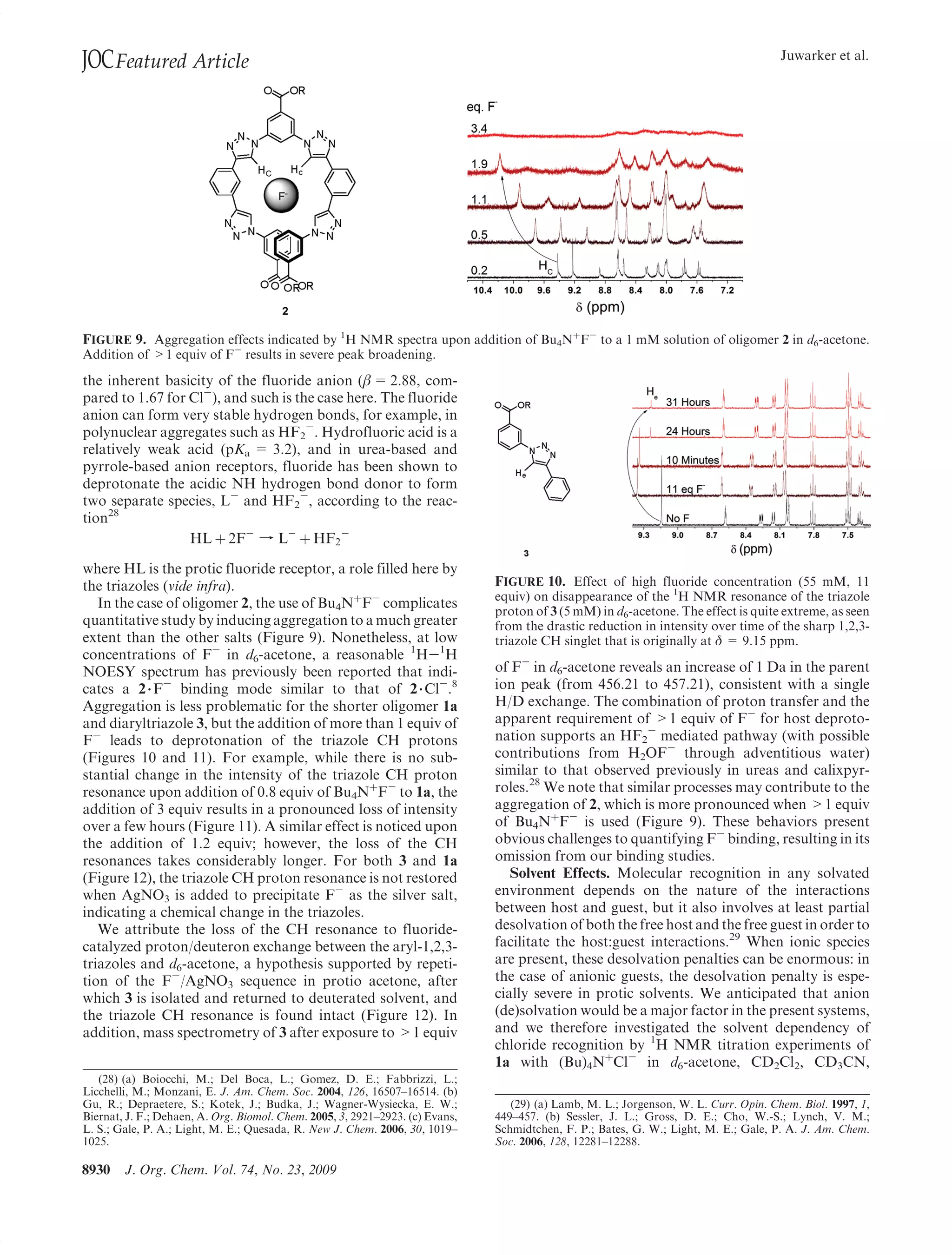
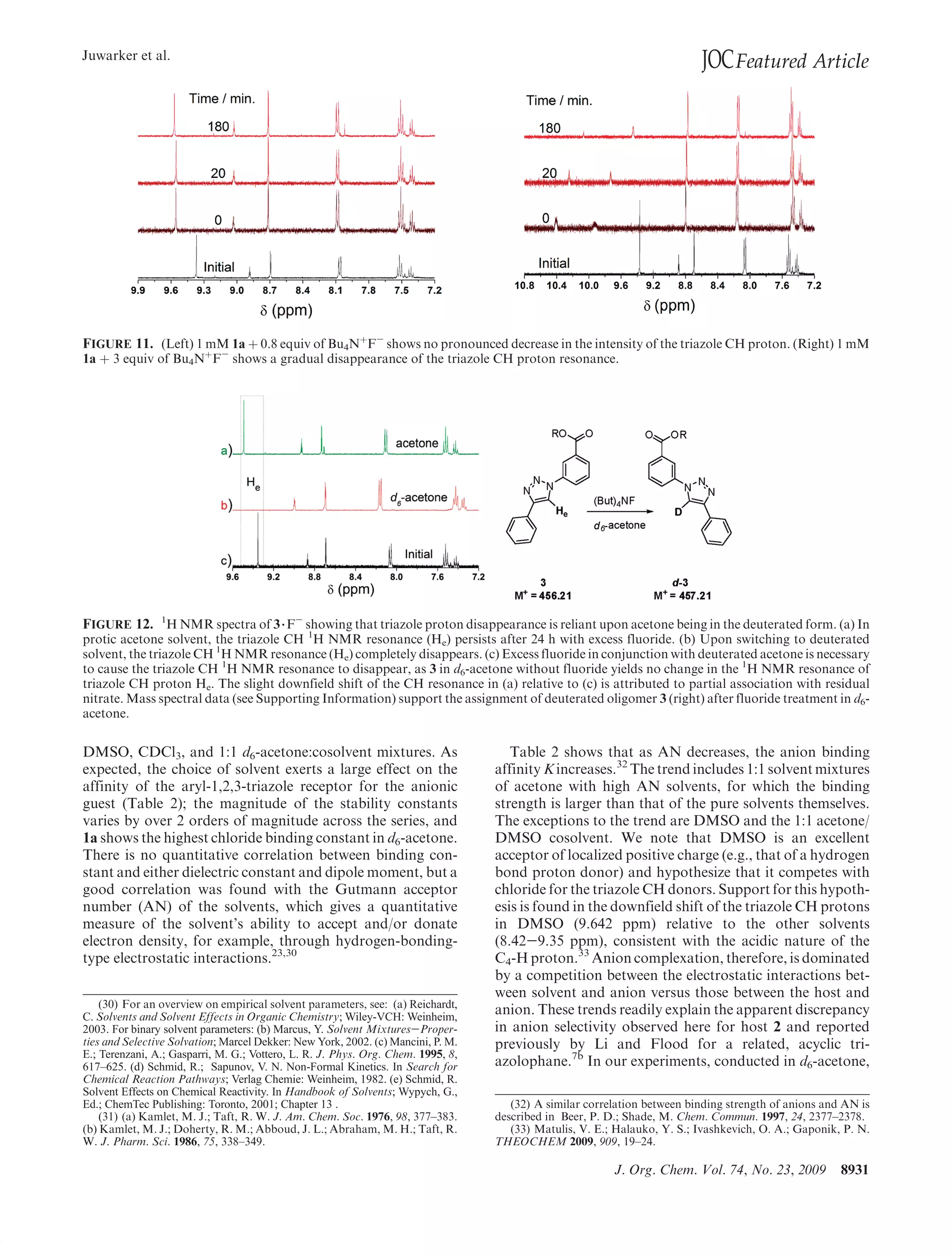
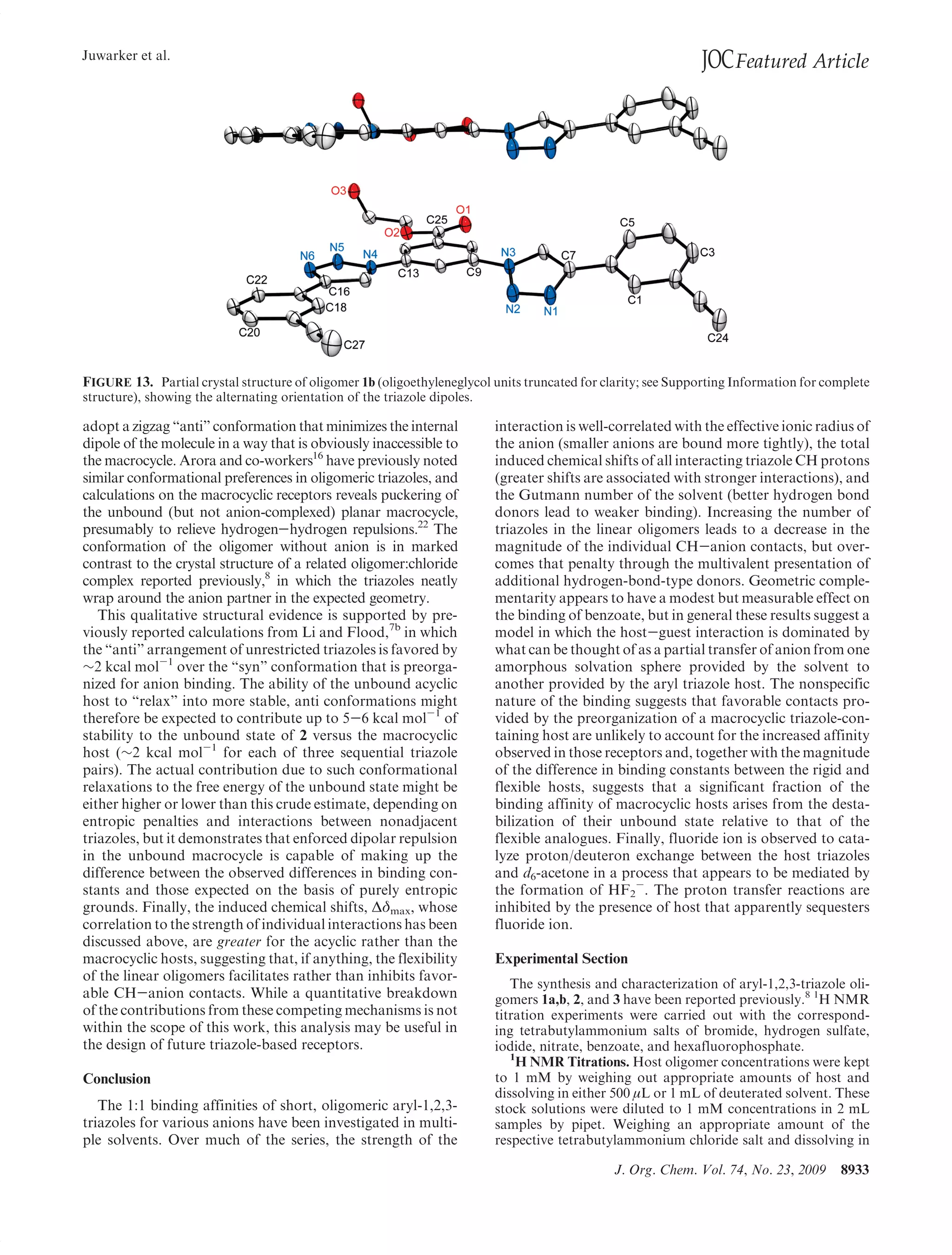
This document summarizes a study on anion binding by short, flexible aryl triazole oligomers. The study determined binding affinities for various combinations of oligomer and anion using 1H NMR titrations. Effective ionic radius was found to be a primary determinant of relative binding interactions, with small deviations for nonspherical anions. Solvent effects were also significant, with binding strength dependent on solvent donor ability. The results provide insight into anion binding by flexible versus rigid hosts containing electropositive triazole protons.