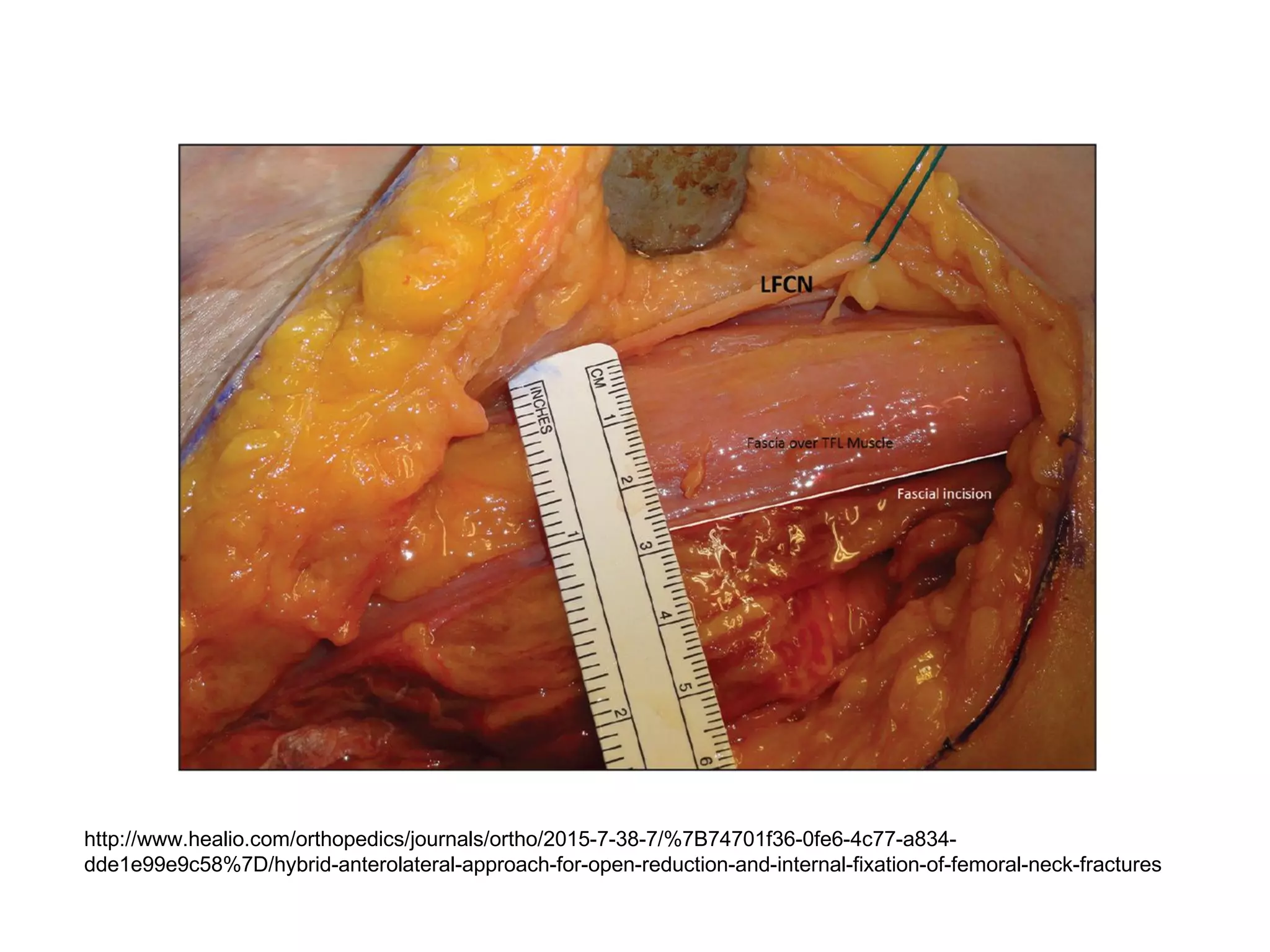
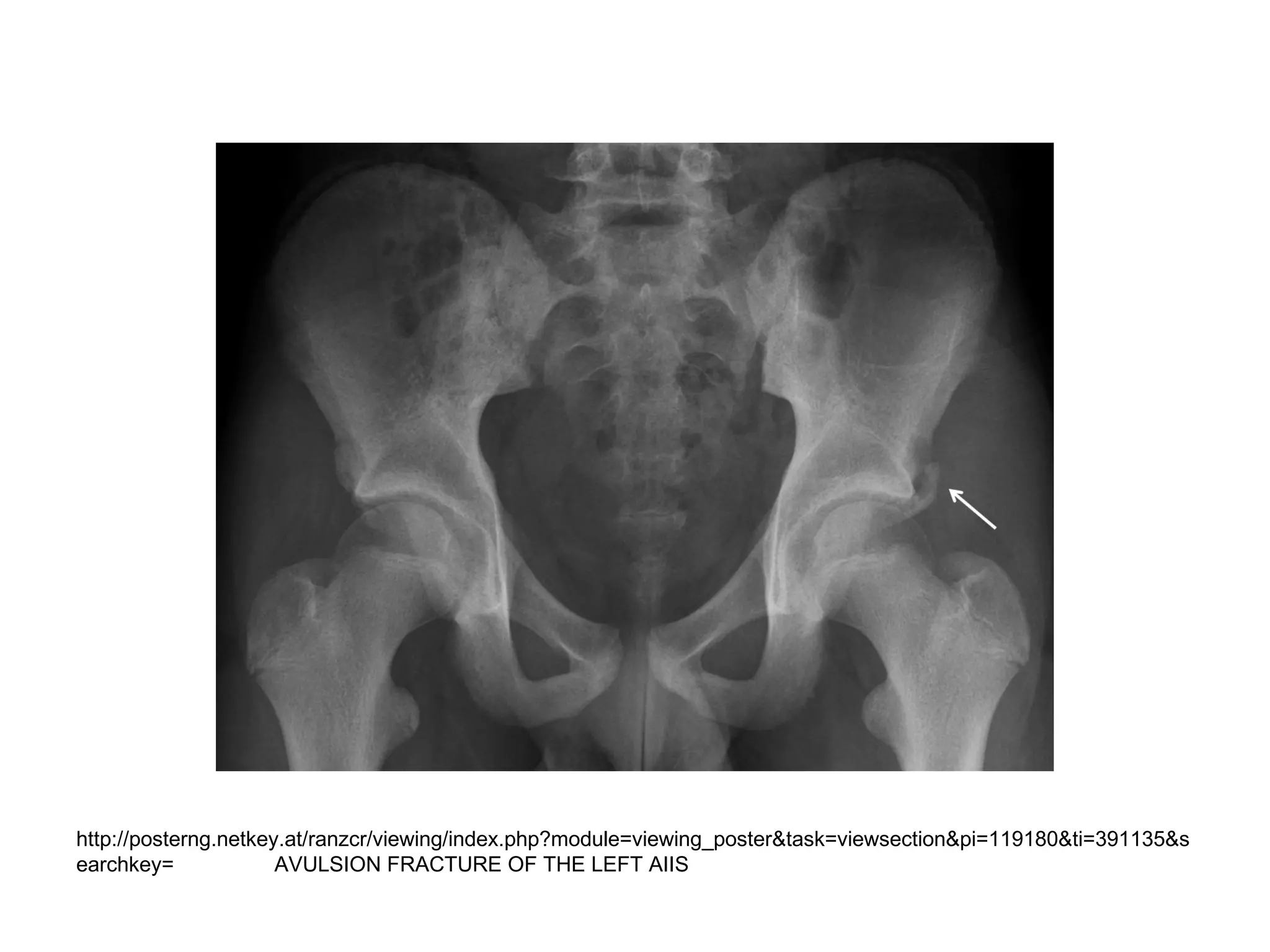
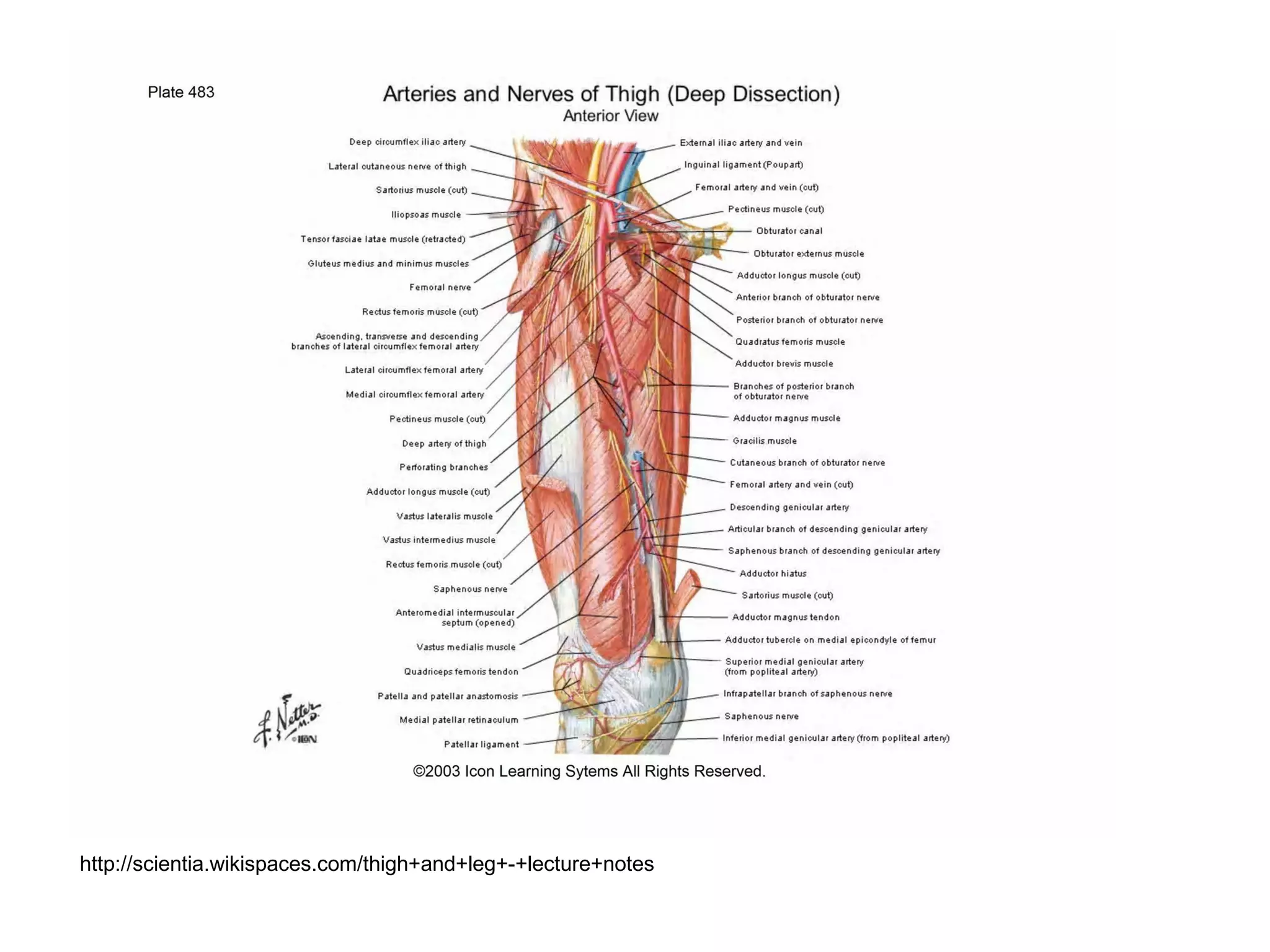
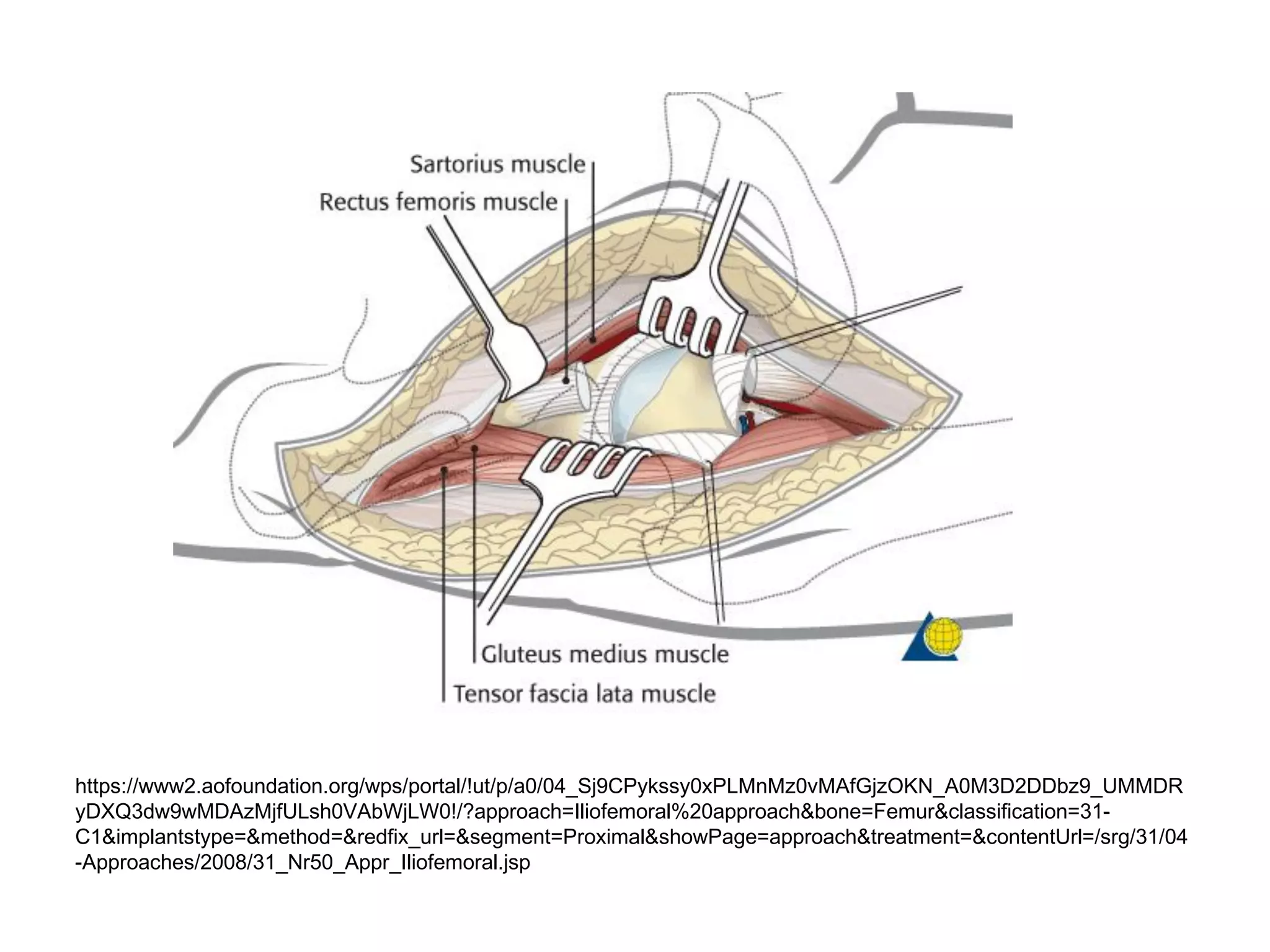
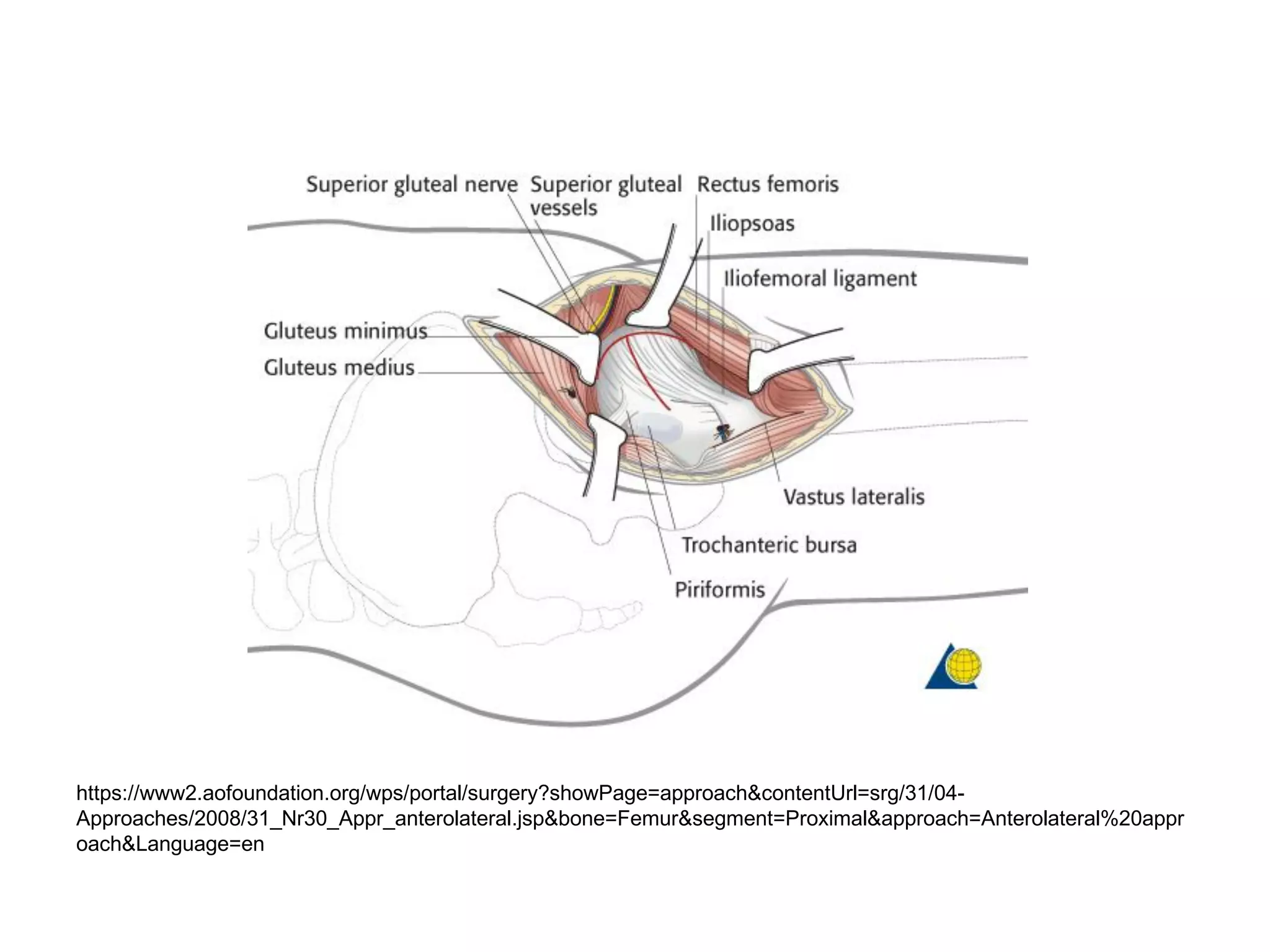
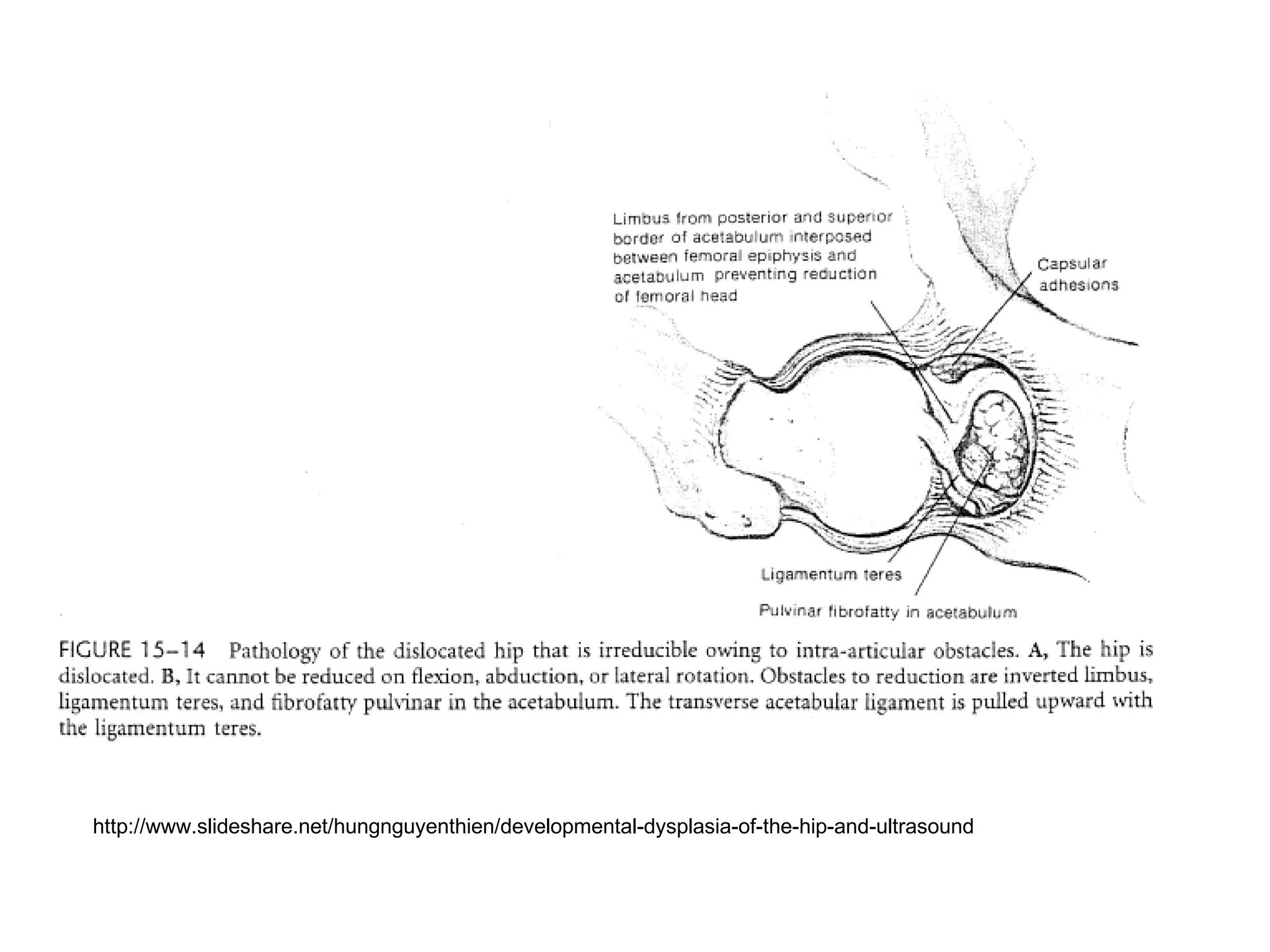
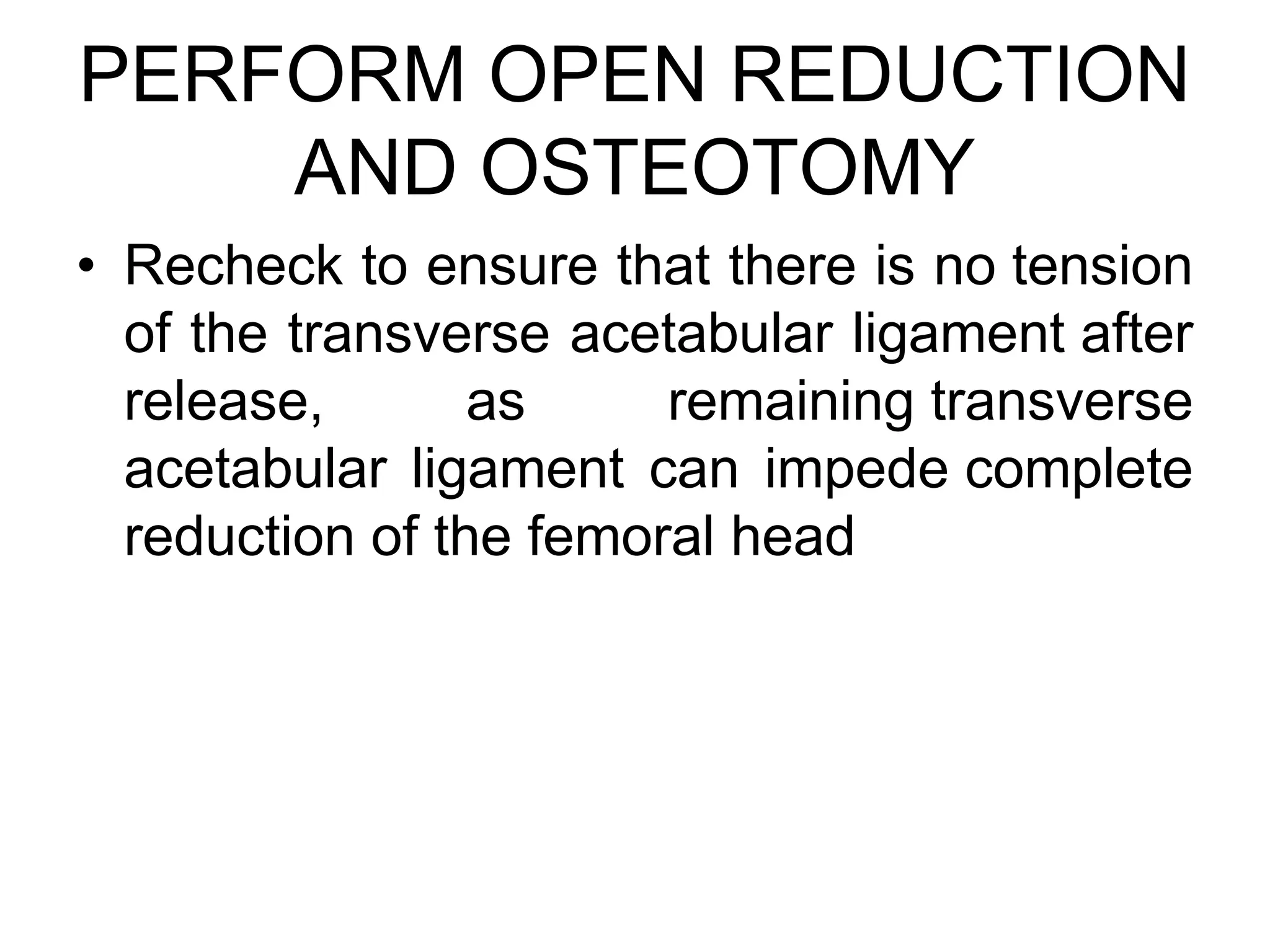
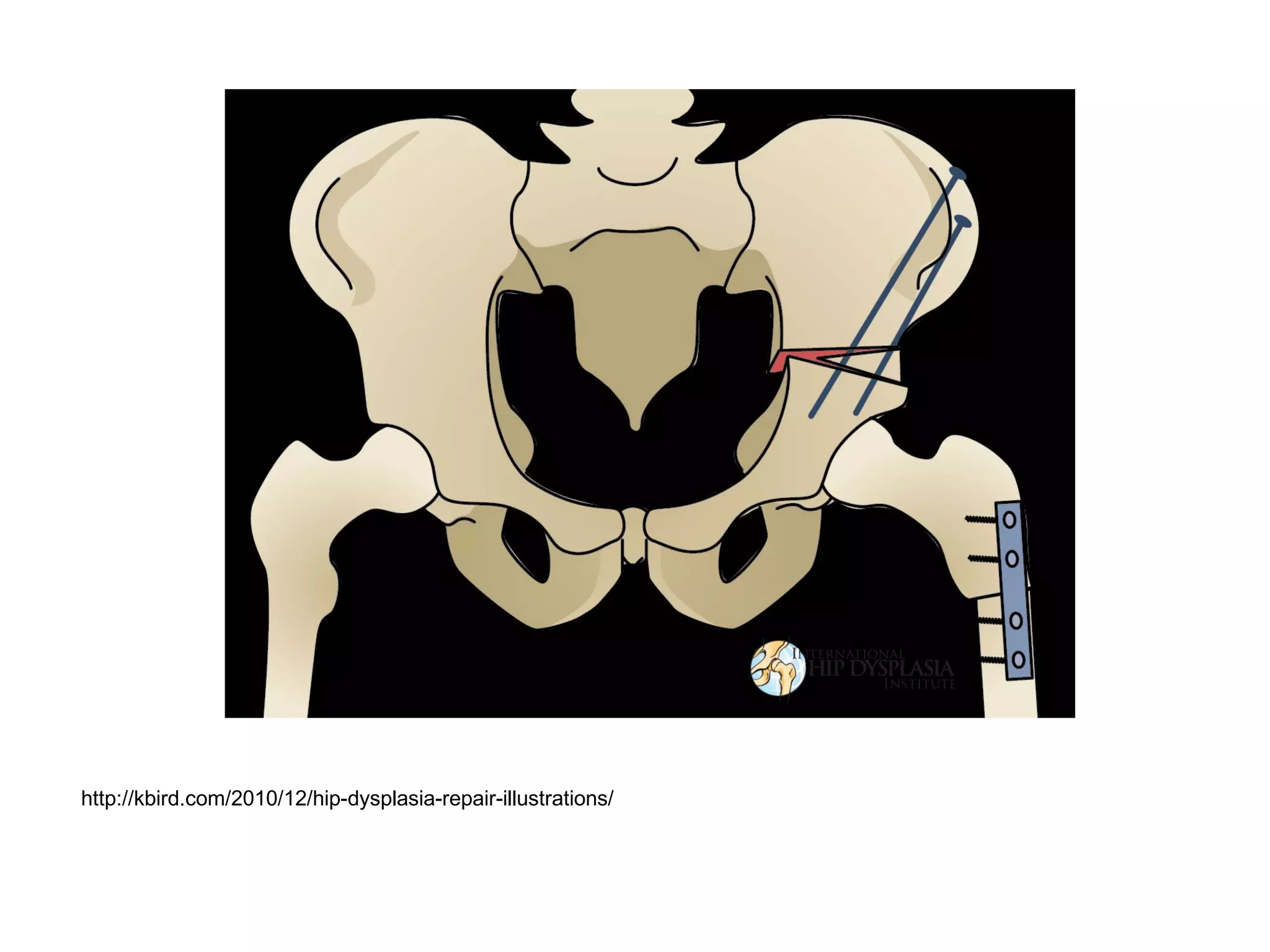
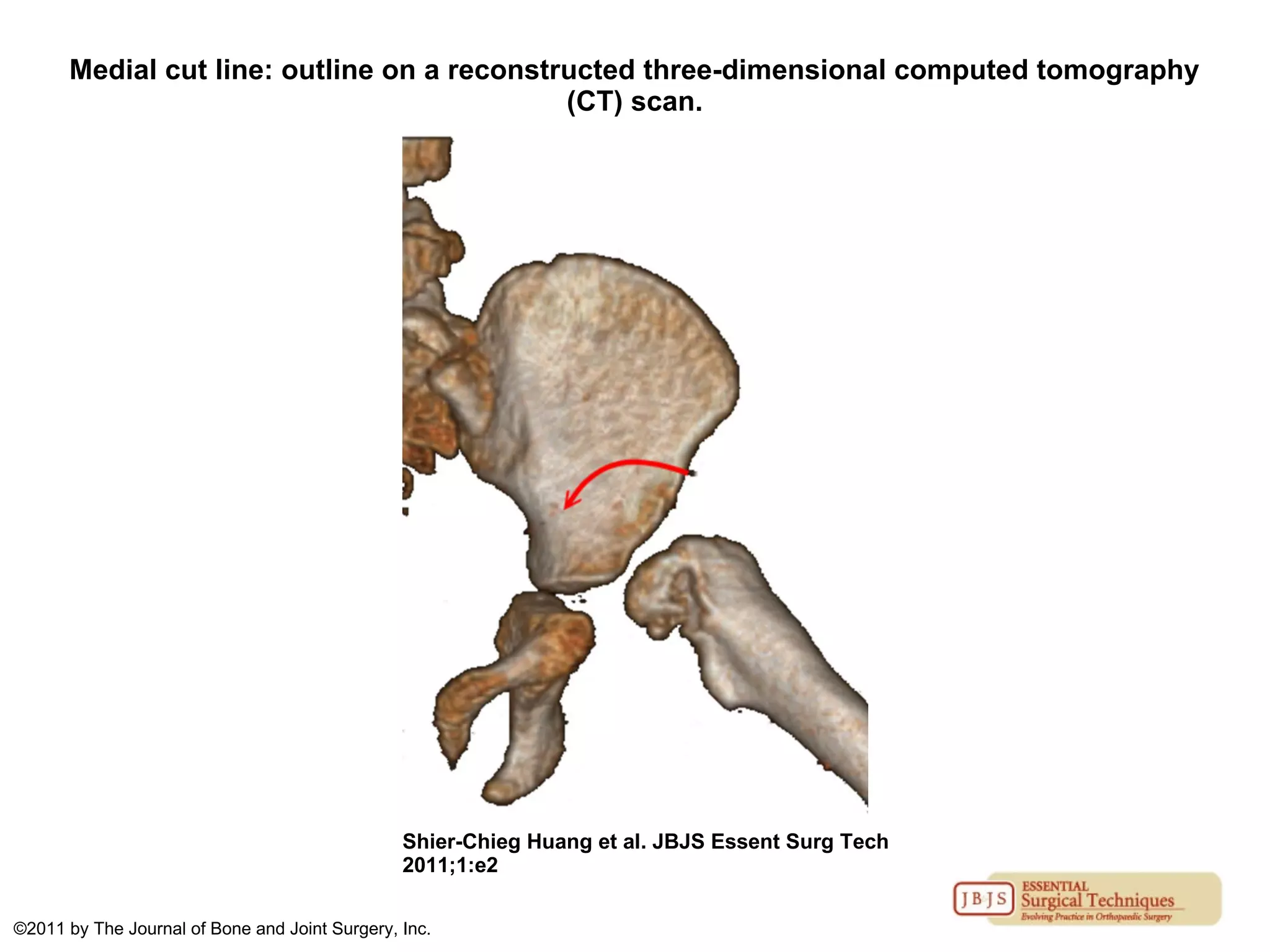
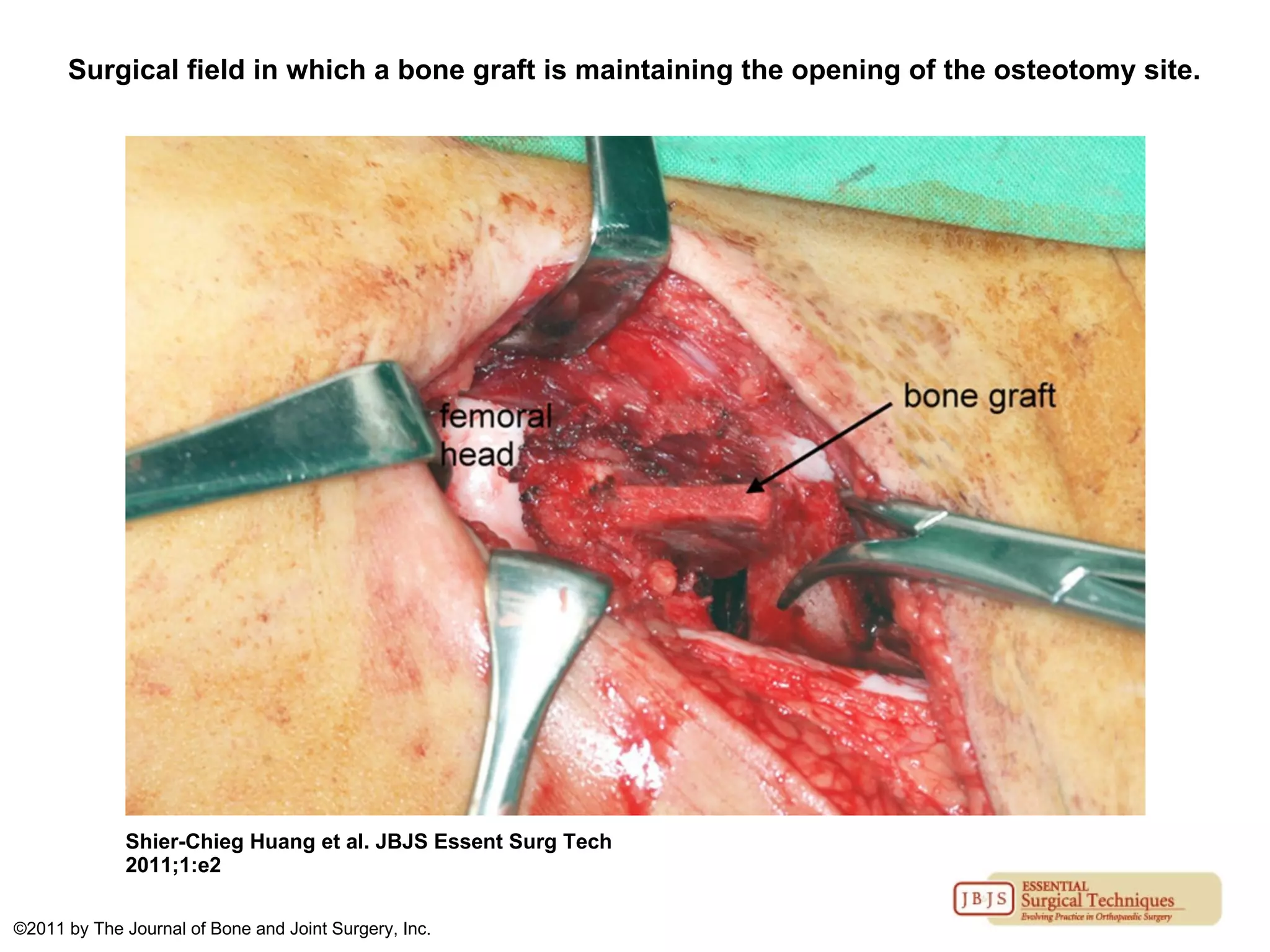
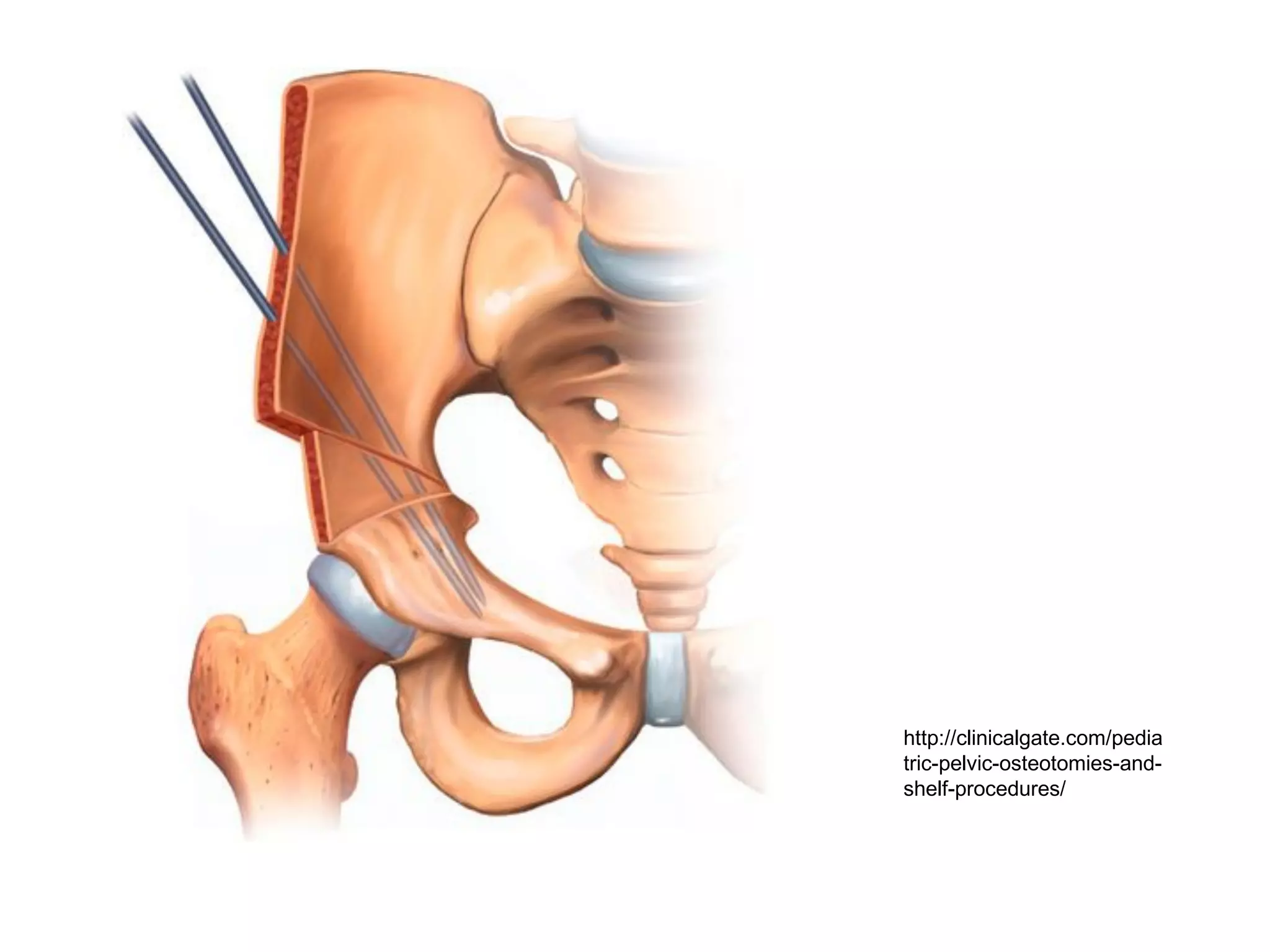
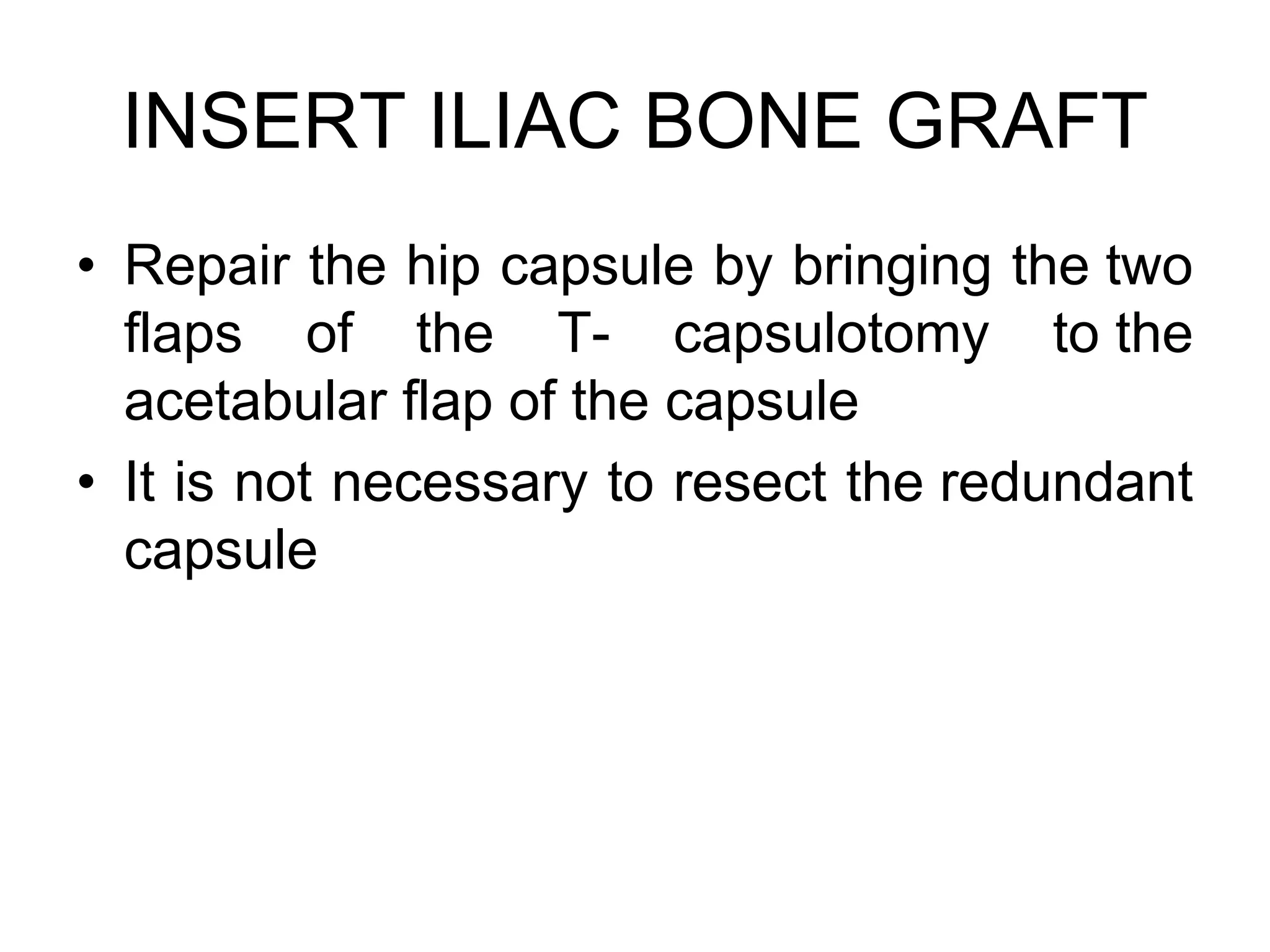
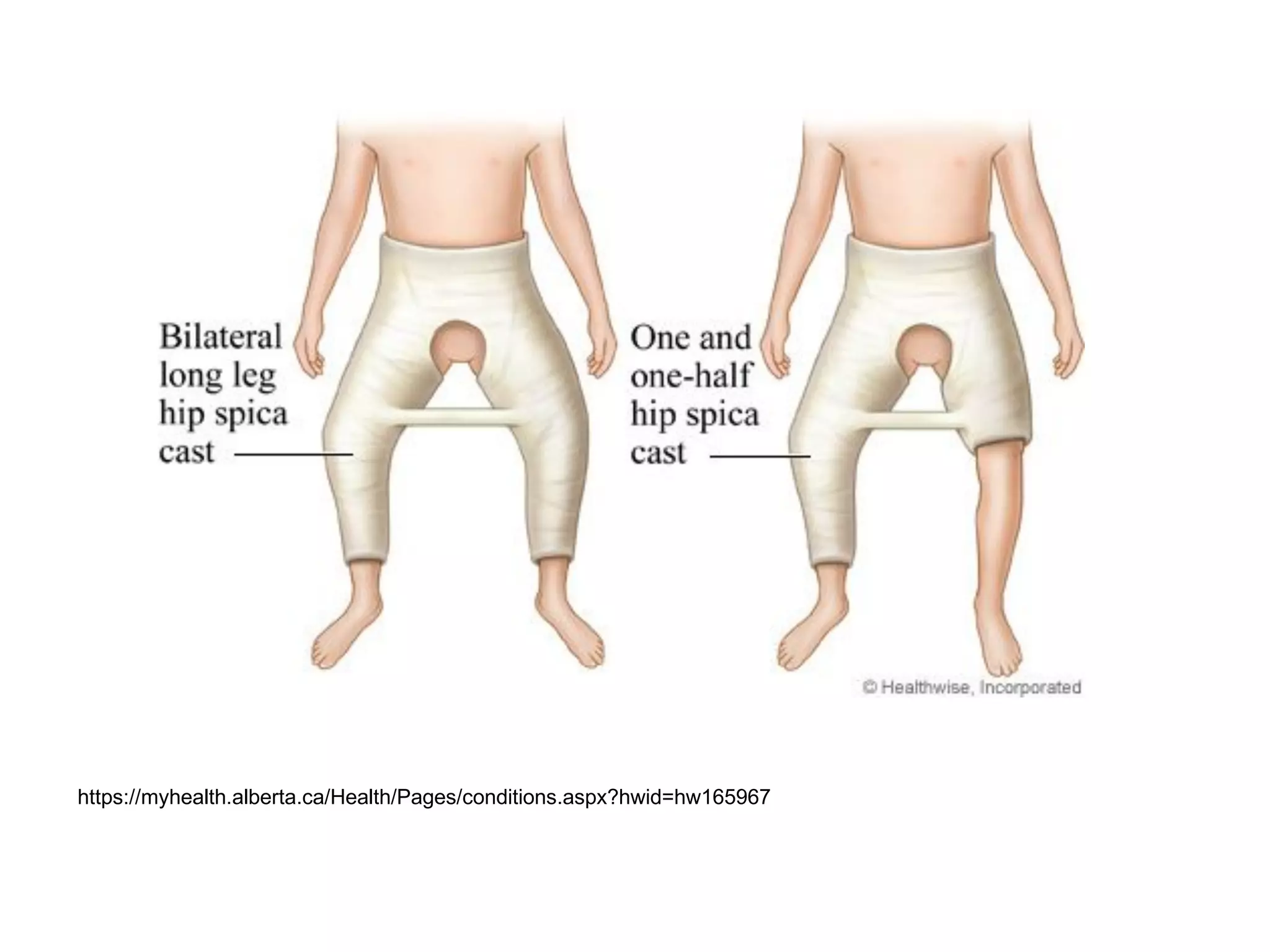
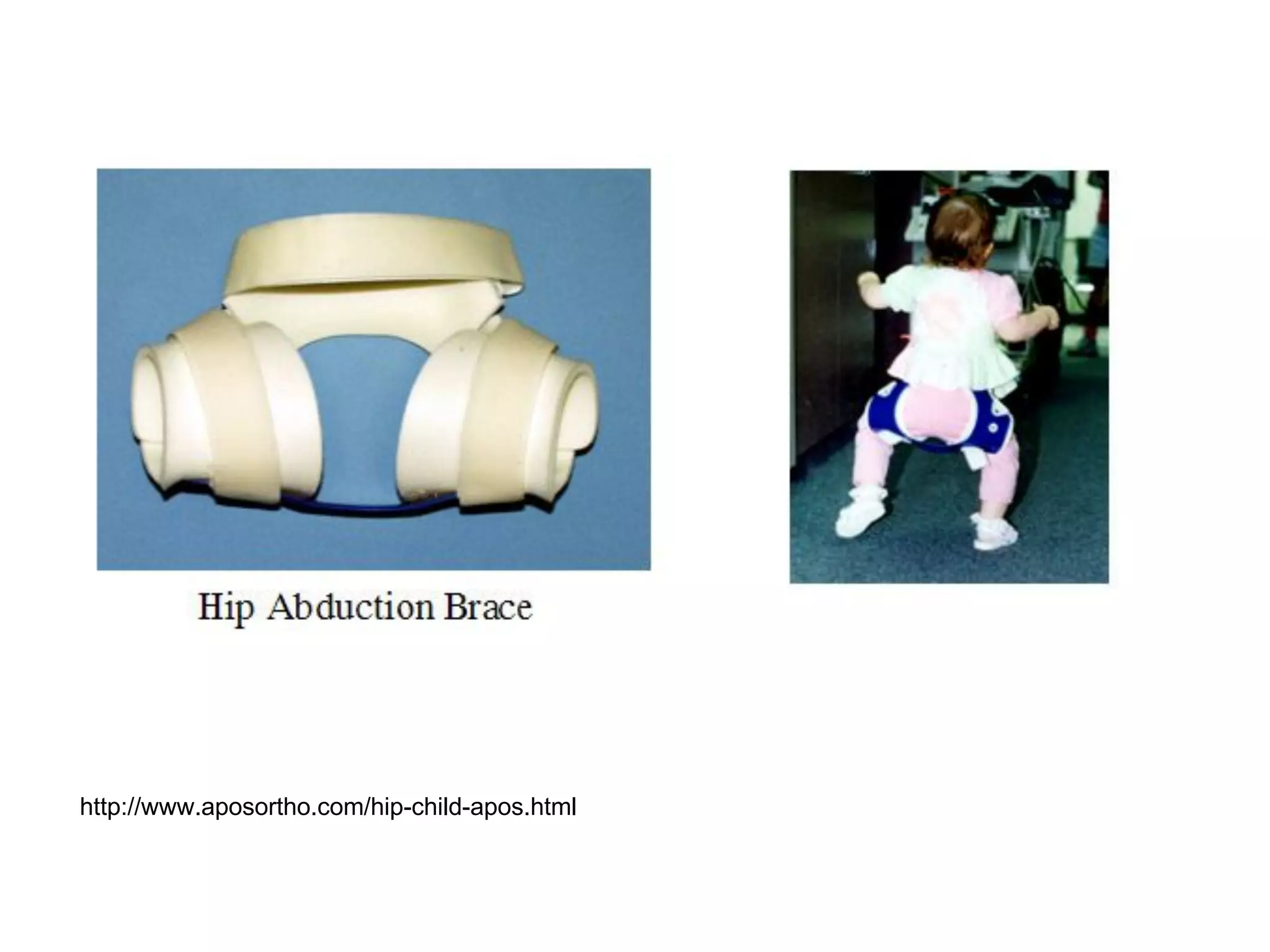
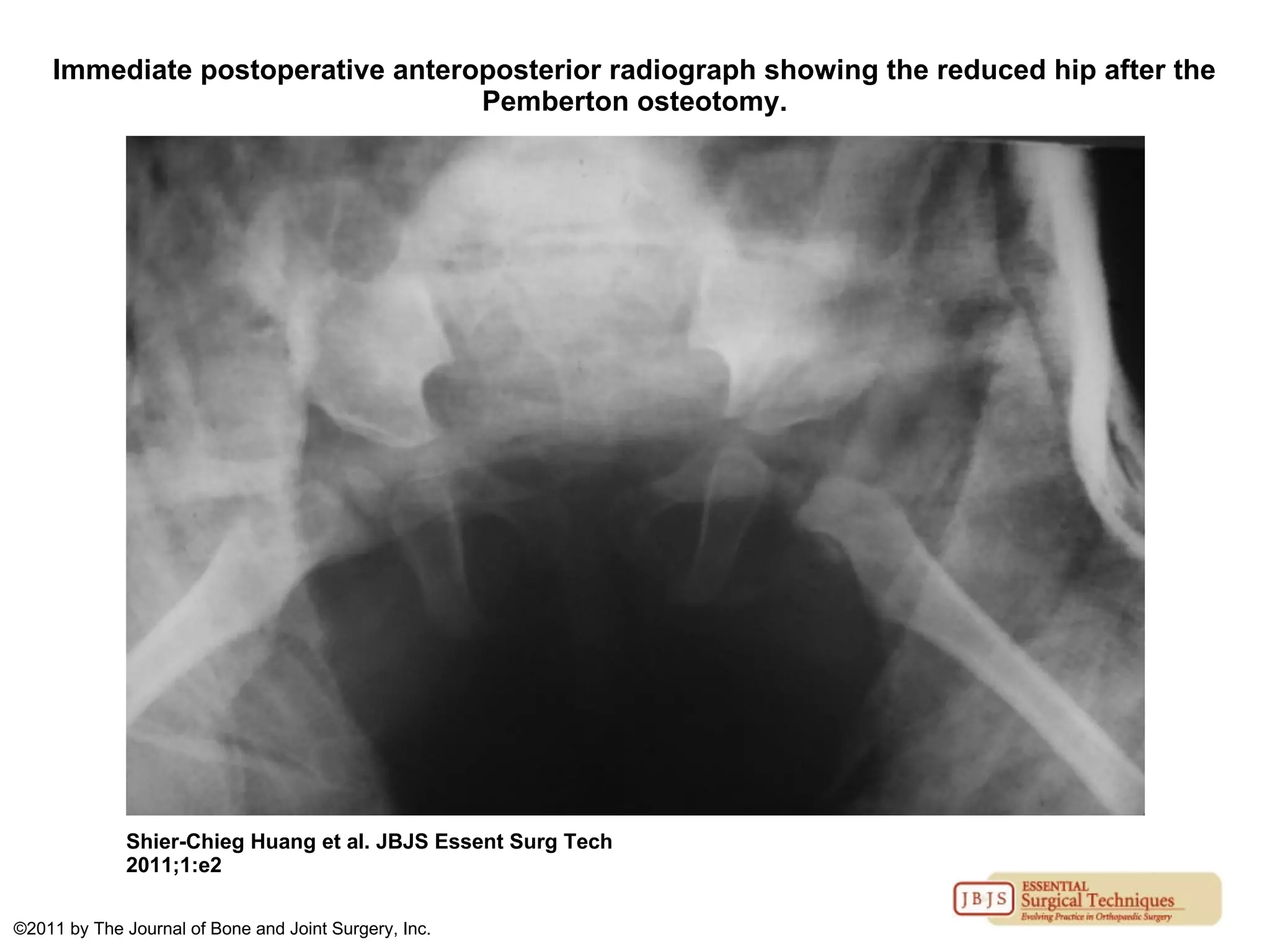
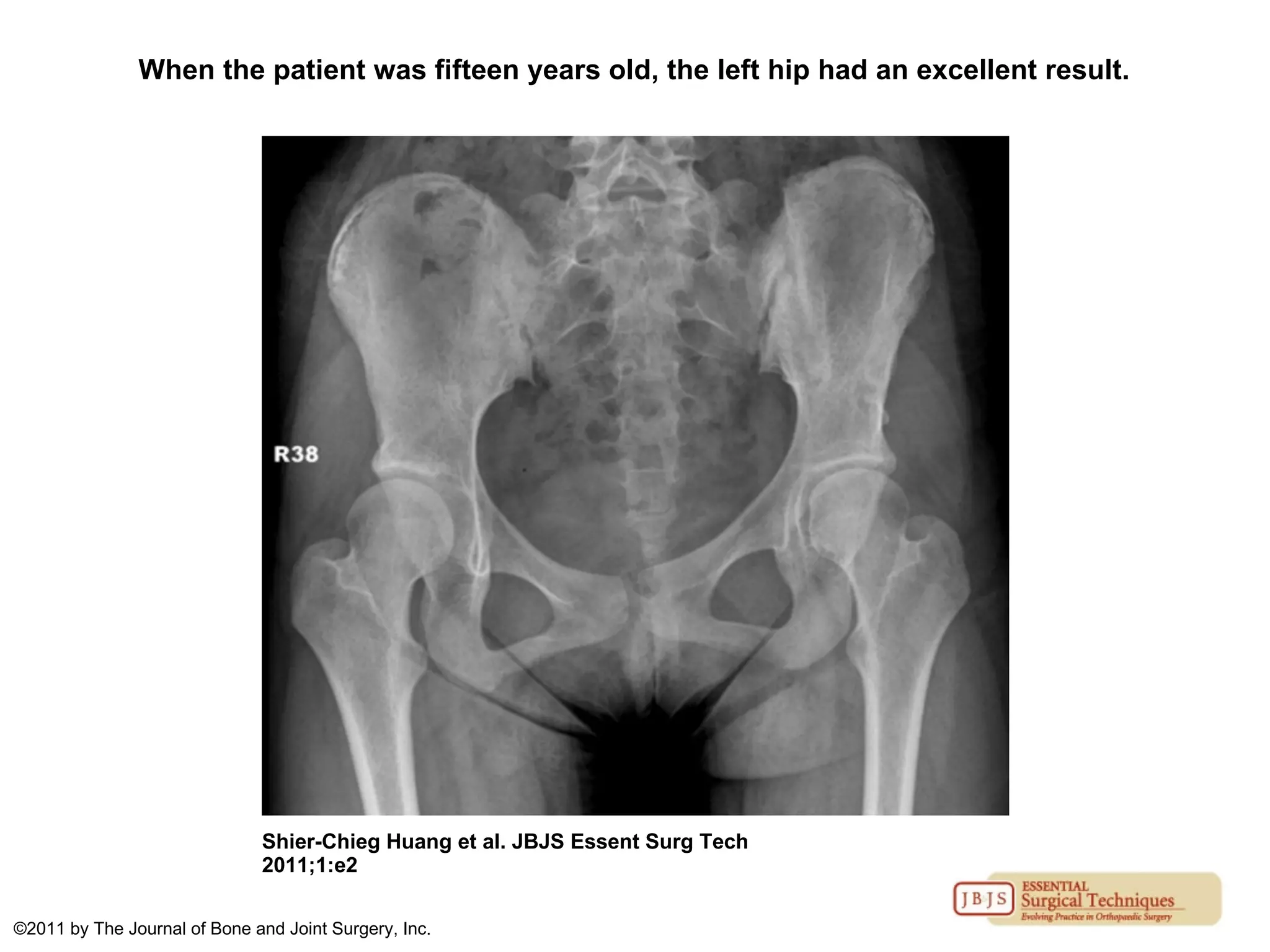
The document discusses the Pemberton osteotomy technique for treating acetabular dysplasia, outlining its historical background, procedural steps, and advantages over other methods like the Salter innominate osteotomy. It emphasizes the importance of careful surgical technique to avoid complications such as damage to the triradiate cartilage. The document also covers the indications and expected outcomes of this surgical approach.