Embed presentation
Downloaded 58 times
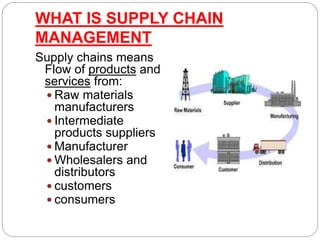







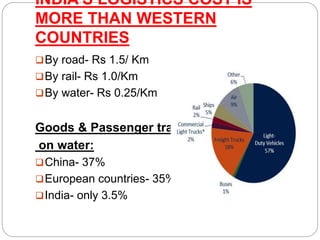
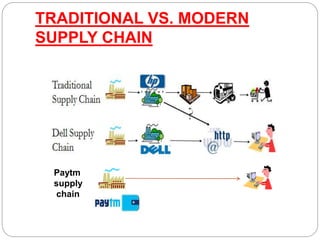


This document discusses supply chain management. It defines supply chain as the flow of products and services from raw material suppliers to consumers through various intermediaries. Key points made include: - Supply chains connect suppliers, manufacturers, distributors and customers through transportation and storage, and are integrated through information sharing. - Supply chain management involves managing demand and supply across organizational boundaries to meet customer needs. - India's logistics costs are higher than Western countries due to reliance on road and rail transport over waterways. The Sagar Mala project aims to invest in port modernization to boost trade and reduce costs. - Traditional supply chains differ from modern digitized examples like Paytm in areas like planning and integration.












