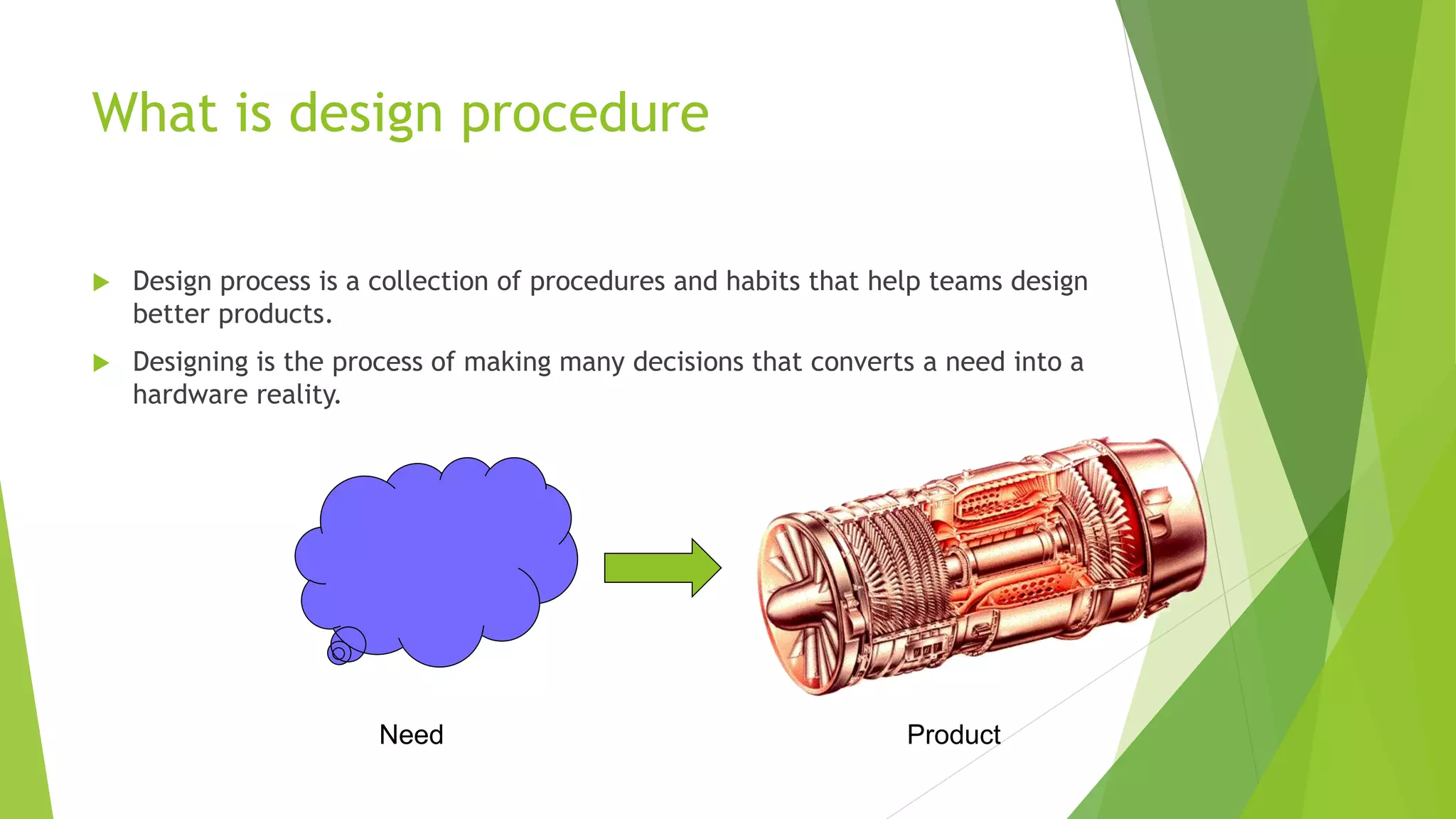
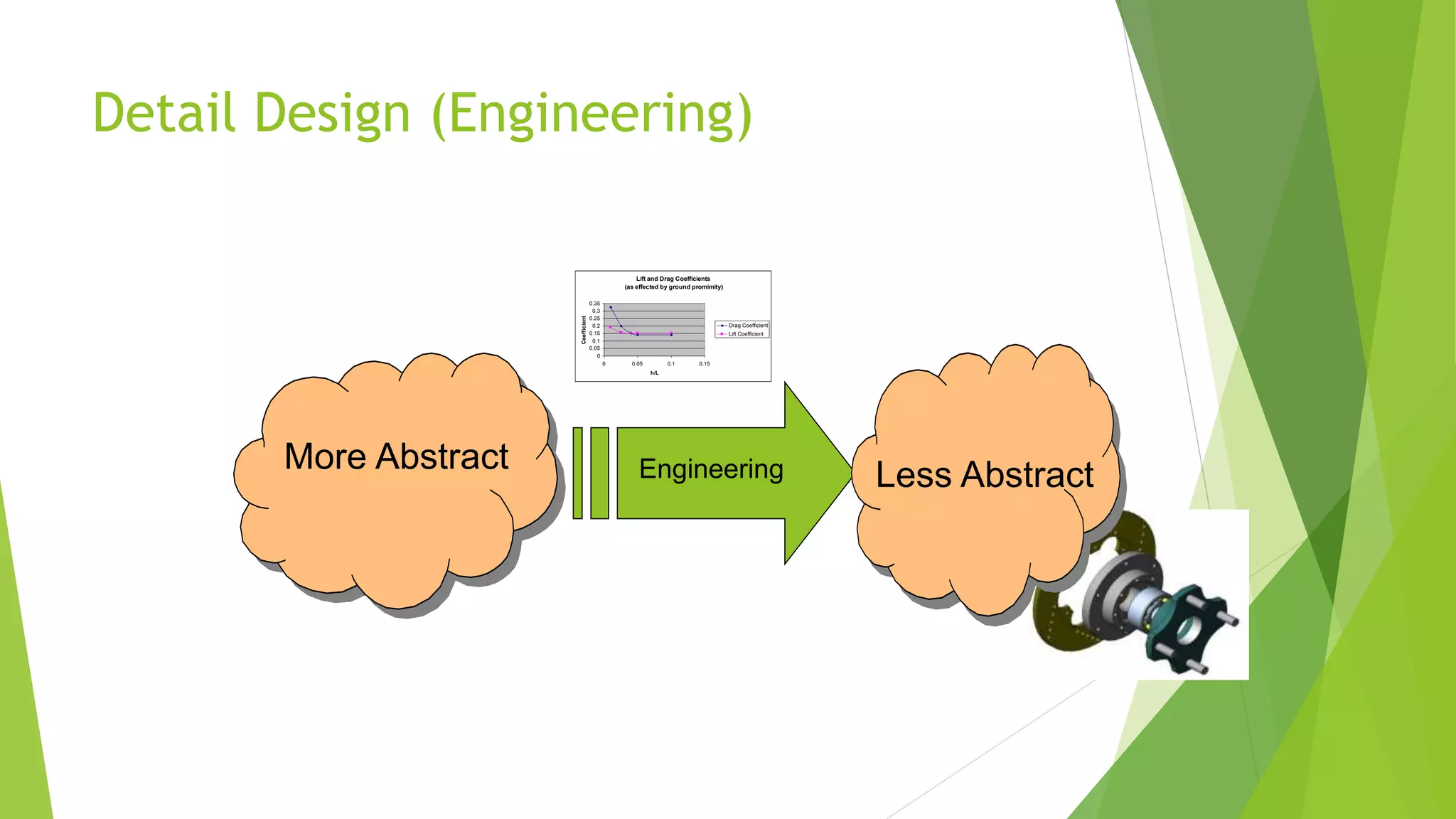
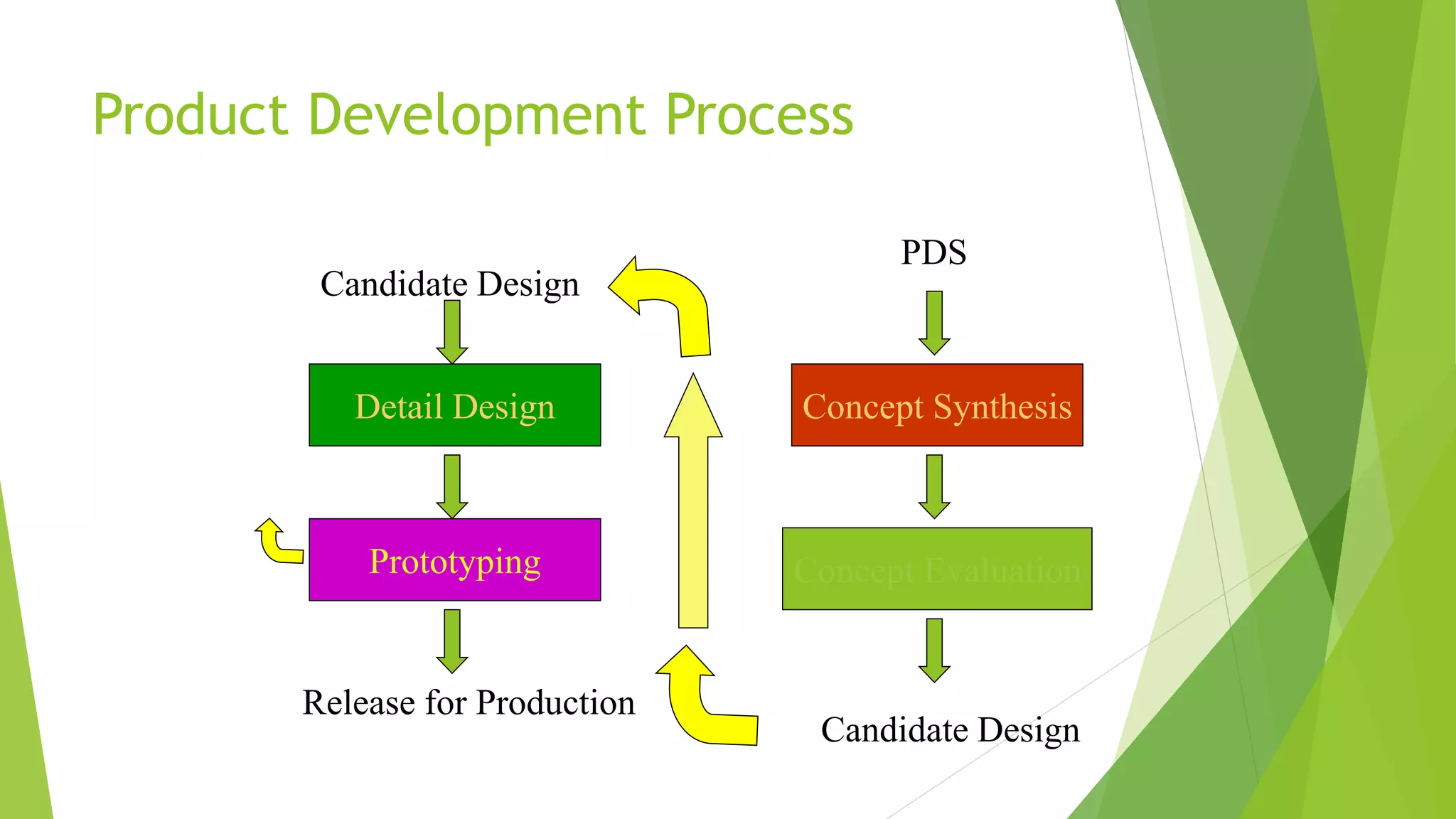
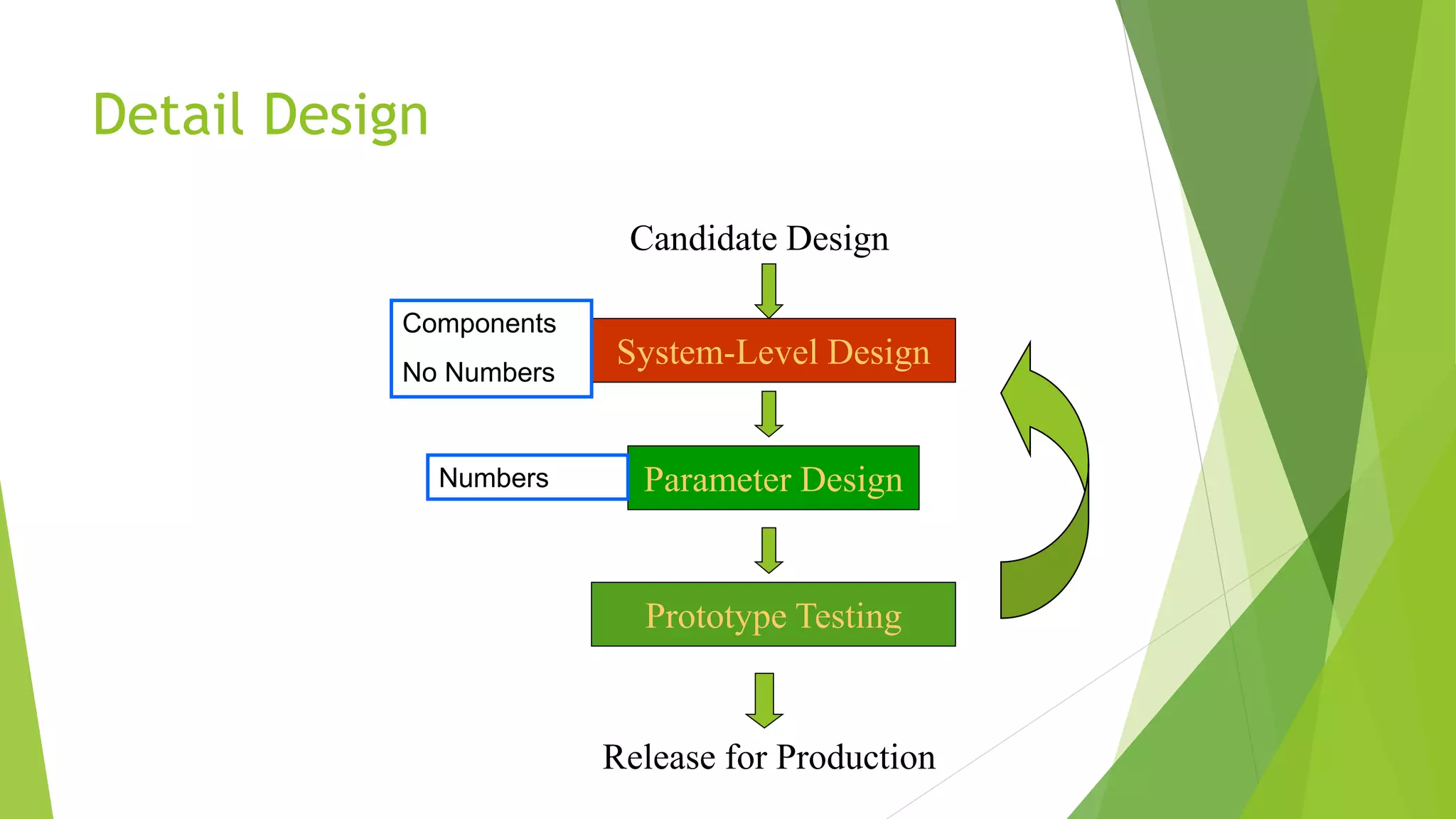
The document outlines the design procedure for a mechanical engineering project. It discusses the 7-step design process, which includes: 1) creating product design specifications, 2) external and internal research, 3) concept evaluation and selection, 4) detail design and engineering, 5) prototyping and testing, and 7) documentation. Each step produces an outcome, such as a PDS document from step 1 and a final design report from step 7. The document also discusses factors that make developing specifications complex, including production concerns, intellectual property, customer base, and clarity of goals.