- Superconductivity occurs when some materials experience zero electrical resistance below a certain temperature. Key discoveries include superconductivity being discovered in 1911, the Meissner effect in 1933, and the BCS theory in 1957 which explained superconductivity in terms of Cooper pairs.
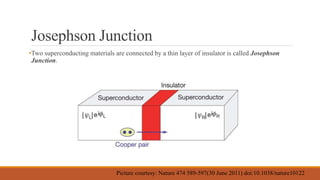
- In superconductors, electrons form pairs called Cooper pairs due to an effective attraction. Cooper pairs act coherently and allow electrical current to flow without resistance.
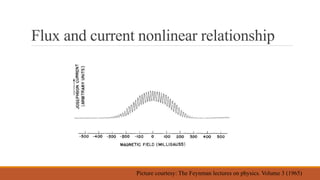
- Magnetic fields are expelled from the interior of superconductors (Meissner effect) due to supercurrents induced at the surface from the London equation. Flux is quantized in units of the magnetic flux quantum in superconductors.


![Historical Overview
•Heike Kamerlingh Onnes (1911), Nobel Prize [1913]
•Meissner and Ochsenfeld (1933)
•Fritz and Heinz London (1935)
•John Bardeen, Leon N. Cooper, J. Robert Schriffer (1957) , Nobel Prize [1972]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/superconductivityasmacroscopicphenomenatermpaperpresentation-140405131649-phpapp02/85/Superconductivity-as-macroscopic-phenomena-term-paper-presentation-3-320.jpg)




























![References
•Phillip W Phillips, Advanced Solid State Physics.
•Michael Tinkham , Introduction to Superconductivity.
•Feynman Lectures in Physics ,Volume 3
•Bardeen Cooper Schreifer, Physical Review, 108,1175[1957]
•Cooper, Physical Review, 104,1189[1956]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/superconductivityasmacroscopicphenomenatermpaperpresentation-140405131649-phpapp02/85/Superconductivity-as-macroscopic-phenomena-term-paper-presentation-34-320.jpg)
