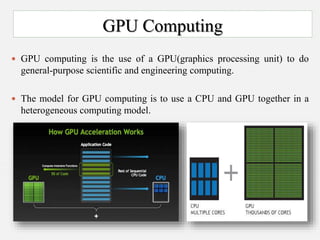
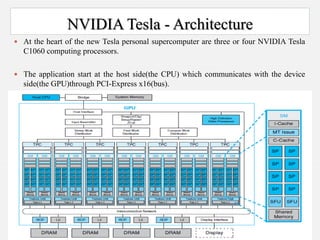
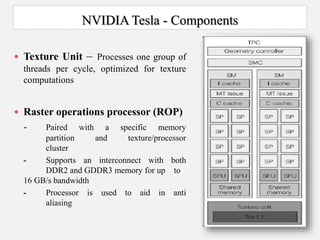
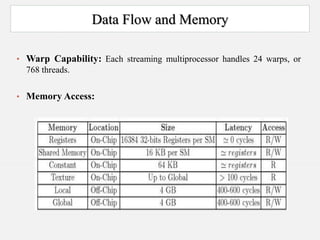
The document discusses Nvidia's Tesla personal supercomputer, which uses multiple Tesla C1060 GPUs to provide supercomputer-level performance. Each C1060 GPU contains 240 processor cores running at 1.296GHz, 4GB of memory, and provides 933 gigaflops of processing power. The GPUs use Nvidia's CUDA parallel computing architecture and can accelerate applications up to 250 times compared to standard PCs. The supercomputers are aimed at scientific and medical research by providing affordable access to high-performance computing.