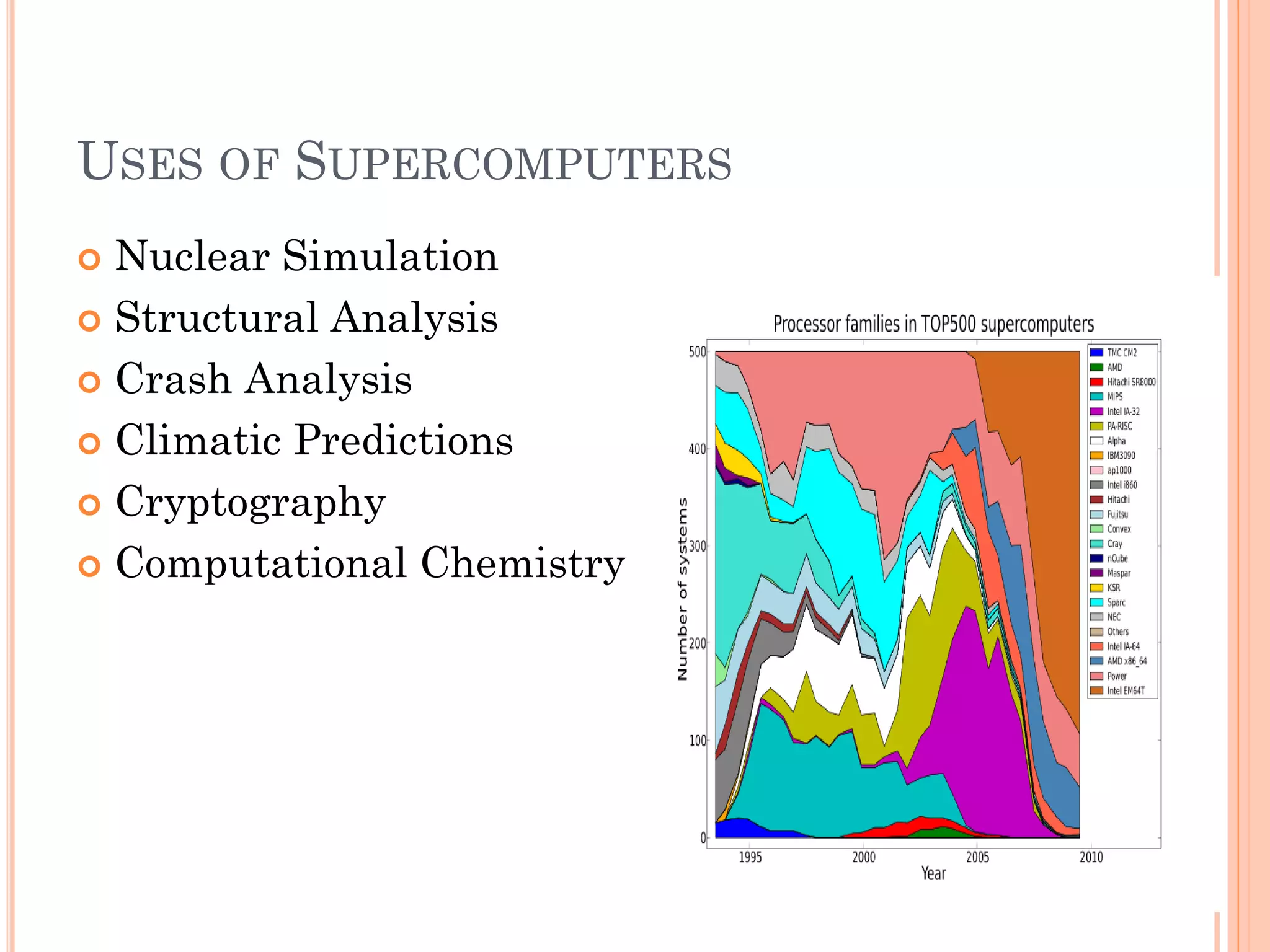
Supercomputers are the fastest and most powerful computers designed to solve complex problems quickly. They were introduced in the 1960s and are used for nuclear simulation, structural analysis, crash analysis, climatic predictions, cryptography, and computational chemistry. Modern supercomputer architectures trade processor speed for low power consumption to support more processors at room temperature. The IBM Blue Gene supercomputer and K computer are examples of large, energy efficient supercomputing systems that use different processor and cooling approaches.