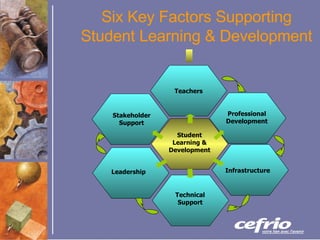
The document summarizes key findings from a study on factors that influence the effective use of information and communication technologies (ICT) to support learning in English school boards in Quebec. It identifies six key factors, including student engagement, stakeholder support, teachers' technical skills, leadership, infrastructure, and professional development. Recommendations are made at the operational and strategic levels to address these factors and ensure ICT is used to support educational goals.