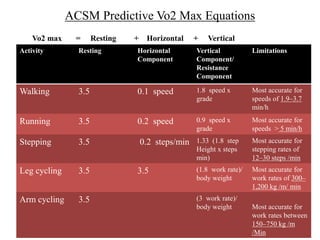
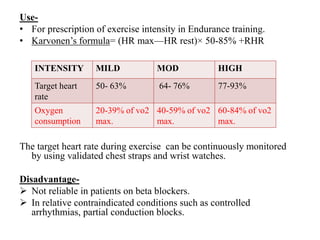
This document discusses objective and subjective measures of exercise intensity. Objectively, it describes VO2 max and how it is measured via ergospirometry to determine cardiorespiratory fitness. It provides normal VO2 max values for Indians and how VO2 max relates to different activities' energy costs. Maximum heart rate is also discussed as related to VO2 max and used to prescribe training intensities via the Karvonen formula. Subjectively, the Rating of Perceived Exertion scale is presented as an easy way to gauge exertion levels, especially for those who can't monitor heart rate. Both objective and subjective measures have limitations but provide ways to prescribe and monitor exercise intensity.










![REFERENCES
1. ROY S, MCCRORY J. Validation of Maximal Heart Rate Prediction Equations
Based on Sex and Physical Activity Status. Int J Exerc Sci. 2015 Oct
1;8(4):318–30.
2. MAXIMUM HEART RATE MEASURED VERSUS ESTIMATED BY DIFFERENT
EQUATIONS DURING THE CARDIOPULMONARY EXERCISE TEST IN OBESE
ADOLESCENTS [Internet]. [cited 2020 Apr 21]. Available from:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6202885/
3. Karvonen method [Internet]. Oxford Reference. [cited 2020 Apr 22].
Available from:
https://www.oxfordreference.com/view/10.1093/oi/authority.201108101
05207569
4. Rate Perceived Exertion as a Measure of Exercise Intensity [Internet].
[cited 2020 Apr 22]. Available from:
//www.nursingcenter.com/journalarticle?Article_ID=4388376&Journal_ID
=2695880&Issue_ID=4388241
5.ACSM GUIDELINES 2019](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hrmaxvo2-200531163248/85/SUBJECTIVE-AND-OBJECTIVE-MEASURE-OF-EXERCISE-TESTING-13-320.jpg)
