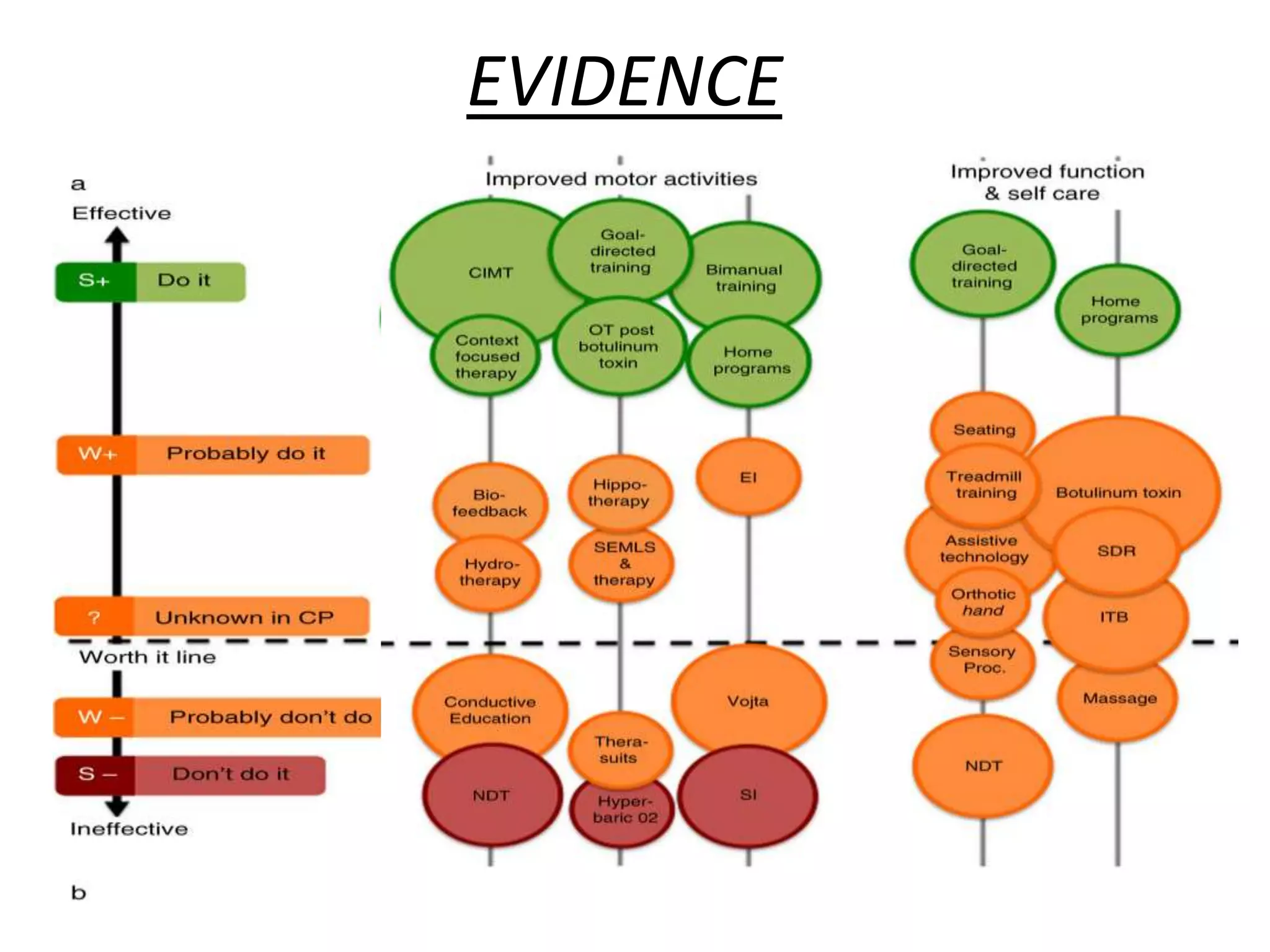
The document discusses the evolution and application of Neuro-Developmental Treatment (NDT) for children with cerebral palsy, highlighting its historical roots, principles of therapy, and current evidence regarding its efficacy. While NDT aims to facilitate typical movement patterns and improve motor function through a hands-on, multidisciplinary approach, evidence suggests that its effectiveness is limited and often lacks robust methodological quality. Alternative evidence-based interventions, such as bimanual training and goal-directed therapy, have shown greater success in enhancing activity levels for children with cerebral palsy.