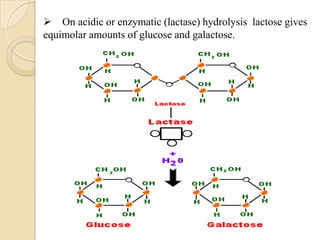
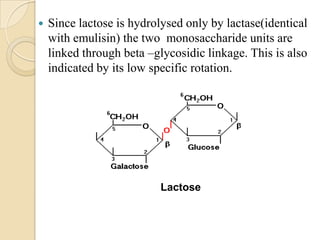
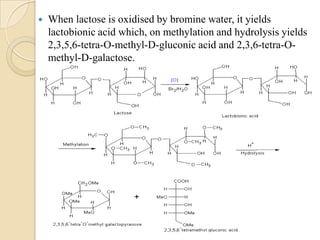
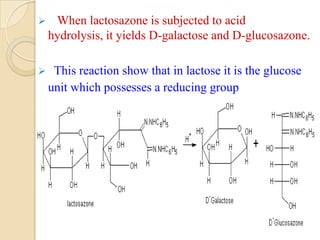
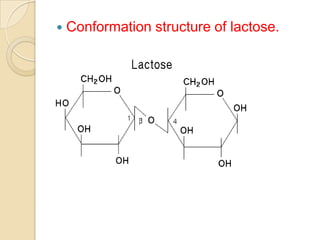
Lactose is a disaccharide composed of glucose and galactose units linked by a beta-glycosidic bond. It occurs naturally in mammalian milk. Upon hydrolysis, lactose yields equimolar amounts of glucose and galactose. Structural analysis through methylation, oxidation, and osazone formation revealed that C-1 of glucose is linked to C-4 of galactose, with glucose being the reducing sugar and galactose the non-reducing sugar in the lactose molecule.