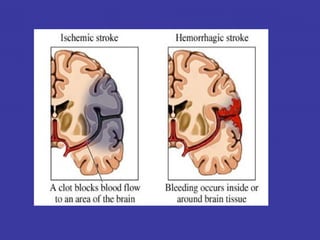
1. Stroke rehabilitation aims to restore abilities, prevent complications, improve quality of life, and educate on preventing future strokes. Rehabilitation success depends on early treatment, injury extent, attitude, and family support.
2. Rehabilitation addresses mobility, daily living, communication, swallowing, pain, and mood issues. Physical therapy focuses on movement, balance, and safety. Occupational therapy targets self-care. Speech therapy facilitates communication recovery.
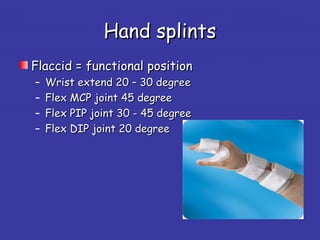
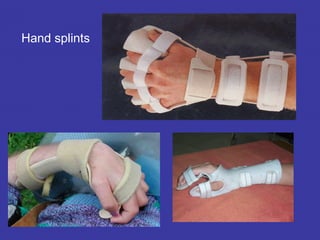
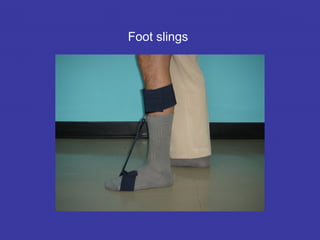
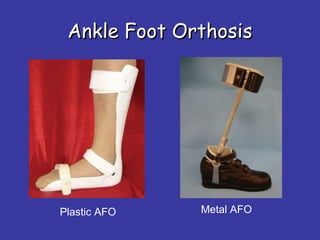
3. Additional challenges include spasticity, cognitive issues, incontinence, and depression. Treatment involves positioning, stretching, splinting, medications, and assistive devices. Regular evaluation monitors patient progress.