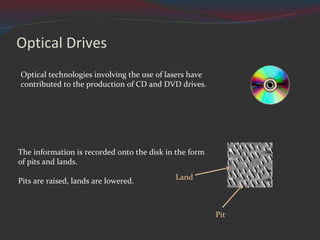
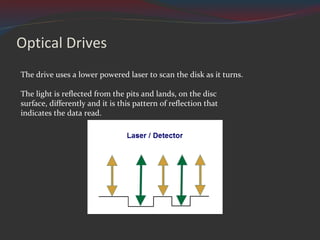
Magnetic storage devices include floppy disks, hard disk drives, magnetic tape, and solid state drives. Optical storage uses lasers to read and write data in the form of pits and lands on discs like CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray. Storage capacity and speeds have increased over time while physical sizes have decreased. Cost per gigabyte has also declined for most storage types.