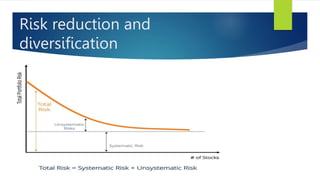
Portfolio risk is the chance that a portfolio of investments will fail to meet financial objectives. It is affected by the risk of individual assets as well as their covariance, which measures how their returns move together. Diversifying a portfolio by combining assets with negatively correlated returns, meaning their prices move in opposite directions, can reduce overall risk even if each asset remains as risky. The standard deviation of a portfolio depends on the standard deviations and covariance of its constituent assets, weighted by their proportions in the portfolio.



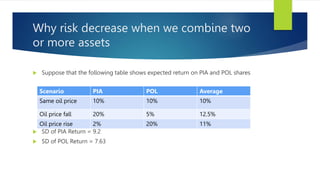









![Example
Suppose POL gave you = 12.12% return
And PIA gave you =15.16% return
SD of POL =21.58 and PIA = 25.97
Correlation coefficient = 0.29
Weights POL = 50% and PIA = 50%
Then what is the standard deviation of the portfolio
σ = (w1
2σ1
2 + w2
2σ2
2 + 2w1w2ρ𝑖,𝑗σ𝑖σ𝑗)1/2
=>[.52
(21.58)2
+.52
(25.97)2
+2(.5)(.5)(.29)(21.58)(25.97)]1/2
[116.42 + 168.61 + 81.26] 1/2
=19.14
.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/portfolioriskanalysis-221217103446-a1b0e2f6/85/PORTFOLIO-RISK-ANALYSIS-pptx-15-320.jpg)