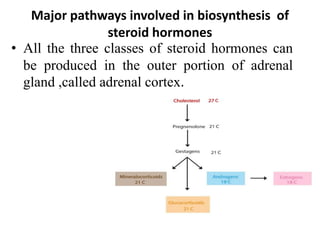
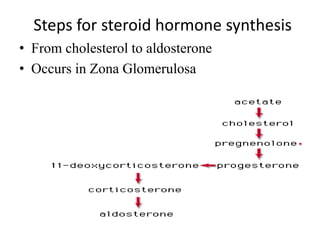
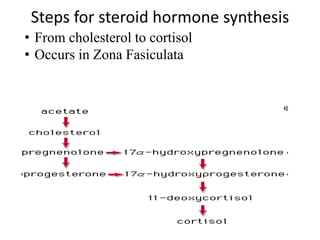
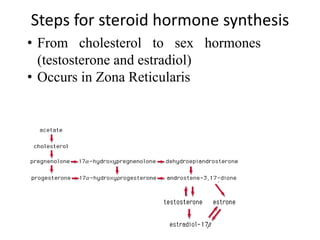
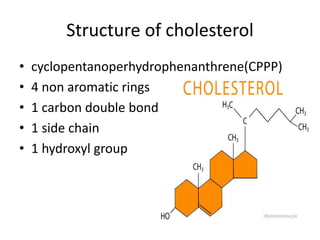
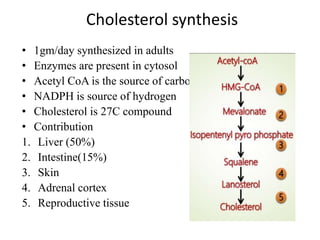
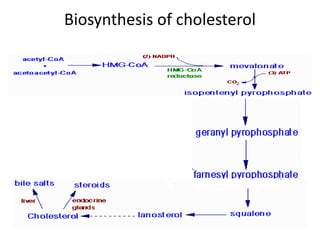
The document provides an overview of steroids and cholesterol, detailing their structures, functions, and the biosynthesis pathways. It highlights the role of steroids in various body functions, diseases caused by hormonal imbalances, and the synthesis and regulation of cholesterol. Additionally, it lists relevant enzymes and the energy requirements for cholesterol synthesis, along with associated health issues from fluctuations in cholesterol levels.