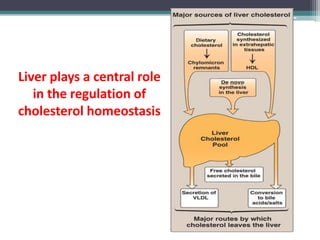
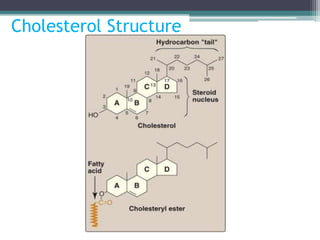
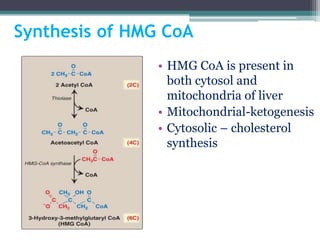
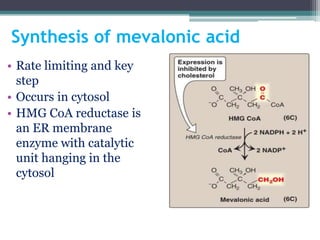
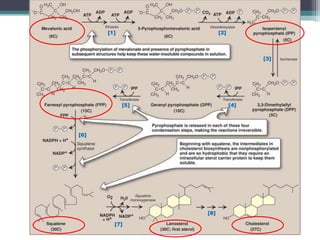
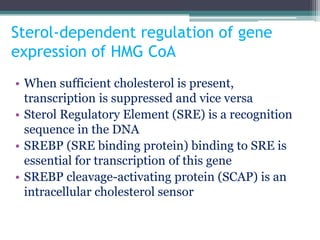
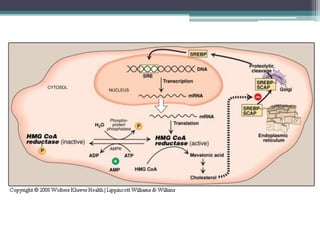
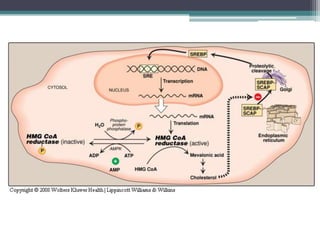
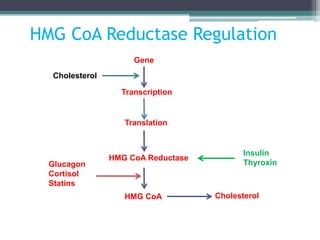
This document discusses cholesterol metabolism. It begins by outlining the objectives, which are to understand cholesterol structure and homeostasis. It then covers cholesterol synthesis, which occurs mainly in the liver, adrenals, and intestines. The rate-limiting step is conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonic acid by the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase. Cholesterol levels regulate reductase levels through effects on gene expression and protein degradation. High cholesterol inhibits synthesis while low cholesterol stimulates it. Hypercholesterolemia results from abnormal metabolism and is treated with statins that inhibit reductase.