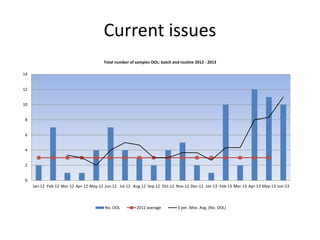
This document discusses microbiology activities related to sterility assurance for pharmaceutical products. It outlines the microbiological testing done on raw materials, processes, water systems, environments and finished products. This includes bioburden testing, pathogen testing, endotoxin testing, and sterility testing. It also discusses environmental monitoring programs for sterile facilities and aseptic filling areas. Key requirements outlined include pre-filtration bioburden limits, media fill qualifications, aseptic process simulations, and staff performance monitoring. Recent issues with increased out of limit environmental monitoring results are also summarized.