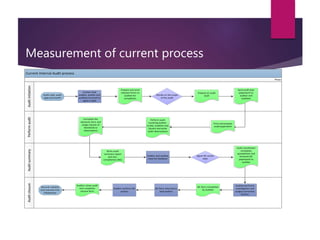
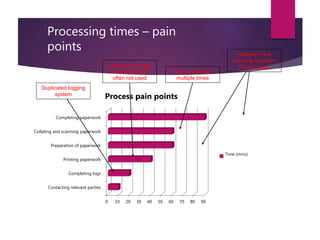
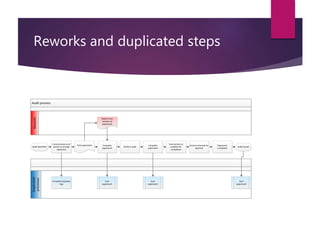
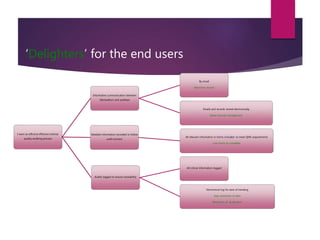
This document discusses improving the efficiency of an organization's internal quality auditing process. Currently, the process is paper-heavy and labor intensive, involving multiple forms, duplicative logging, and scanning documents multiple times. The goals of the project are to make the auditing process more efficient and less time-consuming. Quick wins identified include reducing duplicate logging, reducing unnecessary paperwork, and moving to electronic communication and records. Interviews will gather user feedback and the new process will be measured and analyzed for further improvements. Ultimately, an electronic auditing system is proposed to make the process fully traceable, reduce manual work, and eliminate paper use.