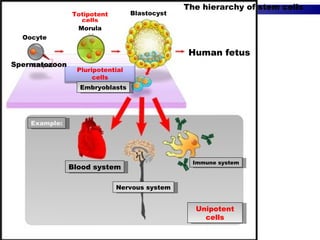
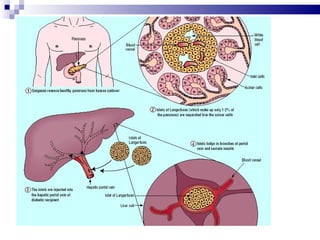
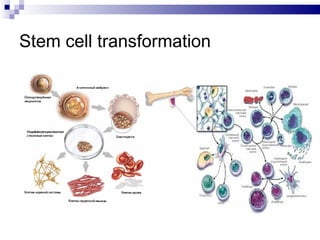
Stem cells have the ability to differentiate into various cell types and self-renew to produce more stem cells. They can be totipotent, pluripotent, or unipotent. Stem cells are found in embryos, fetuses, and specific adult tissues. They have unique properties including telomerase activity that allows indefinite cell division. Stem cells can migrate throughout the body and transform into specialized cells as needed for repair in response to molecular signals from damaged tissues. Mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow are a promising source for regeneration as they can differentiate into many cell types.