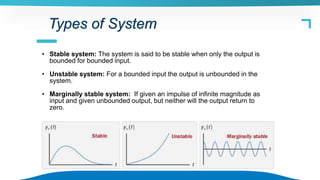
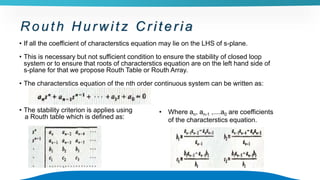
The document discusses the stability of control systems, categorizing stability into stable, unstable, and marginally stable systems. It explains several types of stability criteria including BIBO, asymptotic, absolute, relative, and conditional stability, with emphasis on the Routh-Hurwitz criterion for analyzing stability. Limitations of the Hurwitz criterion are also outlined, emphasizing its complexity in practical applications.