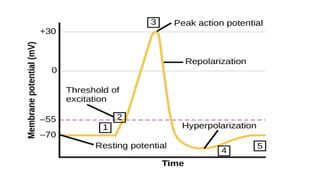
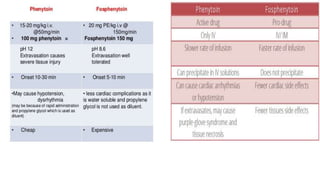
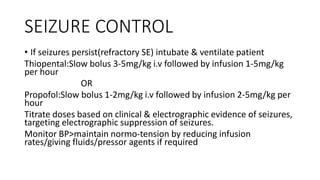
Status epilepticus is a medical emergency that requires prompt treatment to prevent irreversible brain damage. It is defined as continuous seizure activity lasting more than five minutes, or two or more seizures between which consciousness is not regained. Status epilepticus can be classified as generalized convulsive or non-convulsive and has various etiologies including low anti-epileptic drug levels, stroke, electrolyte imbalances, and infections. Treatment involves airway protection, treatment of underlying causes, administration of benzodiazepines or phenytoin to stop seizures, and induction of anesthesia with thiopental or propofol if seizures persist. Outcomes depend on factors like age, etiology, and degree of impaired consciousness,