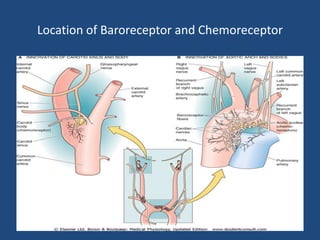
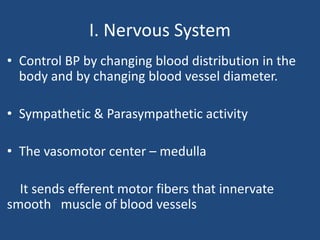
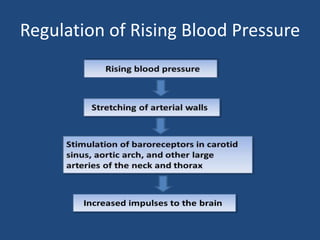
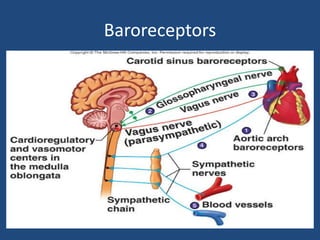
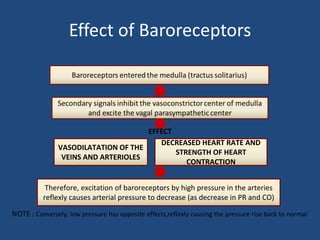
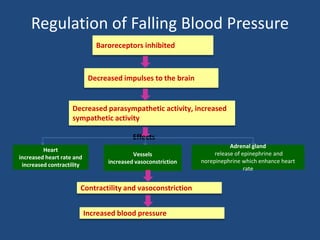
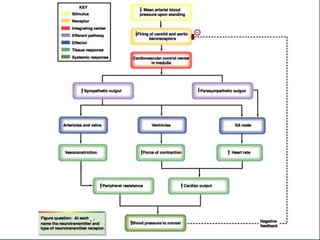
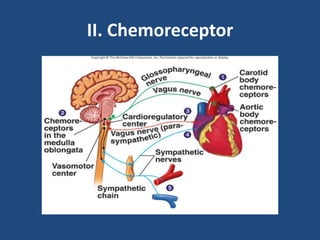
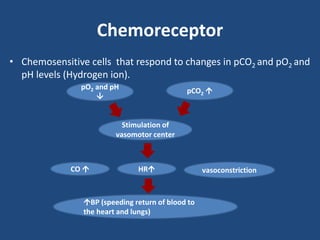
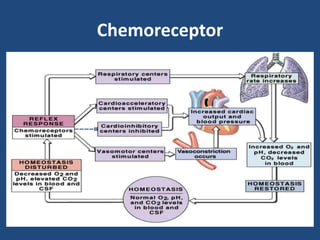
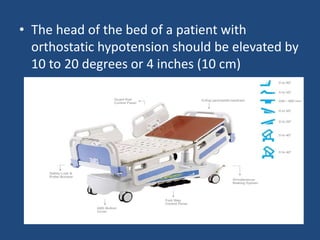
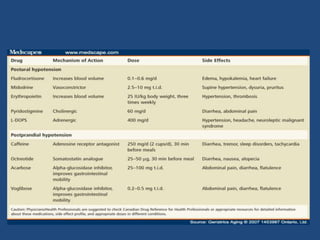
This document discusses orthostatic hypotension, including its definition, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and management. Orthostatic hypotension is defined as a decrease in blood pressure within 3 minutes of standing compared to lying down. It may be caused by neurogenic issues like Parkinson's disease or non-neurogenic issues like dehydration. Symptoms include lightheadedness, dizziness, and weakness. Diagnosis involves measuring blood pressure in lying and standing positions. Management includes both non-pharmacological approaches like compression garments and leg exercises, as well as pharmacological treatments like fludrocortisone and midodrine.