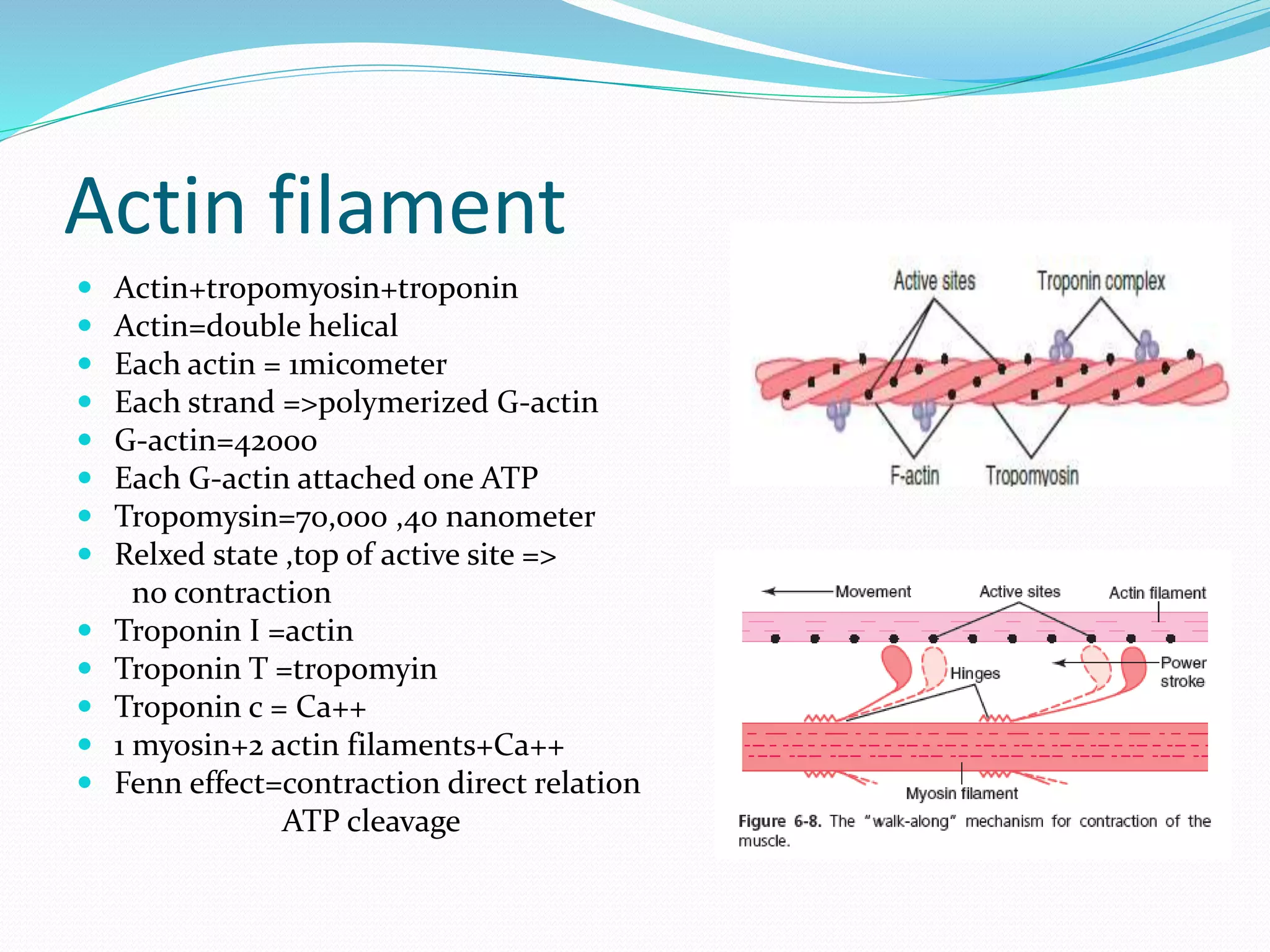
This document summarizes the anatomy and physiology of skeletal muscle contraction. It describes the gross and molecular structures of muscle fibers, including the sarcomere unit composed of actin and myosin filaments. The sliding filament model of contraction is explained, where crossbridges on the myosin head bind to actin and hydrolyze ATP for movement. Calcium released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum initiates the crossbridge cycling. Fast and slow muscle fiber types are compared. The energetics and mechanisms of isotonic and isometric contractions are also summarized.