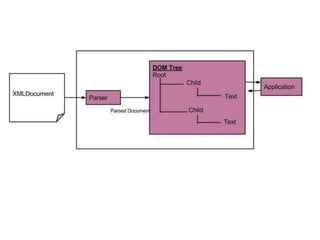
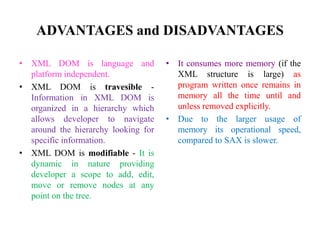
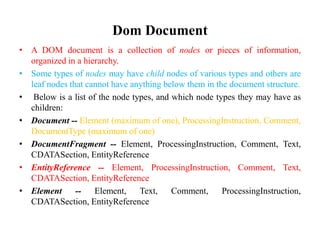
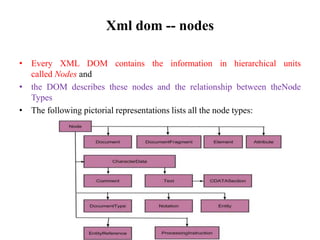
The document discusses the XML DOM (Document Object Model) which defines a standard for accessing and manipulating XML documents. It outlines the core DOM, XML DOM, and HTML DOM standards. The XML DOM provides an API that allows developers to navigate and modify an XML document tree. It has advantages like being language-independent and allowing traversal and modification of the XML tree, but uses more memory than SAX and is slower. The DOM organizes an XML document into a hierarchy of node types that can have child nodes.