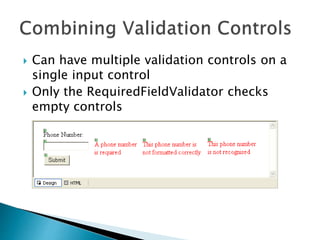
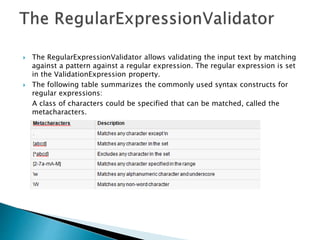
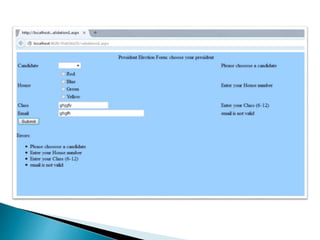
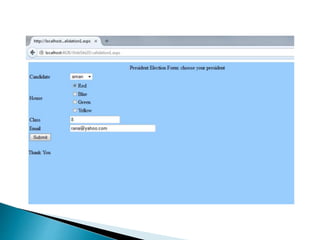
This document discusses validating user input in ASP.NET applications. It describes using validation controls on both the client-side using JavaScript and server-side using C# to check fields for errors like empty values, values outside a specified range, or values that do not match a regular expression. The key validation controls covered are RequiredFieldValidator, RangeValidator, RegularExpressionValidator, CompareValidator, and CustomValidator. It emphasizes best practices of using both client-side and server-side validation for security and usability.