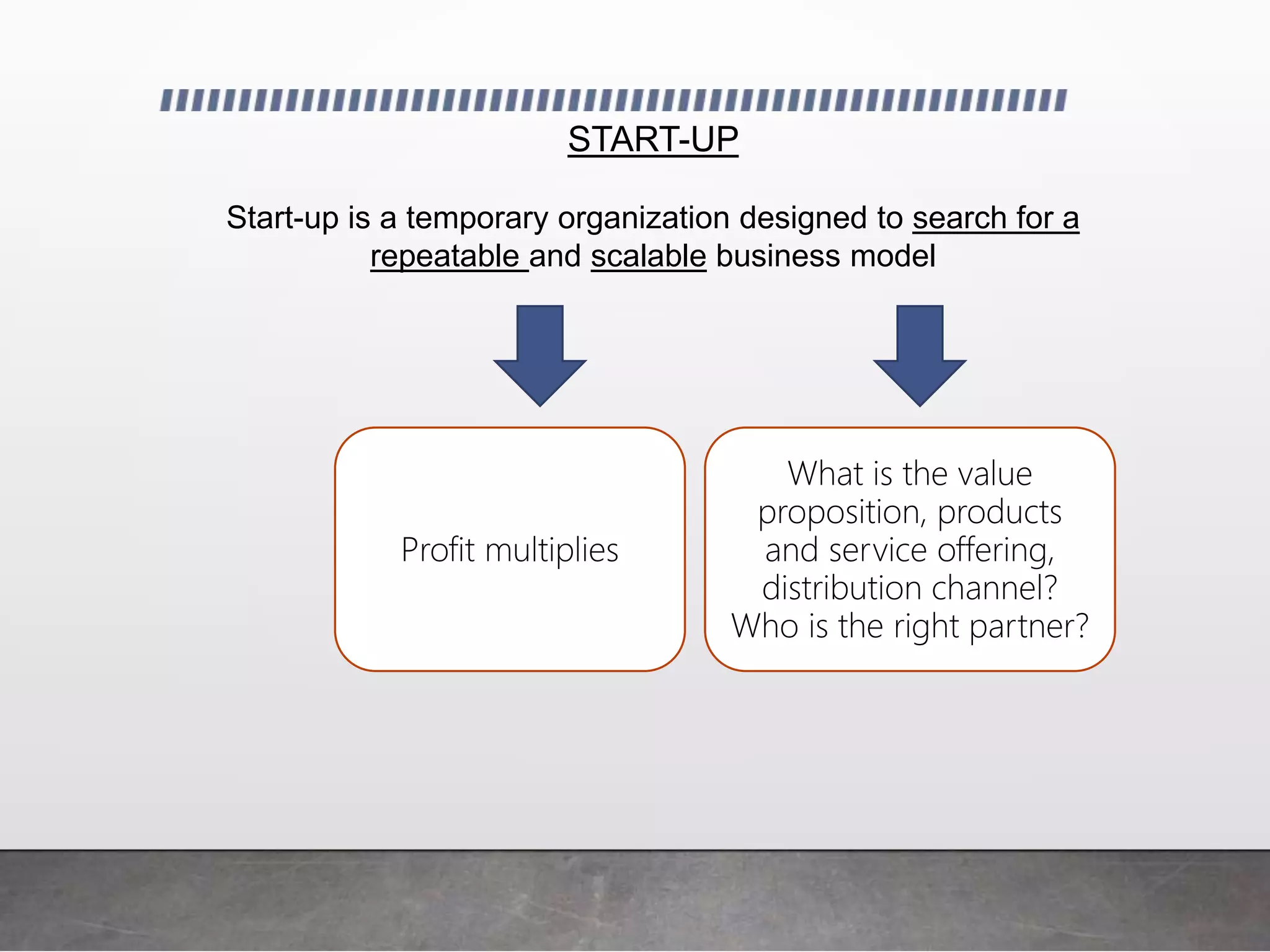
The document provides an introduction to start-ups, explaining that they are temporary organizations designed to search for a repeatable and scalable business model. It discusses different types of market segments for start-ups, including new markets, existing markets, cloned markets, and re-segmented markets. Finally, it identifies four common reasons for start-up failure: failure to achieve product/market fit, lack of focus, being a one-person team, and premature scaling. Techniques are provided for avoiding each of these failure points, such as focusing on users and products, building the right team, and only scaling up when ready.