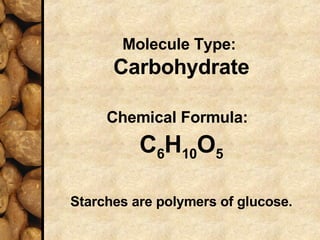
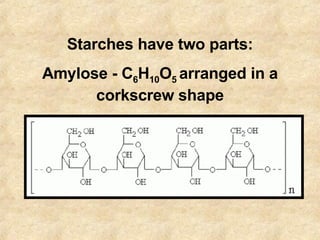
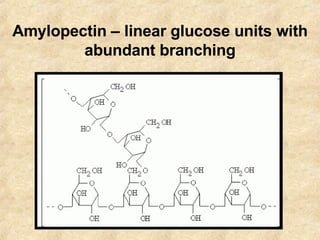
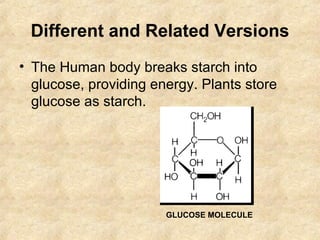
Starch is a carbohydrate polymer of glucose that functions as an energy store for plants and a source of energy for humans and animals. Starch is composed of amylose and amylopectin and is found in foods like grains, potatoes, and green plants. It provides energy through digestion and gelatinization when cooked. Plants produce starch through photosynthesis to store glucose, while starch enters animal and human systems through food as an easily digestible energy source.