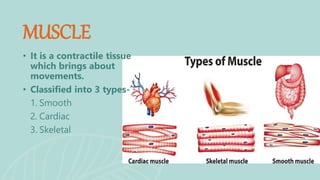
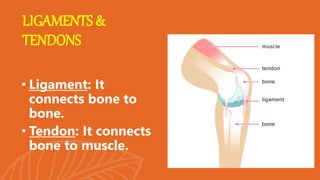
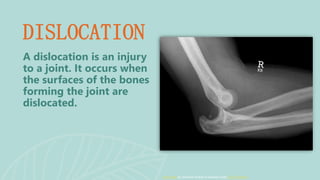
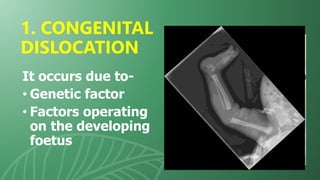
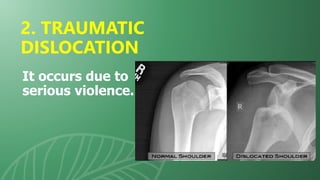
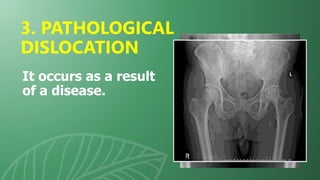
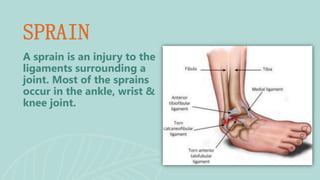
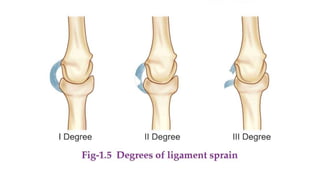
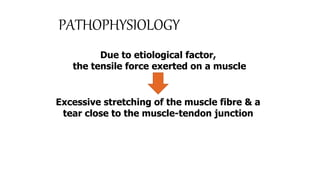
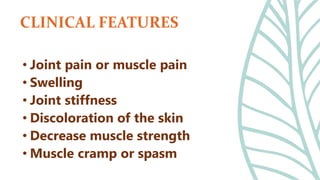
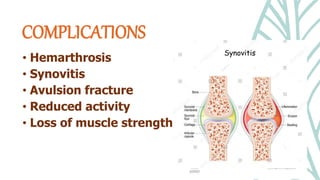
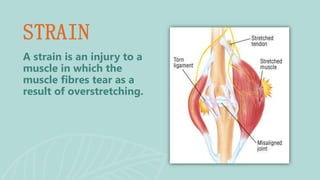
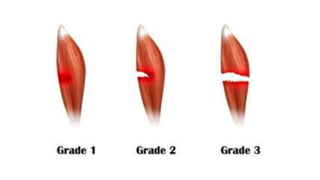
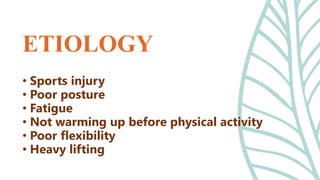
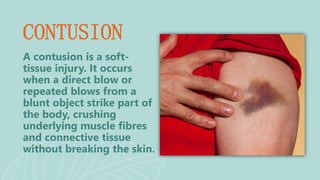
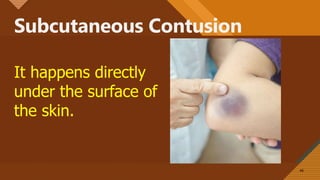
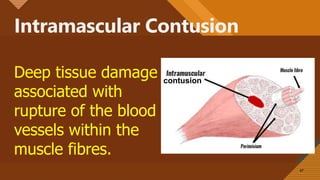
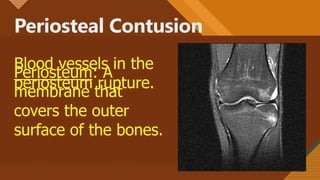
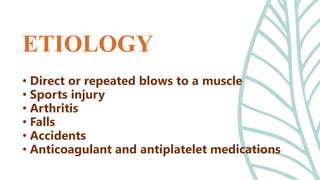
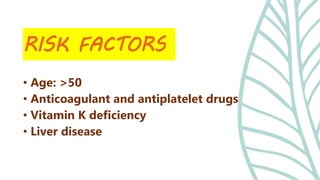
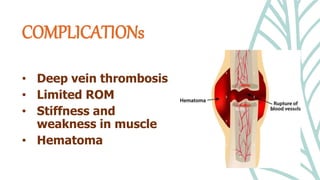
This document presents information on dislocation, sprain, strain, and contusion injuries. It defines each type of injury, describes the anatomy and physiology of bones, joints, ligaments, tendons and muscles. For each injury, it covers etiology, risk factors, clinical features, diagnostic studies, complications, management including medical, surgical and nursing. Nursing management includes developing nursing diagnoses, goals, interventions and expected outcomes to address pain, impaired mobility and tissue integrity issues from these soft tissue injuries.