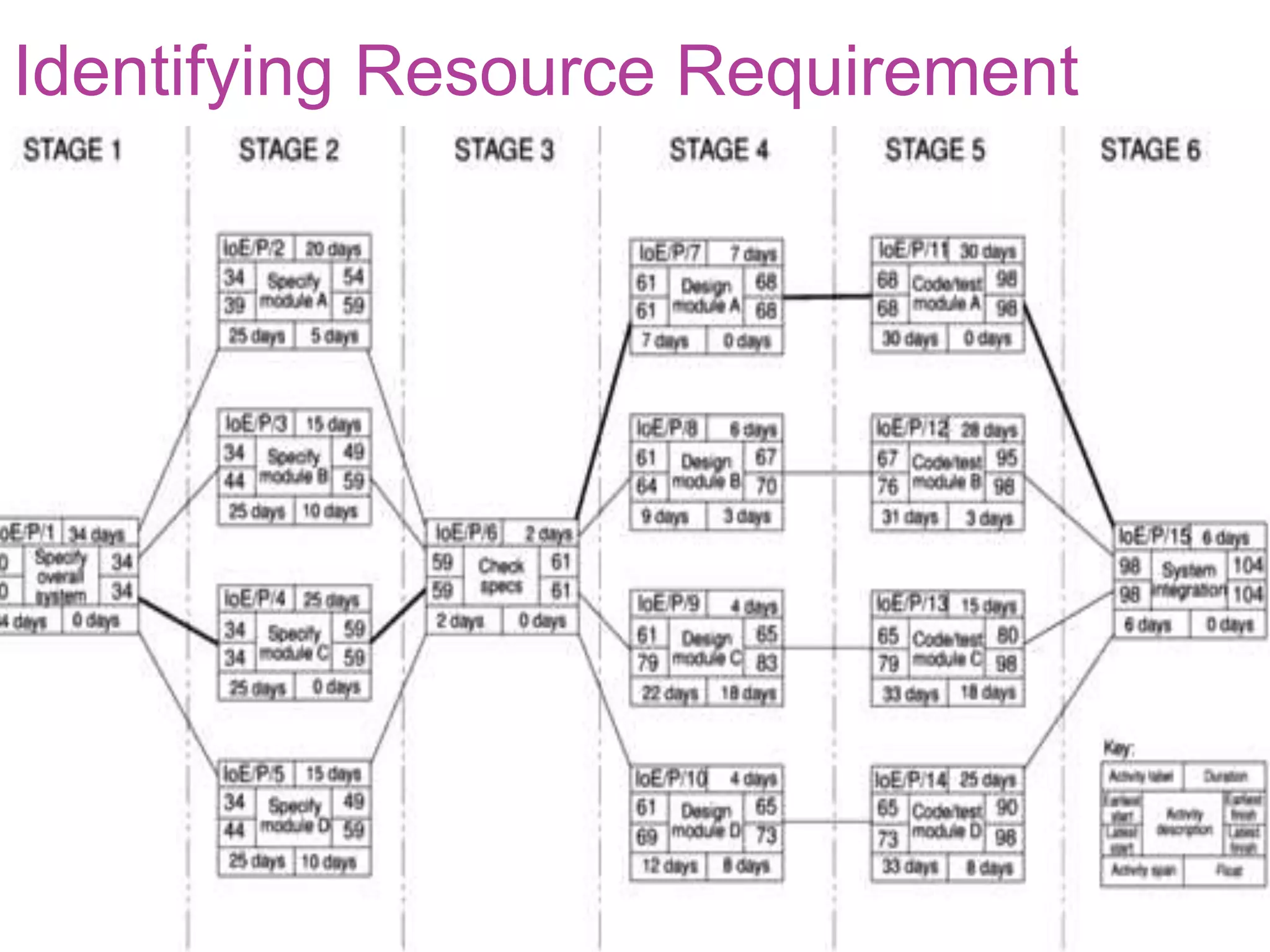
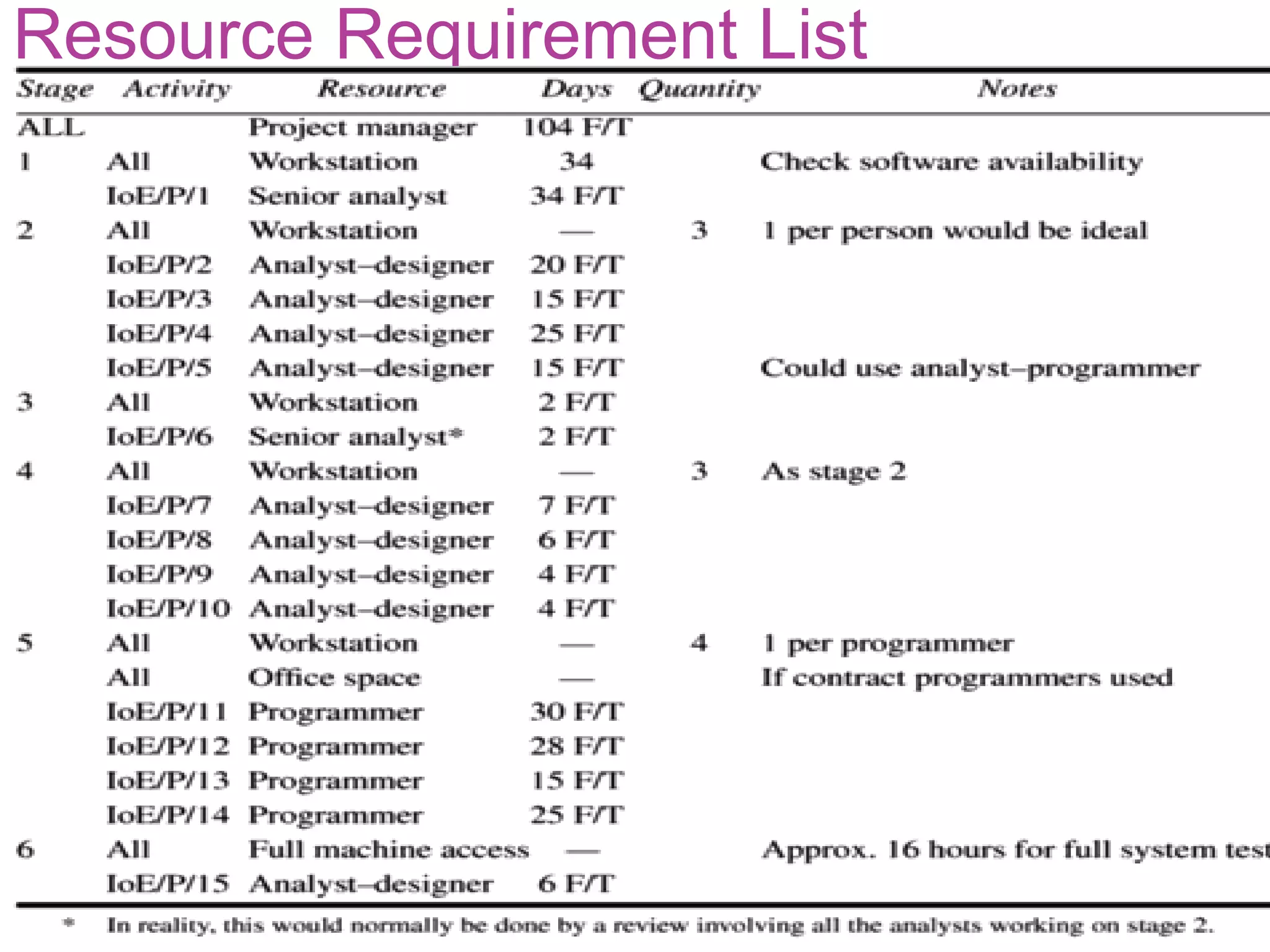
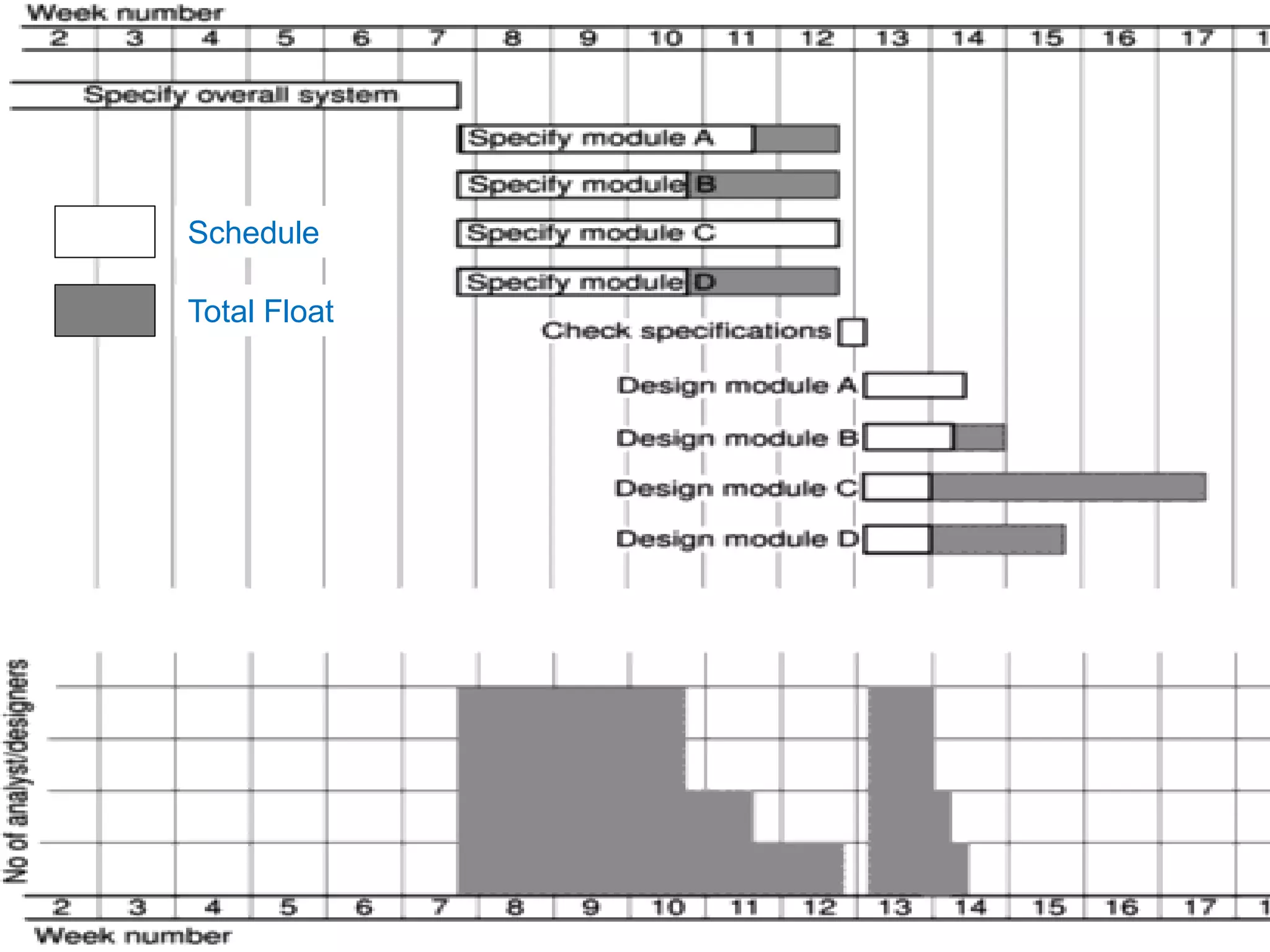
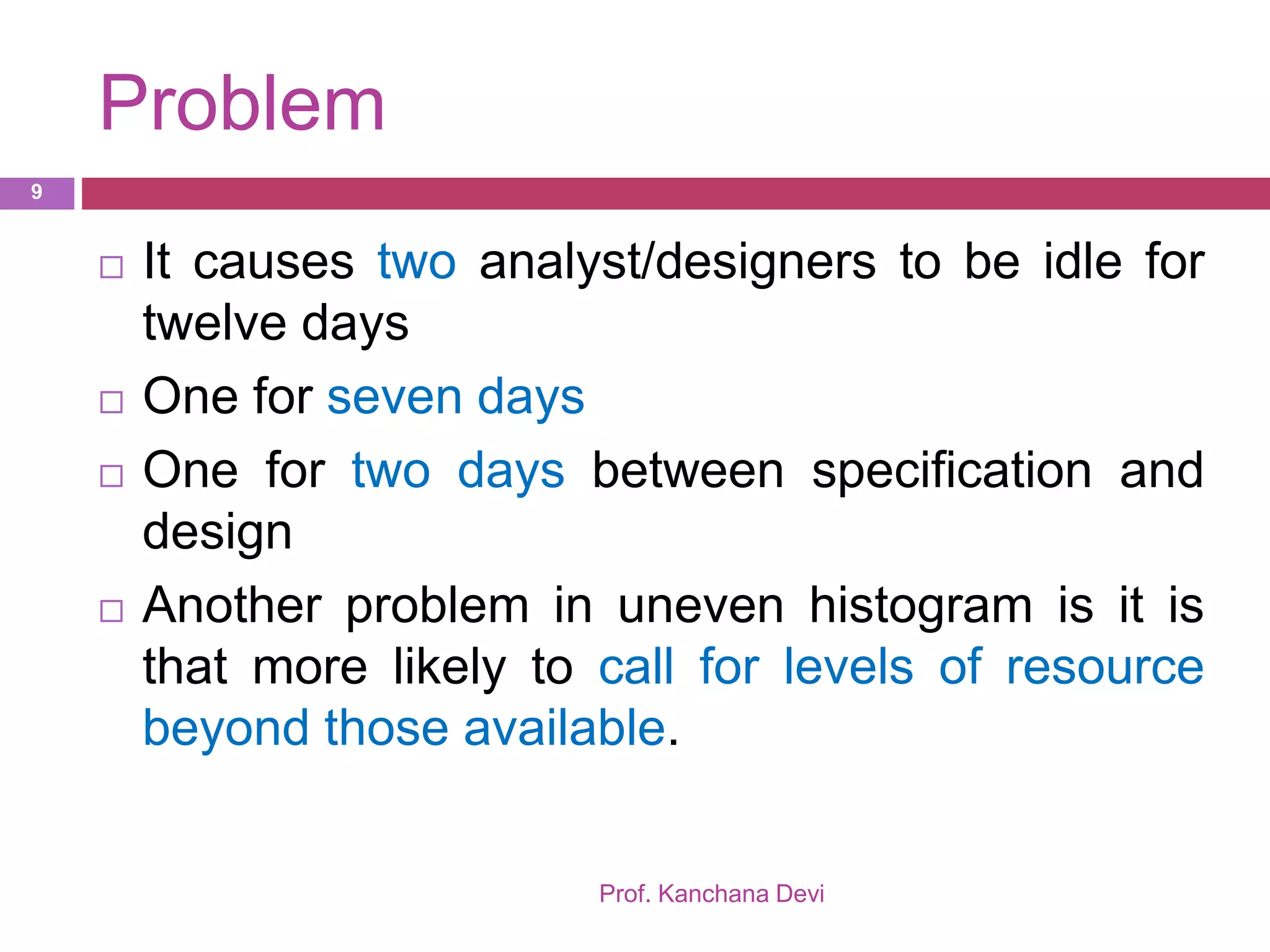
This document discusses resource allocation in project management. It explains that resource allocation helps review and modify activity schedules and project completion dates. The main steps are to identify all resource requirements, map them to activities, and schedule resources to smooth uneven demand over time. Smoothing may involve adjusting activity start dates or splitting activities. Creating resource schedules can also impact critical paths. Individual resource allocation considers availability, critical tasks, risk, training, and team building. The final output is cost, activity, resource, and cost schedules.