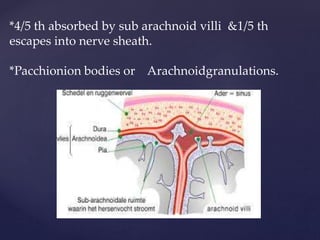
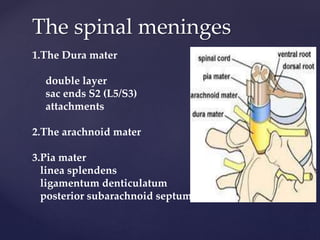
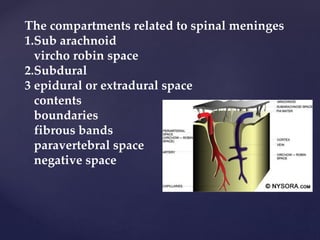
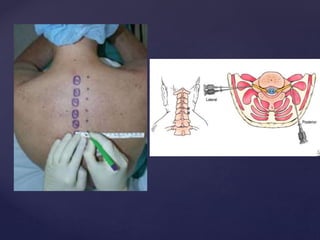
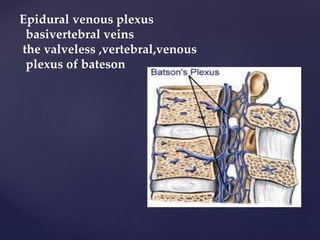
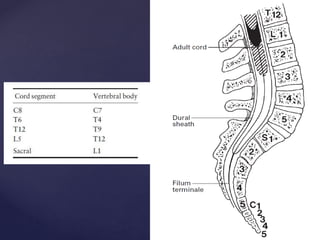
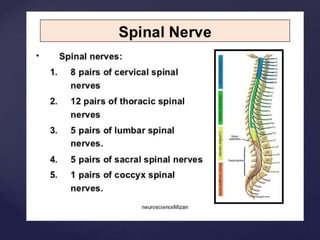
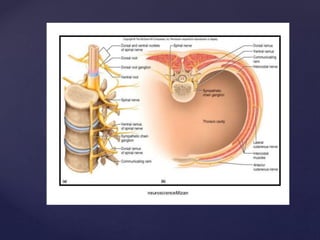
The CSF has a volume of around 150 ml and a pressure between 8-15mmHg. It circulates slowly through the subarachnoid space and cisterns in the brain. The spinal meninges consist of the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. The spinal cord is around 45cm long and has cervical and lumbar enlargements, with 31 pairs of spinal nerves attached. It receives blood supply from the anterior and posterior spinal arteries and associated segmental arteries.