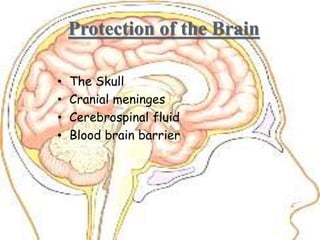
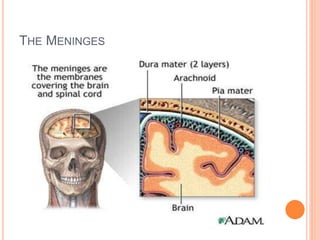
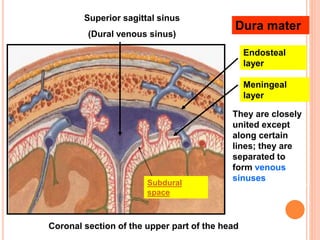
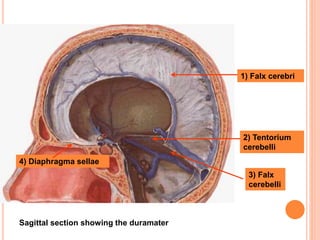
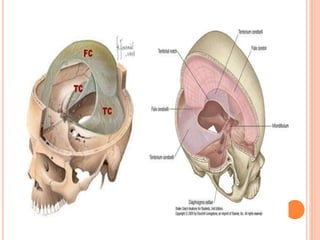
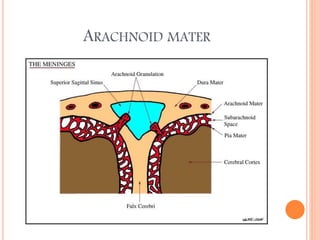
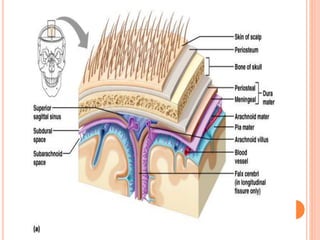
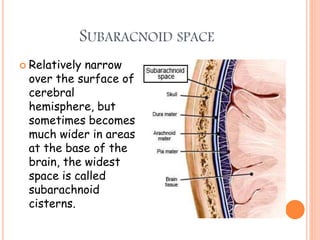
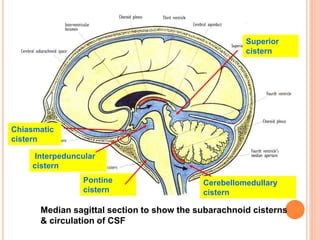
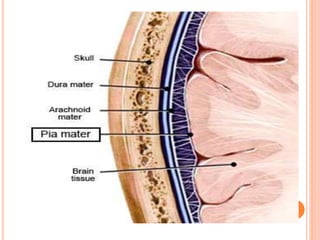
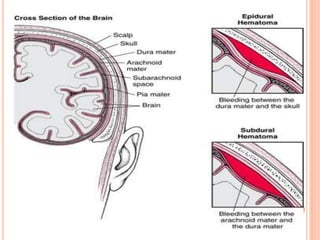
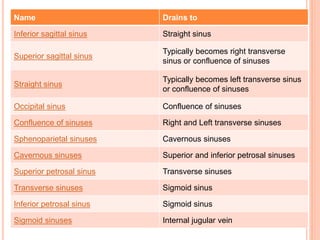
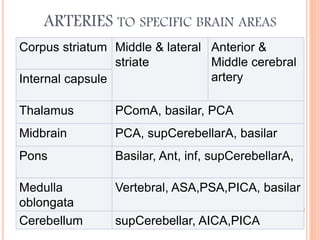
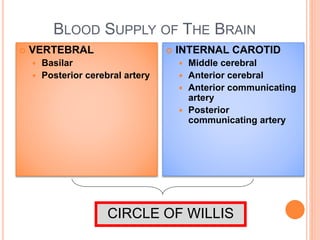
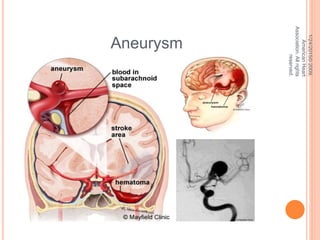
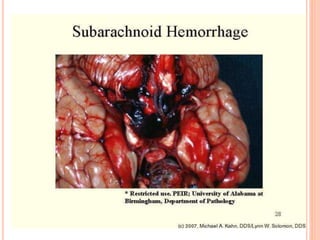
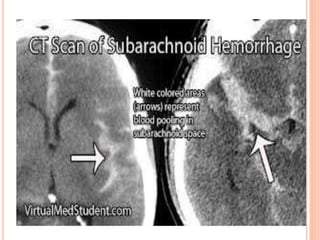
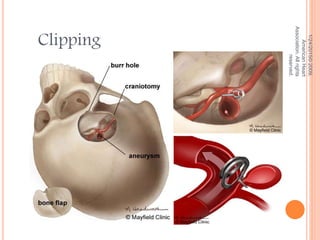
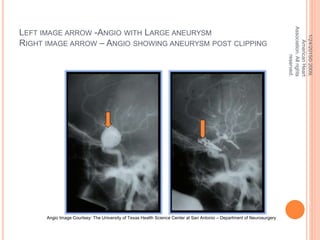
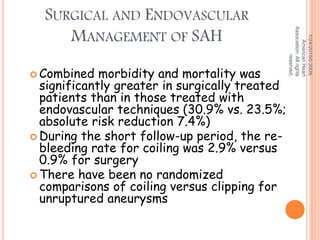
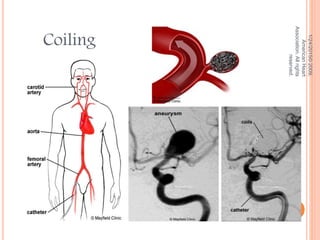
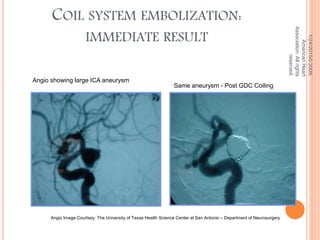
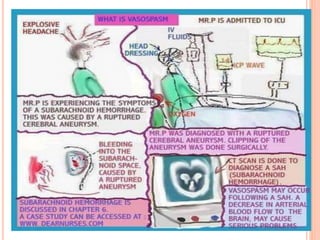
The document discusses the cranial meninges, which are the three protective membranes that cover the brain - the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. It describes the layers and their functions in protecting the brain. It also discusses subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), which is bleeding under the arachnoid layer caused by a ruptured brain aneurysm. Treatment for SAH involves stabilizing the patient, preventing rebleeding by clipping or coiling the aneurysm, and preventing complications like vasospasm. The standard treatment is microsurgical clipping or endovascular coiling of the aneurysm as soon as possible to prevent rebleeding and improve outcomes.