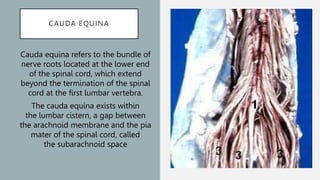
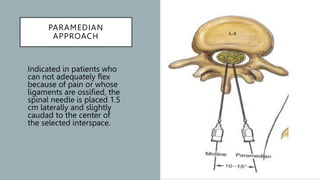
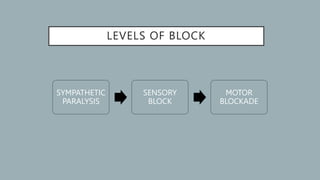
Spinal anesthesia involves injecting local anesthetic into the subarachnoid space to reversibly block sensory and motor function below the injection site. It has several advantages over general anesthesia for certain surgeries, providing anesthesia without airway manipulation. Common complications include hypotension from sympathetic blockade and post-dural puncture headache from a cerebrospinal fluid leak at the injection site. Proper patient positioning, choice of needle and drug, and fluid management can help reduce complications of this technique for lower abdominal, urogenital and lower extremity surgeries.