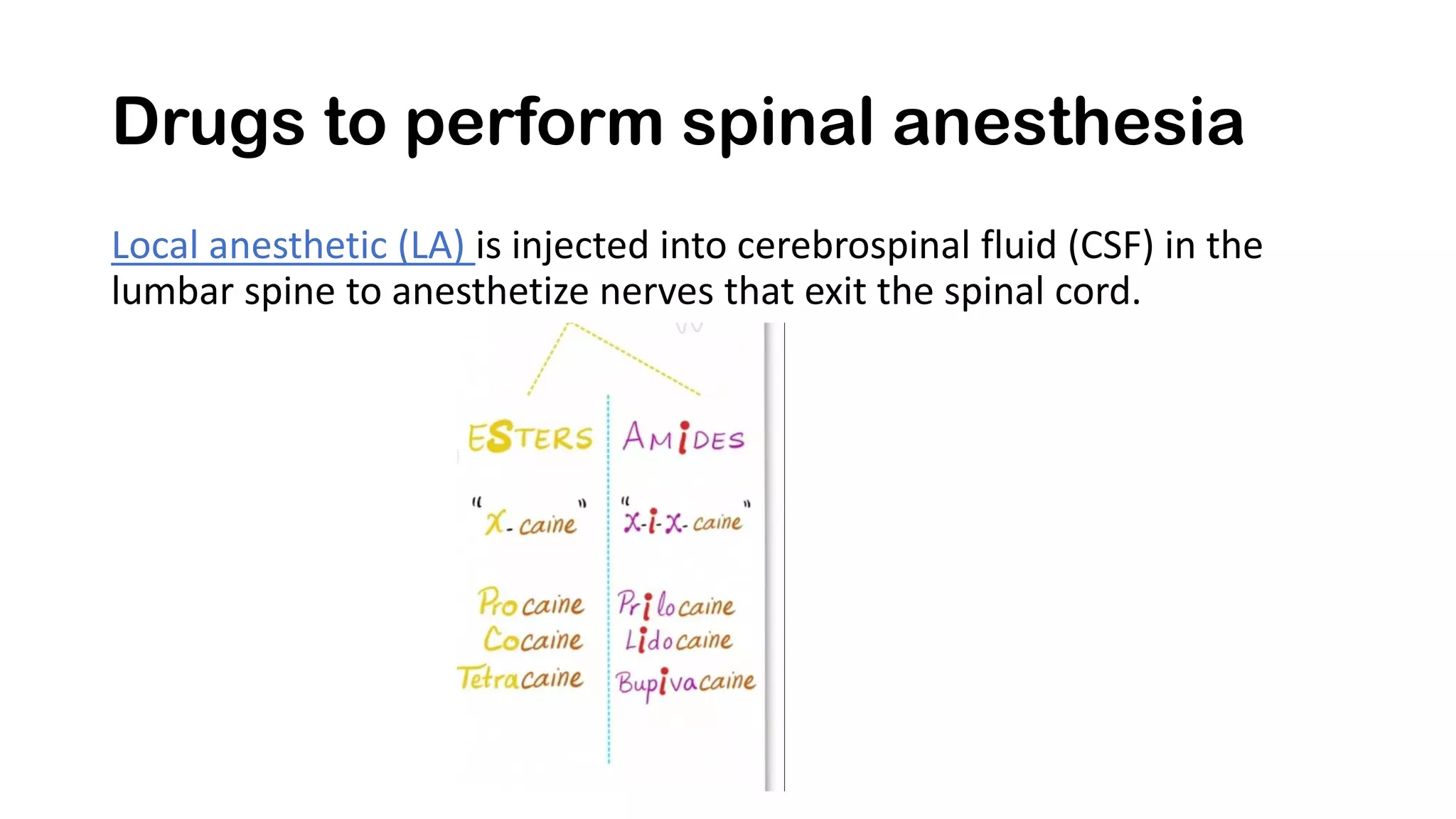
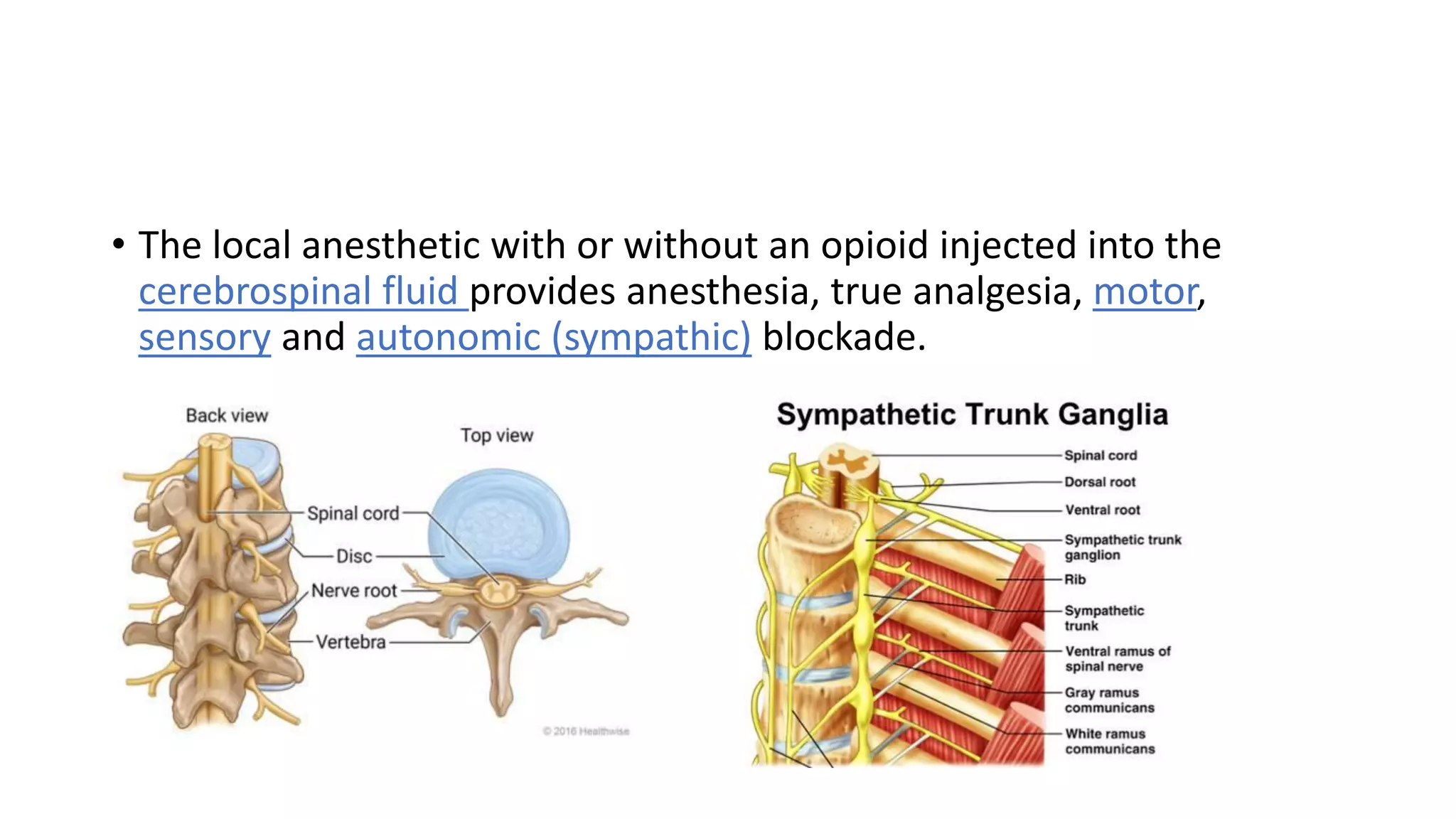
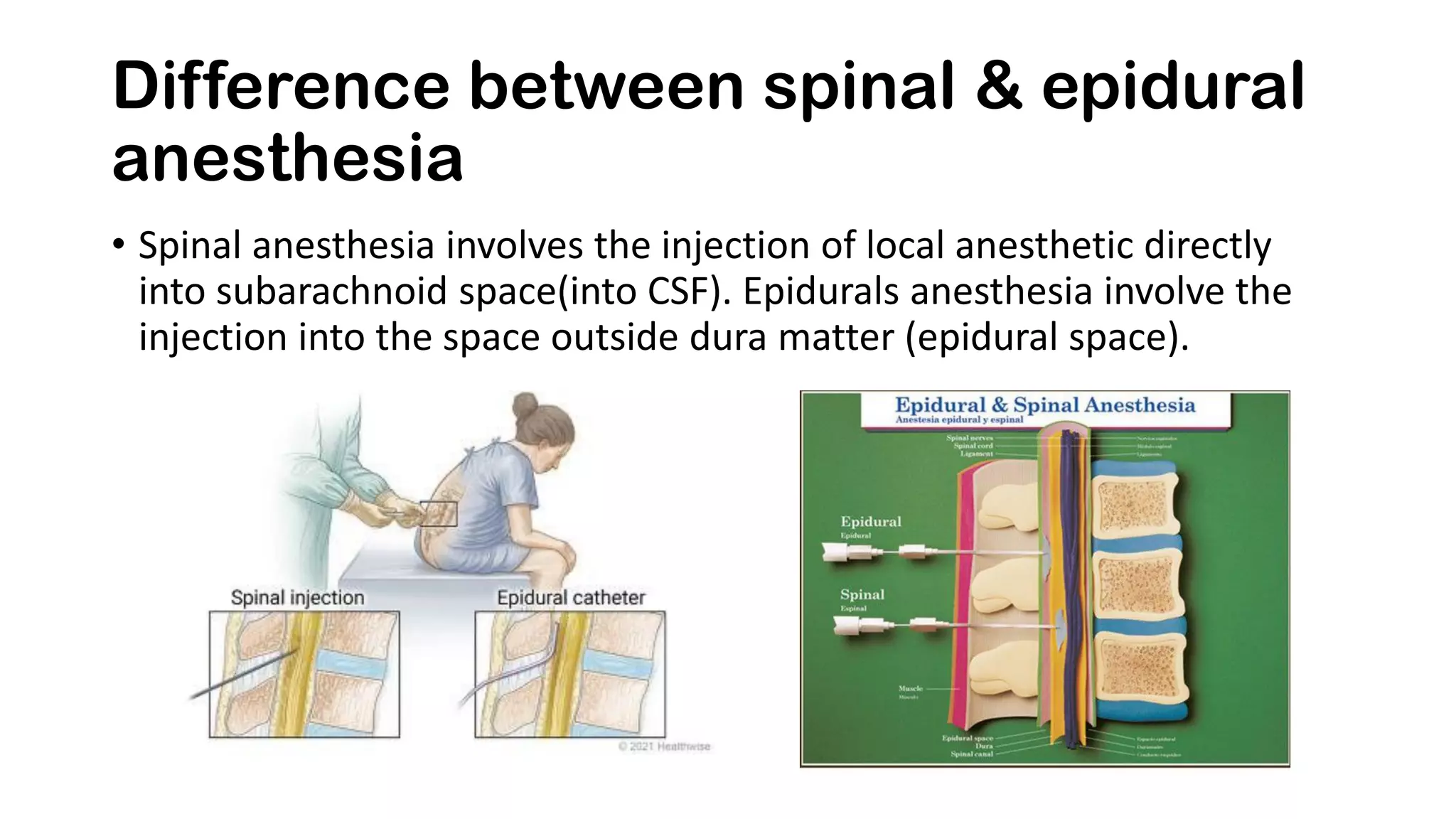
Spinal anesthesia involves injecting local anesthetic into the cerebrospinal fluid in the lumbar spine to anesthetize nerves exiting the spinal cord. It provides anesthesia, analgesia, and motor/sensory/autonomic blockade. It is commonly used for lower extremity and lower abdominal surgeries as an alternative to general anesthesia. The local anesthetic blocks sympathetic activation, reducing risks like hypotension in susceptible patients like diabetics. Potential complications include headache, nausea, hypotension, and nerve injury.