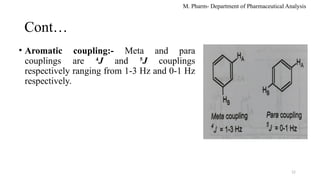
The document discusses spin-spin coupling in NMR spectroscopy, explaining how chemically equivalent protons influence signal peaks in spectra according to the n+1 rule. It specifies types of coupling such as geminal, vicinal, and long-range coupling, each defined by the number of bonds separating protons and their corresponding coupling constants. Additional details on mathematical tools like Pascal's triangle and the impact of molecular structure on coupling constants are also provided.